Tackling Pollution at the Source: Why Emission Monitoring is Vital
Waste incineration plants face increasing challenges in controlling emissions of harmful pollutants. Failure to monitor and manage these emission monitoring effectively can lead to regulatory fines, environmental damage, and harm to public health. This is where AQMS comes in to ensure precision and compliance.

The Modern Solution to Air Quality Monitoring in Waste Incineration
Air Quality Monitoring System (AQMS) provides real-time, accurate data on pollutants emitted by waste incineration plants, helping operators reduce environmental risks while adhering to strict regulatory requirements.
A Growing Need for Efficient Solutions
Managing emissions in waste incineration plants is complex, involving multiple gases, particulate matter, and toxic substances. AQMS simplifies the process, offering state-of-the-art tools for efficient and reliable monitoring, ensuring both regulatory compliance and environmental protection.
Why is Emission Monitoring Critical in Waste Incineration Plants?
The Environmental and Health Risks of Emissions from Waste Incineration
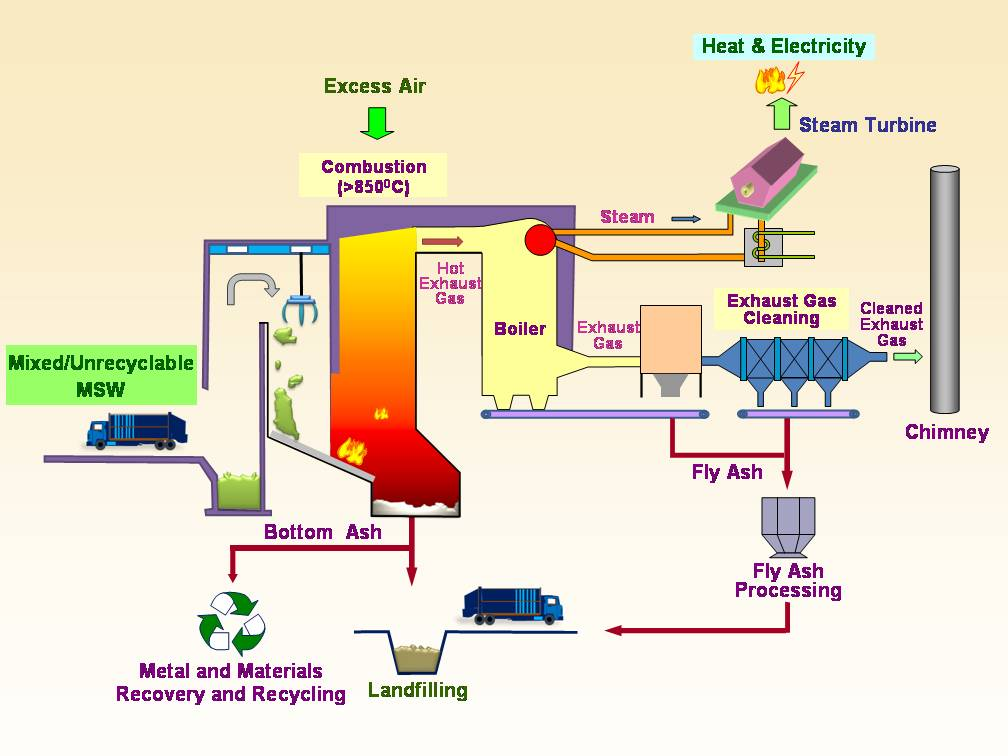
Waste incineration is a key method for managing municipal solid waste, industrial refuse, and hazardous materials. However, the process generates various harmful emissions that pose serious risks to the environment and public health. Common pollutants include:
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): Formed due to incomplete combustion, CO contributes to smog and reduces the oxygen-carrying capacity of blood when inhaled.
- Nitrogen Oxides (NOx): These gases contribute to acid rain and smog formation, harming ecosystems and human respiratory health.
- Sulfur Dioxide (SO2): SO2 leads to acidification of soil and water bodies, damaging crops and aquatic life, while also irritating human respiratory systems.
- Particulate Matter (PM): Fine particles released during incineration can penetrate deep into human lungs, causing respiratory diseases, cardiovascular issues, and even cancer.
- Dioxins and Furans: Toxic compounds produced at low combustion temperatures, which are known to be carcinogenic and can bioaccumulate in the food chain.
- Air Pollution: Emissions like NOx and PM contribute significantly to air quality deterioration.
- Climate Change: Greenhouse gases from incineration, such as CO2, exacerbate global warming.
- Health Risks: Prolonged exposure to pollutants like dioxins and PM leads to respiratory diseases, developmental issues in children, and increased cancer risk.
The Need for Continuous Monitoring
Real-time emission monitoring is critical to detect and control harmful substances before they exceed regulatory limits. Traditional, periodic testing methods are no longer sufficient due to their inability to capture fluctuations in emissions during different operational conditions. Waste incineration plants must rely on continuous emission monitoring systems (CEMS), such as AQMS, to ensure environmental compliance and protect public health.
What Are the Core Functions of AQMS in Waste Incineration Plants?

Real-Time Monitoring of Key Pollutants
One of the most critical functions of AQMS is its ability to continuously monitor the emission of pollutants in real time. Waste incineration processes release a variety of harmful gases, including nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur dioxide (SO2), carbon monoxide (CO), particulate matter (PM), and highly toxic compounds like dioxins and furans. These emissions must be closely tracked to ensure compliance with environmental regulations and to minimize their impact on both human health and the environment.
For example, NOx gases contribute to smog formation and acid rain, while dioxins—produced during low-temperature combustion—are carcinogenic and can accumulate in the food chain. Real-time monitoring provided by AQMS allows plant operators to detect even slight deviations in emission levels and make necessary adjustments to maintain safe and regulated operations.
Continuous data collection also enables the identification of emission trends, empowering waste incineration plants to proactively address issues before they escalate. This level of precision is essential, as it prevents regulatory violations, reduces risks to surrounding communities, and ensures environmental sustainability.
Automated Data Collection and Regulatory Reporting
Another core function of AQMS is automating the collection, storage, and reporting of emission data. In traditional waste incineration systems, monitoring and reporting processes often rely on manual methods, which can be time-consuming and prone to human error. AQMS revolutionizes this by providing accurate and consistent data without the need for extensive manual intervention.
The system collects data on critical pollutants around the clock, creating a comprehensive archive of emissions records. This database is particularly useful during environmental inspections or audits, as it provides regulators with transparent and easily accessible information. Furthermore, AQMS simplifies compliance with stringent regulations, such as those outlined in the EU Industrial Emissions Directive (IED) or the US EPA guidelines. By generating real-time reports and automatically flagging emission spikes, AQMS ensures that waste incineration plants meet legal requirements efficiently.
For instance, a European plant reduced its reporting time by half after implementing AQMS, while achieving full compliance with national emission standards. This function not only reduces the administrative burden but also minimizes the risk of regulatory penalties.
Seamless System Integration for Operational Efficiency
Modern AQMS solutions are designed to integrate seamlessly with existing waste incineration plant systems. This integration enhances operational efficiency and supports optimized combustion processes. By monitoring key gases like carbon monoxide and oxygen levels, AQMS provides critical data that enables operators to fine-tune combustion parameters in real-time. This helps reduce fuel consumption, improve energy efficiency, and minimize the production of harmful pollutants.
In addition to process optimization, AQMS often features cloud-based connectivity and live dashboards that provide plant managers with a clear overview of emissions data. These systems allow for remote monitoring, ensuring that operators and environmental managers can access real-time information from anywhere. This connectivity is particularly beneficial for large-scale or multi-site operations, where centralized monitoring can streamline workflows and improve response times.
Moreover, advanced AQMS systems incorporate predictive maintenance features. By analyzing emission data trends, the system can predict equipment failures or inefficiencies before they occur. This proactive approach reduces unplanned downtime and lowers maintenance costs, ensuring smooth and uninterrupted plant operations.
Advanced Analytics for Continuous Improvement
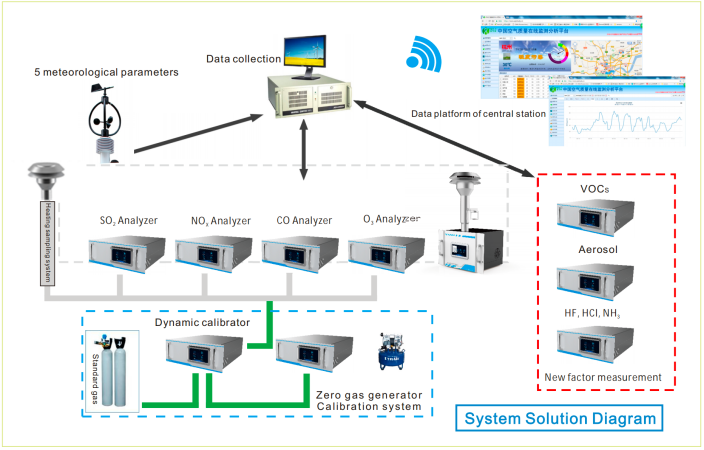
Beyond basic monitoring, AQMS leverages advanced analytics to help waste incineration plants improve their performance and reduce emissions. The system uses historical data to analyze emission trends, identify problem areas, and suggest actionable solutions. For instance, if the system detects recurring spikes in NOx emissions during specific operational conditions, it can recommend changes to combustion processes to mitigate the issue.
Some AQMS systems also use artificial intelligence (AI) to optimize plant performance. AI-driven algorithms analyze vast amounts of data to identify inefficiencies and propose adjustments to improve combustion efficiency or reduce pollutant generation. This capability not only supports regulatory compliance but also enhances the plant’s overall sustainability efforts.
For example, a waste-to-energy plant in South Korea used AQMS analytics to reduce its dioxin emissions by 15% over two years. The system provided actionable insights that allowed operators to address inefficiencies and align their operations with stricter national regulations.
Supporting Environmental and Community Goals
Finally, AQMS plays a vital role in helping waste incineration plants achieve broader environmental and sustainability objectives. By ensuring accurate monitoring and reporting, the system supports plants in reducing their carbon footprint and aligning with global climate goals. Optimized combustion processes not only lower greenhouse gas emissions but also minimize the production of pollutants that harm local ecosystems and human health.
Additionally, AQMS can enhance a facility’s relationship with surrounding communities. In areas where waste incineration plants are often a public concern, transparent monitoring and reporting can help build trust. Some AQMS solutions allow plants to share real-time emission data with the public, demonstrating their commitment to environmental responsibility. This transparency fosters better community relations and reduces the likelihood of opposition to plant operations.
For instance, a German waste incineration plant located in a densely populated urban area used AQMS to address residents’ concerns about air quality. By providing open access to its emission data, the plant reduced complaints by 30% and improved public trust.
How Does AQMS Help Meet Regulatory and Environmental Standards?

Ensuring Compliance with Stringent Emission Limits
Regulatory bodies worldwide enforce strict emission standards for waste incineration plants to mitigate environmental and public health risks. These standards set allowable limits for pollutants like nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur dioxide (SO2), particulate matter (PM), carbon monoxide (CO), and dioxins. Examples of such regulations include:
- The European Union’s Industrial Emissions Directive (IED): This directive imposes rigorous limits on emissions and requires continuous monitoring to ensure compliance.
- The United States EPA Clean Air Act: This law enforces strict National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants (NESHAP) for waste incineration facilities.
AQMS (Automated Air Quality Monitoring System) is critical in ensuring that waste incineration plants adhere to these regulations by continuously measuring pollutant levels in real-time. By providing highly accurate data, AQMS enables plant operators to monitor their emissions against regulatory thresholds and take corrective actions if any exceedances are detected.
For instance, if NOx levels exceed regulatory limits during the combustion process, AQMS triggers an immediate alert, allowing operators to adjust combustion settings or take other remedial measures. This real-time capability minimizes the risk of prolonged violations and ensures consistent compliance with emission standards.
Automating Regulatory Reporting
One of the key challenges for waste incineration plants is the manual preparation and submission of emission reports to environmental authorities. Such processes are time-consuming, prone to human error, and can result in non-compliance if reporting is delayed or inaccurate. AQMS addresses this issue by automating the entire reporting process.
The system continuously collects and stores emission data, ensuring a reliable database for regulatory audits. Many AQMS solutions are equipped with built-in reporting templates that align with specific regional requirements, such as the EU’s IED or the US EPA guidelines. These templates generate detailed reports that include pollutant concentrations, trends, and any deviations from standards.
For example, a waste incineration plant in the UK reduced its reporting time by 60% after implementing AQMS, as the system automatically prepared emission summaries that met local regulatory requirements. This not only reduced administrative burdens but also ensured that the plant remained fully compliant during inspections.
Creating Transparency for Environmental Audits
Environmental authorities often conduct inspections or audits to verify a facility’s compliance with emission regulations. AQMS simplifies this process by maintaining a comprehensive archive of historical emission data. This archived data provides regulators with clear evidence of a plant’s performance over time, making audits faster and more transparent.
In addition to historical data, AQMS systems often include features such as:
- Emission Trend Analysis: Regulators can review trends to assess whether the plant consistently maintains emissions within permissible limits.
- Real-Time Monitoring Access: Some AQMS solutions allow regulators to access real-time data remotely, ensuring ongoing compliance without the need for frequent on-site inspections.
By providing transparent and easily accessible data, AQMS fosters better relationships between plant operators and regulatory authorities, reducing the likelihood of disputes or penalties.
Supporting Environmental Standards Beyond Compliance
While meeting regulatory requirements is a primary objective, AQMS also plays a significant role in helping waste incineration plants align with broader environmental standards and sustainability goals. These include reducing greenhouse gas emissions, improving energy efficiency, and minimizing the overall environmental impact of plant operations.
For example, AQMS enables plants to optimize their combustion processes by monitoring oxygen levels, CO concentrations, and other critical parameters. By fine-tuning combustion efficiency, plants can reduce fuel consumption and lower emissions of CO2—a major greenhouse gas. This contributes to global carbon reduction targets and aligns with initiatives like the Paris Agreement on climate change.
Reducing Regulatory Risks and Penalties
One of the biggest challenges for waste incineration plants is avoiding regulatory penalties, which can result from emission limit violations, reporting delays, or insufficient data transparency. AQMS minimizes these risks in several ways:
- Immediate Alerts for Exceedances: If pollutant levels approach or exceed regulatory thresholds, AQMS sends real-time alerts to plant operators, enabling them to take swift corrective actions.
- Proactive Maintenance: By analyzing emission trends, AQMS can identify potential equipment failures or inefficiencies that may lead to violations, allowing plants to schedule maintenance before problems arise.
- Consistent Data Accuracy: Advanced AQMS solutions are equipped with highly sensitive sensors that deliver precise measurements, ensuring reliable data that meets regulatory standards.
For example, a waste incineration plant in South Korea implemented AQMS to address frequent regulatory violations. Within one year, the plant reduced its non-compliance incidents by 40% and avoided significant fines, thanks to the system’s real-time alerts and automated reporting features.
Enabling Green Certifications and Public Trust
Many regulatory frameworks encourage waste incineration plants to pursue green certifications, such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management Systems). AQMS supports these efforts by providing the accurate and comprehensive data needed to demonstrate environmental responsibility. Facilities that achieve such certifications not only meet regulatory standards but also enhance their reputation as sustainable operations.
In addition, transparent emission monitoring helps plants build trust with local communities. In densely populated areas, public concerns about air quality and health risks are common. AQMS allows facilities to share real-time emission data with the public, demonstrating their commitment to environmental protection. This openness fosters better community relations and reduces opposition to plant operations.
For example, a waste-to-energy plant in Germany used AQMS to address residents’ concerns about air pollution. By sharing its emission data publicly, the plant improved its relationship with the community and reduced complaints by 35%.
Aligning with Evolving Regulatory Frameworks
As environmental standards become more stringent worldwide, waste incineration plants must adapt to new requirements. AQMS systems are highly scalable and can be updated to accommodate changing regulations or expanded operational scopes. Features such as AI-driven analytics and remote monitoring ensure that AQMS remains a future-proof solution for regulatory compliance.
For instance, as the EU tightens its emission standards for NOx and SO2, waste incineration plants equipped with AQMS are already prepared to meet these stricter thresholds by leveraging their system’s advanced capabilities.
The Future of AQMS in Waste Incineration Plants
Driving Innovation in Emission Monitoring
As regulatory requirements grow stricter, AQMS is evolving to meet future demands. Features such as remote monitoring, artificial intelligence for predictive analysis, and automated alerts make AQMS indispensable for modern waste incineration facilities.
Aligning with Global Sustainability Goals
In addition to meeting compliance, AQMS supports global efforts to reduce carbon footprints and achieve sustainability targets, making it an essential tool for responsible waste management in the 21st century.
Conclusion: The Key Role of AQMS in Modern Waste Incineration
Efficient emission monitoring is no longer optional for waste incineration plants. AQMS not only ensures compliance with strict environmental regulations but also enhances operational efficiency and sustainability. As a forward-thinking solution, AQMS empowers waste incineration plants to address pollution challenges effectively while contributing to a cleaner and healthier future.
If you have any questions, don’t hesitate to contact us; we will respond as soon as possible!