
Refineries perform intricate chemical operations that generate various gases and emissions. Efficient gas analysis matters—not only to fine-tune combustion but also to shield sensitive catalysts and to meet tough environmental rules. Infrared gas analyzers step in here: they instantly sample fuel and exhaust gases, guiding engineers as they balance air-to-fuel ratios, catch leaks early, and assure product quality. Think of them as the refinery’s real-time eyes on its gas flows. Without them, operations run blind.
Moreover, these analyzers empower teams to react swiftly when conditions shift. They monitor flue-gas in boilers and heaters, helping reduce waste while maintaining safety. By blending technical precision with intuitive feedback, infrared gas analyzers become indispensable tools—enhancing efficiency, safeguarding equipment, and curbing emissions with finesse.
Having framed the refinery’s complex demands and the need for real-time insights, now we’ll delve into how an infrared gas analyzer actually works. Understanding it’s optical, non-reactive design will reveal why it delivers the accuracy and reliability that modern refining demands.
What Is an Infrared Gas Analyzer and How Does It Work in Refineries?
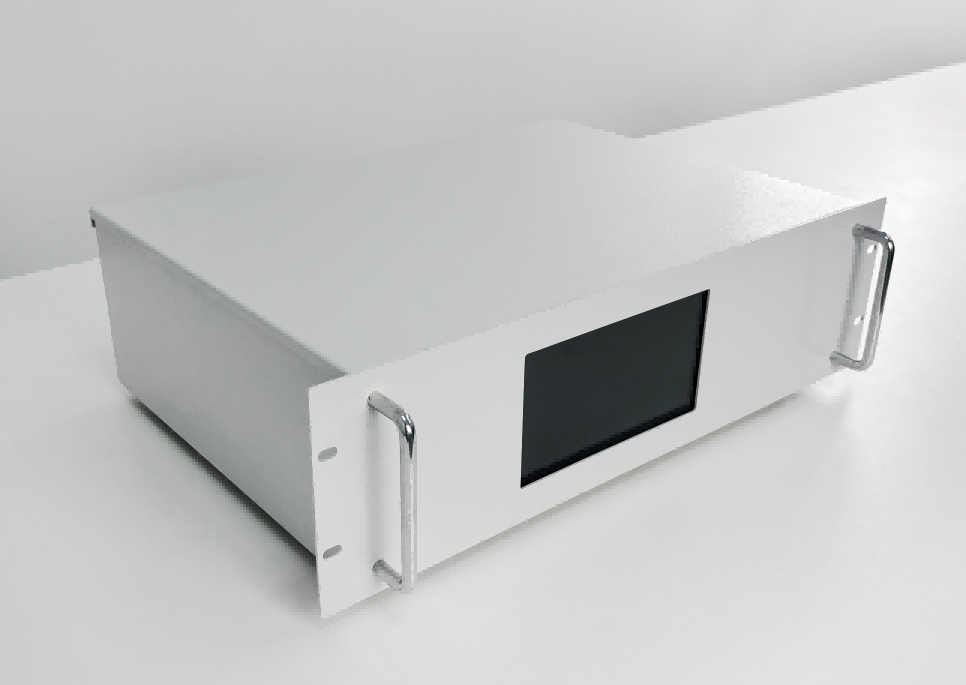

(ESEGAS’s Infrared Gas Analyzer)
An infrared gas analyzer—most often using non-dispersive infrared (NDIR) technology—detects gases by measuring how they absorb infrared light. The instrument shines a beam of IR light through a gas sample. As the light passes through, specific gases absorb it at unique wavelengths. By measuring how much light is lost, the analyzer calculates the gas concentration with high precision.
Different gases have distinct IR “fingerprints”. For example, CO₂, CO, and CH₄ each absorb IR energy in their own spectral bands. A modern analyzer can house several optical channels or filters, allowing it to measure multiple gases at the same time. ESEGAS’s IR-GAS-600 series, for instance, can track up to five gases—such as CO, CO₂, and CH₄—alongside a TCD for H₂ and paramagnetic or electrochemical for O₂.
Because this method is purely optical, it is non-destructive. There are no chemical reagents, no consumables, and minimal maintenance. That means stable, repeatable measurements over long periods—exactly what refineries need for continuous process control and emissions compliance.
With its core mechanics and strengths clear, it’s time to explore how infrared technology translates into real-world value. Let’s unpack the key applications where these analyzers make a tangible difference—from combustion control to leak detection.
How Do Infrared Gas Analyzers Support Critical Refining Processes?
Infrared gas analyzers power many vital tasks in a refinery. Let’s break these down into clear, digestible sections—each highlighting how these tools enhance safety, efficiency, and compliance.
Combustion and flue gas monitoring:
Infrared analyzers sit directly in furnace or boiler flue gas streams to measure O₂, CO, and CO₂. This helps teams:
-Minimize excess air, saving fuel
-Prevent CO buildup and higher emissions
-Continuously adjust burner settings for peak combustion efficiency
This active, real-time monitoring makes a real difference in fuel use and emissions control.
FCC Regenerator Optimization
In the fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) unit, spent catalyst is regenerated by burning off coke. Infrared analyzers keep a constant watch on O₂ and CO levels in the regenerator exhaust. By doing so, they:
- Ensure complete combustion
- Maximize heat recovery
- Preserve catalyst life and prevent damage due to imbalance
This steady oversight safeguards both efficiency and equipment longevity.
Amine & Sulfur Recovery Control
Amine units “sweeten” sour gases by removing H₂S and CO₂, and then recycle the amine after regeneration. Infrared analyzers in these units help by:
- Tracking acid gas concentrations continuously
- Optimizing the lean/rich amine balance
- Preventing upset conditions that could risk corrosion or cause emission violations
Simply put, IR tools keep the chemistry where it needs to be for smooth, reliable operation.
Continuous Emissions Monitoring (CEMS)
Refiners must comply with regulations by tracking stack emissions like CO, NOₓ, SO₂, and CO₂ around the clock. Infrared analyzers play a central role in CEMS by:
- Sampling flue gases consistently
- Feeding accurate data to DCS or DAHS for reporting
- Helping avoid costly fines and meet environmental mandates
Regulations drive this need—and IR analyzers meet it head-on.
Gas Composition & Leak Detection
Beyond combustion and emissions, infrared analyzers also check fuel gas quality and detect leaks. They excel at spotting:
- Hydrocarbons in gas lines
- Acid gases that could affect downstream units
By continuously scanning these streams, they help avert safety risks and maintain smooth processing.
We’ve seen where infrared gas analyzers fit into refinery operations. Next, let’s zoom out and examine the underlying technical advantages—why they do their job so well compared to older methods.
What Technical Advantages Make an Infrared Gas Analyzer Essential in Refining?

(Benefits)
Infrared gas analyzers bring a mix of accuracy, durability, and versatility that refineries cannot ignore. Their performance in high-demand environments often surpasses traditional detection methods, making them a preferred choice for both continuous process control and emissions monitoring.
- High sensitivity and accuracy
NDIR sensors detect gases down to parts-per-million with impressive stability. Narrowband optical filters, tuned to each target gas, allow the analyzer to distinguish between gases in complex mixtures. This means CO, CO₂, and CH₄ can be measured accurately even in streams with multiple interfering components. Modern units hold calibration for months, reducing the need for frequent checks. - Selective, multi-component detection
By focusing on specific IR absorption bands, infrared gas analyzers maintain low cross-sensitivity. A single unit can measure several gases at once—ESEGAS’s IR-GAS-600 handles up to five simultaneously. This detects five gases or more in one unit, simplifies installation, and cuts maintenance overhead. Operators gain a complete picture of process conditions without juggling multiple devices. - Non-consumptive and low maintenance
Infrared analysis uses an optical, non-destructive method—no reagents, no moving parts, and no consumables. The result? Fewer breakdowns, lower operating costs, and minimal waste. In many refineries, these units run for years with only occasional zero or span checks. That kind of reliability translates directly into reduced downtime and higher process availability. - Fast, real-time measurements
An infrared gas analyzer can deliver results in seconds, providing real-time insights for dynamic process control. Quick feedback is critical for operations such as burner air-fuel ratio adjustments, where even a short delay can impact efficiency and emissions. This rapid response ensures that control loops work exactly as intended. - Wide measurement range
From trace emissions to high-concentration process streams, infrared gas analyzers handle it all. Dual-beam and multi-path designs maintain accuracy across this wide span, allowing engineers to monitor both compliance thresholds and process-critical concentrations with a single device.
Beyond precision and performance, an infrared gas analyzer must also meet stringent regulatory and safety standards. Up next, we’ll explore how these instruments serve as the backbone of compliance and risk management across modern refineries.
How Does an Infrared Gas Analyzer Elevate Compliance and Safety in Refineries?
Refineries operate under strict environmental rules and rigorous safety standards. The infrared gas analyzer plays a dual role—ensuring both legal compliance and protecting human and plant safety.
Meeting Regulations with Precision Monitoring
Regulators demand real-time tracking of key pollutants like CH4, CO, and CO₂. In the U.S., EPA mandates Continuous Emissions Monitoring Systems (CEMS)—often built around NDIR analyzers—for precise, ongoing gas sampling at stack outlets. These systems must meet performance standards, including daily calibration and QA per Appendix F, and performance testing at initial setup and at scheduled intervals. In the EU, the Industrial Emissions Directive (IED) requires adoption of best available techniques and tighter emissions limits, with permits tied to real emission data. Infrared analyzers provide the reliable data needed to satisfy both U.S. and EU regulatory expectations, steering clear of penalties and shutdowns.
Enhancing Process Safety with Early Warning Systems
Beyond legal obligations, infrared gas analyzers enhance safety by offering real-time alerts. By continuously monitoring for flammable or toxic gases—like CO or H₂S—they can trigger alarms or shutdowns before conditions deteriorate. This proactive monitoring not only shields personnel but also prolongs equipment life. Since many IR units are built for hazardous areas and tolerate heat and corrosion, they deliver resilience where people cannot enter safely.
Enabling Rugged Safety Management Systems
Infrared analyzers fit perfectly into safety protocols. Many are explosion-proof and fit for remote placement, using heated sample lines to withstand harsh conditions. This design principle aligns with modern process safety management strategies—where reliability in tough environments underpins safety and operational continuity.
We’ve walked through their roles in operations, technical strength, and safety. Now, let’s bring it all together—looking ahead to how infrared gas analyzers will shape the future of refining as digital transformation and environmental expectations accelerate.
Conclusion
Refineries today face rising demands for efficiency, safety, and environmental compliance. Infrared gas analyzers meet these challenges by delivering continuous, accurate measurements of critical gases—such as flue oxygen, combustion CO₂, trace hydrocarbons, and acid gases. These insights allow operators to fine-tune combustion, safeguard catalysts, and maintain strict emissions control.
In short, the future of refining will depend heavily on precise gas measurement. With tightening regulations and a constant push for efficiency, the demand for infrared gas analyzers is set to rise sharply.
If you want to know more, contact with us please!

























