As industrial emissions continue to impact the environment, the need for ambient AQMS effective monitoring of air quality around factory perimeters has never been greater. Without the right monitoring tools, factories risk violating air quality regulations, causing pollution, and threatening public health. The solution? Air Quality Monitoring Systems (AQMS) help factories maintain environmental compliance while safeguarding the health of surrounding communities.

AQMS provides real-time data on air quality at factory perimeters, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and safeguarding public health. By accurately monitoring pollutants like SO2, NOX, O3, CO, and particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), AQMS helps to mitigate environmental risks and improve operational practices.
In this article, we will explore how AQMS functions in monitoring factory air quality, the benefits it offers, and its significance in reducing industrial environmental impacts. Whether you’re in manufacturing or simply concerned about air quality, AQMS offers a powerful tool for ensuring cleaner air and more responsible industrial operations.
What is AQMS and How Does It Monitor Air Quality?
What is AQMS?
Air Quality Monitoring Systems (AQMS) are advanced technological solutions designed to measure and assess the quality of the air in a specific location, such as the perimeter of industrial facilities, urban areas, or even remote locations. AQMS typically consists of a combination of sensors, data loggers, software platforms, and communication networks that work together to provide continuous and accurate data on air pollution levels. These systems are widely used by industries, governments, and environmental agencies to ensure air quality compliance and to protect public health and the environment.
An AQMS can monitor various pollutants, such as particulate matter (PM2.5, PM10), gases (NO2, SO2, CO, O3), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and others. These systems are critical for real-time monitoring and data collection, enabling swift decision-making regarding the air quality status.
How Does Ambient AQMS Monitor Air Quality?
AQMS typically operates through a network of monitoring stations equipped with a variety of sensors designed to detect and measure specific air pollutants. The process of monitoring air quality is composed of several stages:

1. Sensor Deployment
The AQMS consists of strategically placed sensors around the factory perimeter or at other critical monitoring points. These sensors measure specific pollutants such as nitrogen dioxide (NO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), ozone (O3), carbon monoxide (CO), and particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10). Some systems also measure temperature, humidity, and other environmental factors to give a more comprehensive view of air quality.
2. Data Collection
The sensors continuously collect data at regular intervals (e.g., every minute or hour), providing real-time information about pollutant concentrations. These sensors typically use optical, chemical, or electrochemical technologies to detect specific pollutants. For example:
- PM sensors measure airborne particulate matter through laser light scattering or gravimetric methods.
- Gas sensors use chemical reactions to detect gases like NO2, SO2, and CO.
- These sensors are highly sensitive, allowing AQMS to detect even low concentrations of pollutants, which is critical for identifying pollution before it reaches dangerous levels.
- Data Transmission and Processing
Once sensors collect the data, it is transmitted to a central data acquisition system via wired or wireless networks like Wi-Fi, Ethernet, or cellular. Specialized software processes and analyzes the raw data, often using cloud-based platforms for real-time remote access, enabling instant air quality monitoring for managers and specialists.
3. Data Analysis and Alerts
The processed data is compared against predetermined thresholds or regulatory standards. If any pollutants exceed safe levels, the system triggers an alarm or sends a notification to the factory operators or environmental authorities. This allows for rapid action to mitigate emissions or other pollution sources. For example, if PM2.5 levels exceed the acceptable limit, the system could suggest stopping a particular industrial process or activating air filtration systems to reduce the particle concentration.
4. Reporting and Compliance Monitoring
AQMS also generates reports that detail air quality levels over time. These reports are crucial for regulatory compliance, as they provide concrete evidence of whether the factory’s emissions meet environmental standards. Many industries are required to submit such reports to local environmental agencies as part of their permit conditions. AQMS also assists in verifying compliance with national and international air quality standards, such as those set by the World Health Organization (WHO) or the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
5. Long-Term Trends and Optimization
Over time, AQMS allows industries to gather historical air quality data. By analyzing long-term trends, factory operators can assess whether their emissions are improving, staying constant, or worsening. This helps them identify specific operational changes or processes that might be contributing to increased pollution, offering opportunities to optimize factory operations, improve equipment, or implement cleaner technologies. This proactive approach ensures that emissions are managed effectively, reducing long-term environmental impacts.
Why is it Important for Factories to Monitor Perimeter Air Quality?
Factories have the potential to emit harmful pollutants that not only affect the surrounding environment but also pose serious health risks to nearby communities. Monitoring the perimeter air quality ensures that factories take responsibility for their emissions.
By consistently monitoring the air around factory perimeters, AQMS helps detect any dangerous pollutants that might escape beyond the factory boundaries. If any level of pollution exceeds set limits, the system alerts factory operators so they can implement corrective measures promptly. This proactive approach prevents environmental degradation, ensures compliance with local air quality regulations, and maintains the factory’s social responsibility toward nearby residents.
How does AQMS Help in Reducing Industrial Environmental Impact?
Industries have long been a significant source of air pollution, with emissions from factories affecting not only the local environment but also contributing to global environmental challenges such as climate change and public health issues. Key pollutants like NO2, SO2, PM2.5, and CO are often released into the atmosphere as a result of industrial activities, leading to adverse effects such as smog, acid rain, respiratory diseases, and more.

To mitigate these environmental impacts, industries must adhere to environmental standards and regulations, but managing emissions effectively is challenging without reliable data. This is where Air Quality Monitoring Systems (AQMS) come in. AQMS plays a pivotal role in identifying, managing, and reducing the environmental footprint of industrial operations.
1. Real-Time Pollution Monitoring and Early Detection
AQMS helps industries by providing real-time data on air quality, enabling them to detect pollution sources immediately. Early detection is crucial for minimizing industrial environmental impact and ensuring that corrective actions are taken before pollutants reach harmful levels.
One of the most significant ways AQMS helps in reducing industrial environmental impact is through its ability to monitor air quality in real time. By using an array of sensors to measure pollutants such as NO2, SO2, CO, and particulate matter (PM2.5), AQMS offers continuous data that can identify pollution spikes before they escalate.
For example, if a factory’s emissions exceed regulated limits, the system can send alerts to operators or environmental managers. This immediate feedback allows for swift corrective actions, such as halting operations that are causing excessive emissions or activating air filtration systems to bring pollution levels back to acceptable standards. By acting quickly, factories can prevent long-term environmental damage and avoid breaching regulations.
2. Reducing Emissions Through Data-Driven Insights
AQMS provides detailed insights into pollutant levels over time, helping factories identify trends and optimize their operations. By analyzing the collected data, industries can make more informed decisions to reduce emissions and improve sustainability.
AQMS doesn’t just provide real-time data; it also offers valuable historical data that can help industries understand pollution patterns over time. With long-term monitoring, factories can identify specific processes or operational behaviors that consistently result in higher emissions, allowing for targeted improvements.
For instance, a factory might notice that pollutant levels rise at specific times of the day or when certain machines are in use. By analyzing this data, the factory can pinpoint the root cause of these emissions. This allows them to make adjustments, such as upgrading equipment, modifying processes, or introducing more energy-efficient technologies.
By continually optimizing processes based on real-time and historical data, AQMS helps reduce emissions, leading to a lower overall environmental footprint. Over time, these changes contribute significantly to reducing the factory’s contribution to air pollution, minimizing their negative impact on local and global environments.
3. Compliance with Regulatory Standards and Preventing Violations
Ensuring compliance with environmental regulations is essential for reducing industrial environmental impact. AQMS assists factories by keeping them within legal emission limits, thus preventing violations that could lead to environmental harm and costly penalties.
AQMS plays a key role in helping industries comply with local and international air quality standards. Regulatory bodies, such as the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the European Union, have established strict emission limits for factories and industrial sites.
By providing continuous air quality monitoring, AQMS ensures that factories can stay within these legal limits. If emissions exceed permissible levels, AQMS sends immediate alerts, allowing factory operators to take corrective actions before violations occur. This proactive approach prevents environmental damage and helps the factory avoid the environmental fines and penalties associated with non-compliance.
Furthermore, AQMS helps industries prepare for audits and inspections by maintaining accurate records of air quality data. These records demonstrate that the factory has adhered to environmental regulations, ensuring both regulatory compliance and environmental sustainability.
4. Supporting Sustainable Practices and Eco-Friendly Technologies
AQMS not only ensures compliance but also encourages factories to adopt eco-friendly technologies and practices by providing data-driven feedback on how their operations impact the environment.
Another significant benefit of AQMS is its ability to drive sustainable practices within industries. By providing precise data on pollutant levels, AQMS helps factories track their environmental performance and identify areas where improvements can be made. This data can encourage industries to implement cleaner technologies and adopt sustainable practices, further reducing their environmental footprint.
For example, if AQMS reveals consistently high levels of particulate matter from a specific manufacturing process, a factory may decide to invest in improved filtration systems or shift to cleaner production technologies that generate fewer emissions. Additionally, AQMS can help factories monitor the performance of these eco-friendly technologies over time, ensuring they are functioning as expected and delivering the intended environmental benefits.
In essence, AQMS provides the tools to guide industries toward more sustainable operations. With its real-time and historical data, factories are empowered to reduce emissions, minimize waste, and invest in cleaner technologies, leading to a significant reduction in their overall environmental impact.
5. Enhancing Public Health Protection
By reducing harmful air pollutants, AQMS plays a vital role in protecting public health, especially in areas surrounding industrial facilities. Cleaner air leads to fewer health problems in local communities, which is a major benefit for society as a whole.
AQMS doesn’t just benefit industries; it also contributes to the health and well-being of nearby communities. AQMS helps control industrial emissions, reducing harmful pollutants in the air. Pollutants like NO₂, SO₂, and PM2.5 can cause respiratory issues, heart disease, and other health risks.
When AQMS detects pollutants at dangerous levels, it helps factories take immediate action to prevent them from reaching the local population. This is particularly important in areas where communities live in close proximity to factories. By ensuring that emissions remain at safe levels, AQMS helps protect the health of nearby residents and reduces the incidence of pollution-related diseases
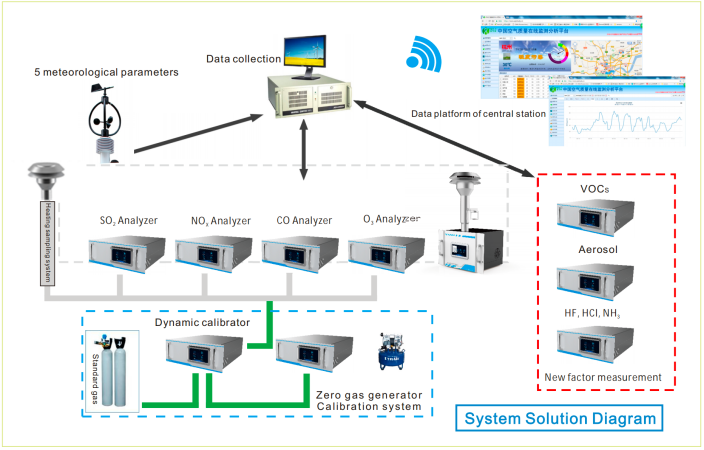
The Important Role of ESE AQMS in Plant Boundary Monitoring
The Auto & Continuous Ambient Air Quality Online Monitoring System is designed to track changes in the concentration of conventional pollutants such as SO2, NOX, O3, CO, and particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10). Additionally, it can accommodate specialized pollutants like aerosols, VOCs, NH3, and halides (HF/HCl) based on client requirements. By integrating with a Five Meteorological Parameters Analyzer—which measures temperature, humidity, wind direction, wind speed, and atmospheric pressure—the system enables continuous 24-hour online monitoring of the regional environment. This facilitates air quality assessment through comprehensive data collection, storage, and analysis.


Typical parameters measured by an AQMS include:
- PM2.5 and PM10: Particulate matter of different sizes.
- NOx: Nitrogen oxides.
- SO2: Sulfur dioxide.
- CO: Carbon monoxide.
- O3: Ozone.
- VOC: Volatile organic compounds.
These measurements help identify air quality trends and ensure compliance with environmental standards.
Here’s a table showing the key measurement principles used in AQMS for various air quality parameters:
| Parameter | Measurement Principle | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 / PM10 | Optical Light Scattering / Beta Attenuation | Measures particulate matter concentration based on how particles scatter light or attenuate beta radiation. |
| NOx (Nitrogen Oxides) | Chemiluminescence | Detects NOx by measuring the light emitted during a chemical reaction with ozone. |
| SO2 (Sulfur Dioxide) | UV Fluorescence | Measures sulfur dioxide concentration by detecting fluorescence emitted when SO2 molecules are excited by UV light. |
| CO (Carbon Monoxide) | Non-Dispersive Infrared (NDIR) Absorption | Detects carbon monoxide based on the absorption of infrared light by CO molecules. |
| O3 (Ozone) | UV Absorption | Ozone absorbs UV light at specific wavelengths, allowing for concentration measurement. |
| VOC (Volatile Organic Compounds) | Photo-Ionization Detector (PID) / Flame Ionization Detector (FID) | VOCs are detected by ionizing them with UV light (PID) or using combustion (FID). |
This table outlines the core principles used to measure common pollutants in air quality monitoring systems.
Conclusion
AQMS is an essential tool for ensuring that factories maintain strict air quality management at their perimeters. By providing real-time monitoring, AQMS helps mitigate environmental risks, promote healthier surroundings, and contribute to sustainable industrial practices that align with modern environmental standards.
If you have any questions, don’t hesitate to contact us; we will respond as soon as possible!























