In a world increasingly affected by climate change, monitoring greenhouse gases (GHGs) has never been more critical. A greenhouse gas analyzer (GGA) is a pivotal tool that aids in accurately measuring the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. It provides vital data to support climate action and regulatory compliance.

A Greenhouse Gas Analyzer Explained
A greenhouse gas analyzer is an advanced device designed to detect, measure, and analyze the concentration of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide (CO₂), methane (CH₄), and nitrous oxide (N₂O) in various environments. Used across industries, these analyzers provide precise readings to support environmental monitoring, research, and compliance with emissions standards.
Why Are Greenhouse Gas Analyzers Essential Across Multiple Fields?
The need for accurate GHG measurement is central to global environmental goals. This is especially true in the context of mitigating climate change impacts. Greenhouse gas analyzers contribute to several fields, from research to industry regulation. They provide data that influences both policy and practical initiatives. Here, we will explore the primary applications and their significance.
1. How Do Greenhouse Gas Analyzers Aid in Environmental Monitoring?
Pollution and climate change are urgent issues; GHG analyzers are at the forefront of environmental protection.

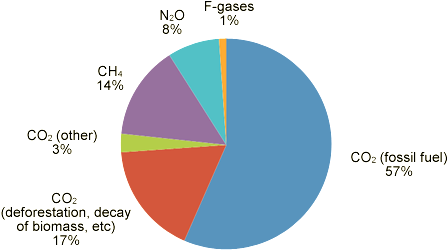
Environmental agencies use GHG analyzers to track gas levels in the atmosphere, analyzing trends and impacts on climate. Through continuous monitoring of carbon dioxide, methane, and other emissions, these analyzers help gauge the effectiveness of emissions control efforts. They also inform global climate models. Environmental monitoring is essential for understanding long-term trends in greenhouse gas concentrations and their impacts on climate.

Greenhouse Gas Analyzer
The most commonly analyzed gas using a greenhouse gas analyzer is carbon dioxide (CO2). Other common gases that can be detected include methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and various fluorinated gases. The two primary measurement techniques used for detecting these greenhouse gases are absorption spectroscopy and non-dispersive infrared detection.
We mainly use NDIR-GFC technology to detect CH4, CO2, CO, N2O gases
Environmental monitoring applications are often conducted by governmental organizations, environmental NGOs, and research institutions who aim to provide accurate, real-time data. Continuous data gathering via GHG analyzers enables scientists to model future emissions scenarios. It also helps assess compliance with emissions targets and develop initiatives to lower the overall environmental footprint.
2. How Do Industrial Processes Benefit from Greenhouse Gas Analyzers?
Industrial sectors are among the highest contributors to GHG emissions, and monitoring is key to regulation and compliance.
GHG analyzers support industries in monitoring emissions from manufacturing, refining, and other processes, ensuring compliance with strict regulations. This includes providing data for reporting requirements and enabling industries to make informed decisions to reduce their greenhouse gas output. By monitoring gas outputs in real-time, companies can quickly identify high-emission areas. They can then take corrective measures to optimize energy use and reduce waste.
Industries such as oil and gas, chemical production, and cement manufacturing use GHG analyzers to adhere to environmental laws and avoid heavy fines. These analyzers can also play a role in internal sustainability goals. Companies work toward becoming carbon-neutral or achieving net-zero emissions. By implementing GHG analyzers, companies gain insight into their environmental impact. They can plan more effectively for greener operations.
3. How Are Greenhouse Gas Analyzers Applied in Agriculture and Land Use?

Agricultural practices and land use changes are significant sources of greenhouse gases, primarily methane and nitrous oxide.
In agriculture, GHG analyzers provide crucial data on emissions from livestock and soil, enabling better management practices to minimize emissions. For instance, methane emissions from livestock and nitrous oxide emissions from fertilized soil are two critical areas where analyzers play a role. By tracking these gases, farmers and agronomists can make data-driven decisions to reduce emissions through alternative practices, such as modifying livestock diets or improving fertilizer use.
GHG analyzers also contribute to understanding the impact of land-use changes, such as deforestation or reforestation, on greenhouse gas emissions. By quantifying emissions from these activities, analyzers help policymakers and conservationists implement sustainable practices. This minimizes the release of stored carbon from soils and plants. This data is essential for promoting sustainable land use and reducing emissions from food production and land management.
4. What Role Do Greenhouse Gas Analyzers Play in Scientific Research and Climate Studies?
Scientific research relies on accurate data from GHG analyzers to investigate the causes and impacts of climate change.
Researchers use GHG analyzers to study greenhouse gases’ chemical composition, source, and dispersion, aiding in climate science advancements. This data allows scientists to develop models that predict how greenhouse gas emissions will impact global temperatures, sea levels, and extreme weather patterns. GHG analyzers help quantify emissions from various natural and human-made sources. This offers valuable insights into the specific drivers of climate change.
Additionally, researchers studying atmospheric chemistry use GHG analyzers to assess how gases interact with sunlight, water vapor, and other atmospheric particles. These studies are essential for understanding the full impact of greenhouse gases and devising more effective strategies to mitigate their effects. Through climate studies, the data generated by GHG analyzers contributes directly to the development of global policies and climate agreements aimed at reducing emissions and curbing global warming.
5. How Do Greenhouse Gas Analyzers Support Renewable Energy Development?
As the energy sector moves towards sustainability, renewable energy sources are being integrated to reduce emissions.
Greenhouse gas analyzers aid renewable energy projects by providing emissions data that demonstrate their environmental benefits over fossil fuels. For instance, biogas plants use GHG analyzers to ensure that methane is properly captured and utilized as a renewable fuel. This avoids its release into the atmosphere. Similarly, GHG analyzers monitor carbon dioxide levels during the production of renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydropower. They provide proof of lower emissions compared to traditional energy sources.
By tracking emissions reductions and ensuring clean energy standards, GHG analyzers help renewable energy projects meet environmental targets and maintain transparent records of their carbon footprint. This application supports energy companies and governments in showcasing the environmental benefits of transitioning to renewables. It also encourages further adoption of sustainable energy sources.
6. What Is the Future Potential for Greenhouse Gas Analyzers?
The potential applications for GHG analyzers are expanding, with new technologies promising enhanced accuracy and accessibility.
Future GHG analyzers are expected to be more compact, affordable, and accurate, broadening access to emissions monitoring. These advancements will enable even more sectors, including small businesses and communities, to monitor their emissions and contribute to global climate efforts. Portable and real-time GHG analyzers may also play a role in providing emissions data directly to consumers. This would raise awareness and drive individual climate action.
As GHG analyzer technology advances, its impact on environmental monitoring, industry regulation, and scientific research will likely increase. Enhanced analyzers could provide deeper insights into the effectiveness of emissions-reduction initiatives. This directly contributes to a sustainable future by supporting environmental policy and sustainable development goals.
Conclusion
Greenhouse gas analyzers are essential for monitoring and reducing emissions across various sectors. With applications in environmental monitoring, industry, agriculture, research, and renewable energy, they provide critical data to combat climate change and promote sustainability. As technology progresses, these analyzers will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping a greener, more sustainable world.























