Are you ready for a deep dive into Hydrogen Chloride Analyzers? These devices measure Hydrogen Chloride in the air. You’ll learn all about them here! With this knowledge, you can keep your workplace safe and sound. Let’s jump in!
Understanding Hydrogen Chloride!
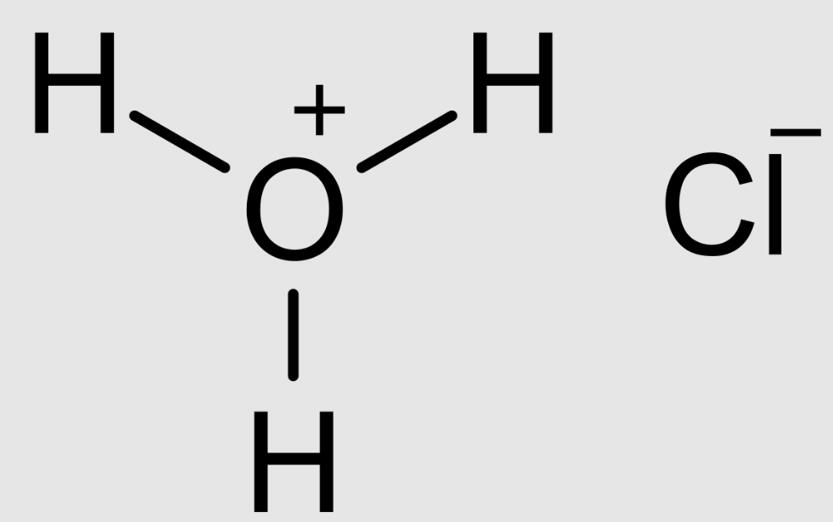
What is Hydrogen Chloride (HCL)?
Hydrogen Chloride, or HCL, finds application in numerous sectors. In simple terms, HCL is a colorless, pungent gas. Professionals often rely on Hydrogen Chloride Analyzer for accurate HCL measurement. With such an analyzer, HCL’s exact parameters get scrutinized. Hence, the industry deems the analyzer crucial for safety.
The physical and chemical properties of HCL
– Colorless Gas
An intriguing feature of HCL is being colorless. With no visible color, identifying HCL requires precision tools. A Hydrogen Chloride Analyzer excels in this task.
– Pungent Odor
Despite being colorless, HCL can’t escape detection due to its strong, pungent odor.
– Corrosive
HCL poses risks due to its corrosive nature. Therefore, handling HCL necessitates care, precaution, and accurate tools for analysis.
– Nonflammable
HCL lacks the property of flammability, making handling somewhat safer in controlled environments.
– Acidic Solution
In water, HCL forms an acidic solution. Hence, neutralization often involves bases.
– High Solubility
HCL exhibits high solubility in water. This property results in hydrochloric acid formation.
– Proton Donor
In chemical reactions, HCL stands as a robust proton donor. In essence, HCL loses a hydrogen ion, becoming a chloride ion.
– Reacts with Metals
Interaction with metals, HCL forms metal chlorides and hydrogen gas, signifying its reactivity.
– Forms Crystals
Cool temperatures result in HCL forming white crystals. Here, the analyzer aids in identification.
– Reacts with Ammonia
Upon encountering ammonia, HCL forms a white cloud of ammonium chloride.
– Denser than Air
HCL’s density surpasses air. Consequently, HCL gas settles lower in environments.
– Hydrogen Bonding
HCL forms hydrogen bonds, a unique chemical property vital in many reactions.
– Exothermic Dissolution
HCL dissolves exothermically in water, releasing heat.
– Strong Electrolyte
On dissolution, HCL forms ions, classifying it as a strong electrolyte.
– Fumes in Air
Contact with air causes HCL to fume, again demanding careful handling.
Hydrogen Chloride and its Impact!
Role of HCL in industrial processes
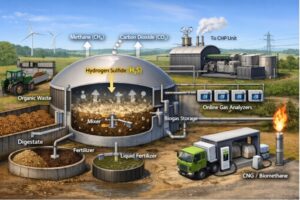
Industrial processes often involve Hydrogen Chloride (HCL). With a strong, pungent smell, HCL plays a vital role. Being a crucial component in the production of chemicals like vinyl and alkyl chloride, HCL’s role is paramount.
In steel mills, HCL helps in the pickling process. With precise control, Hydrogen Chloride Analyzer allows effective management of HCL.
Through rigorous detection, the analyzer ensures HCL’s optimal use. In addition, the analyzer ensures the safe handling of HCL, which is highly corrosive.
Significance of monitoring HCL concentrations
HCL concentration monitoring holds immense importance. A slight increase in concentration can turn situations dire. High HCL levels can damage machinery, impairing industrial operations. Plus, it can cause serious health problems.
The analyzer identifies HCL levels with accuracy, aiding in maintaining desired concentrations. A reliable analyzer provides real-time data, making it possible to manage HCL effectively and avoid dangerous exposure.
Impact of unregulated HCL emission
Unregulated HCL emission can have far-reaching effects. With no control, HCL can contaminate air and water. Such contamination can cause severe harm to the environment and human health. Long-term exposure can lead to respiratory issues.
An effective Hydrogen Chloride Analyzer comes to the rescue here. The analyzer can detect HCL levels in the emission, allowing industries to keep emissions under control.
Furthermore, it assists industries in complying with emission standards, ensuring a safer environment for all.
Hydrogen Chloride Analyzers: A Detailed Insight!
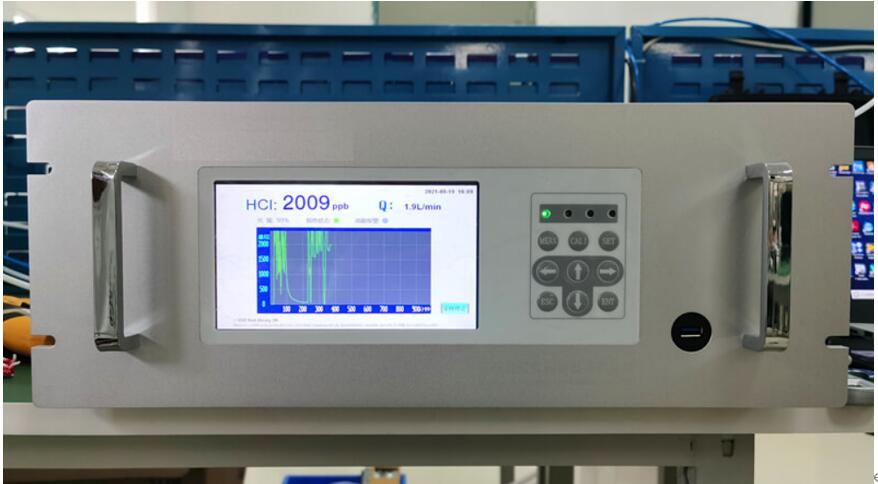
What is a Hydrogen Chloride Analyzer?
In simple terms, a Hydrogen Chloride Analyzer measures HCl in the air. This special tool senses the presence of Hydrogen Chloride, a gas dangerous for human health.
Every HCl analyzer uses smart tech, reading HCl levels accurately, fast, and safely. With the device, you can identify harmful gas leaks, ensuring safety in your space.
Components of an HCL analyzer
– Sensor Module
This is the heart of the HCl analyzer. The sensor detects the presence of Hydrogen Chloride in the air.
– Calibration Unit
This part guarantees the analyzer’s readings stay correct over time. Regular calibration helps maintain accuracy.
– Pumping System
This system draws air samples into the analyzer. It helps ensure consistent flow for reliable results.
– Filtration Component
It filters out unwanted particles that might interfere with the HCl detection process.
– Display Screen
This shows HCl readings. Some models also display other helpful information such as battery life, unit status, and more.
– Power Supply
It powers the HCl analyzer and can be either batteries or an electrical connection.
– Processor Board
Processor board is the brain of the analyzer. It processes the data from the sensor module and manages the operation of other components.
– Signal Converters
These convert signals from the sensor into readable data. The information is then displayed on the screen.
– Data Storage
It holds previous reading data for future reference. This allows comparison of HCl levels over time.
– Connectivity Ports
Enable connection to external devices. Useful for data transfer or analyzer updates.
– Cooling System
Helps maintain the temperature within safe limits. This prevents overheating and potential damage.
Principles of operation
– Gas Sampling
Here, the air containing Hydrogen Chloride is taken in. It’s crucial for obtaining an accurate reading.
– Pump Activation
This step ensures that air samples move through the system. A vital part of the analysis process.
– Filtration Process
Particles are separated from the gas sample. It ensures purity and precision in results.
– Sensor Activation
The sensor comes to life in this stage. It detects the presence of Hydrogen Chloride.
– Signal Conversion
The sensor’s reading is converted into an electronic signal. It is critical for data processing.
– Data Processing
The signal gets converted into understandable information. It is vital for accurate measurement display.
– Measurement Display
The Hydrogen Chloride concentration is displayed. The display is usually digital for clarity.
– Data Storage
The readings are stored for future reference. It’s essential for trend analysis and tracking changes over time.
– Calibration Check
The analyzer self-checks its calibration. It ensures reliable and accurate results.
– Alarm Triggering
If Hydrogen Chloride levels exceed safe limits, an alarm is triggered. Ensures immediate action can be taken.
– Fault Detection
Any issues in the system are identified. Keeps the analyzer working at optimal levels.
– Power Management
Ensures the analyzer operates within its power limits. It prolongs battery life and efficiency.
– Connectivity Maintenance
The analyzer stays connected to the control system and enables remote monitoring and control.
– Battery Usage
The analyzer uses battery power wisely. Extends operational time and reduces costs.
Different Types of Hydrogen Chloride Analyzers!
- TDLAS Analyzers – Absorption Spectroscopy, known as TDLAS, excels in gas measurement. Laser light interacts with gas molecules. Results arrive within milliseconds, with accuracy at the parts-per-billion level.
- NDIR Analyzers – NDIR gas analyzers operate in the infrared spectrum. They rely on specific gas absorption properties. For HCl, the absorption peak occurs at 3.4 micrometers. NDIR excels in continuous emission monitoring systems, CEMS.
- Electrochemical Analyzers – These analyzers work using a chemical reaction. They monitor changes in an electrical circuit. When measuring HCl, a sensor electrode reacts with the gas. The current change measures the concentration. Accuracy lies in the parts-per-million range.
- PID Analyzers – PhotoIonization Detectors, PIDs, use high-energy photons. These break gas molecules into ions. For HCl, the ionization potential is 8.07 eV. The detector measures the charge quantity, revealing the concentration.
- FID Analyzers – Flame Ionization Detectors, FIDs, use a hydrogen flame. Organic compounds like HCl get ionized in the flame. The ions produced are measured. FID is a reliable method for organic gas tracing.
- Mass Spectrometers – These devices ionize gas molecules. They then separate the ions based on their mass-to-charge ratio. For HCl, this is approximately 36.5 amu. Mass spectrometers offer high sensitivity and broad-spectrum detection.
- Ion-Selective Electrodes – For these, a specific ion creates a voltage. This voltage is then measured. For HCl, the response time is rapid, less than 10 seconds. Electrodes are sensitive, accurate, and cost-effective.
- Colorimetric Analyzers – These use chemical reactions to change colors. The color degree shows the gas concentration. For HCl, the reaction time is typically less than 15 minutes. This method is simple, portable, and cost-effective.
- Gas Chromatographs – Gas samples are separated and measured. They get passed through a column. For HCl, the retention time is around 4.5 minutes. High precision and reliability make this method highly desirable.
- UV-DOAS Analyzers – Ultraviolet Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy, UV-DOAS, absorbs light. For HCl, the wavelength range is 260-290 nm. This method offers real-time, high sensitivity detection. It is widely used in environmental monitoring.
| Analyzer Type | Sensing Method | Sensitivity | Data Speed | Application |
| TDLAS Analyzers | Uses tunable diode laser | High | Fast | Industry, research |
| NDIR Analyzers | Based on infrared absorption | Moderate | Moderate | Industrial emissions |
| Electrochemical Analyzers | Electrochemical reactions detection | High | Slow | Laboratory use |
| PID Analyzers | Photoionization detection | High | Fast | Air quality monitoring |
| FID Analyzers | Flame ionization detection | High | Fast | Environmental monitoring |
| Mass Spectrometers | Mass-to-charge ratio measurement | High | Slow | Research, labs |
| Ion-Selective Electrodes | Respond to specific ions | Low | Slow | Clinical, research |
| Colorimetric Analyzers | Color change detection | Moderate | Slow | Environmental testing |
| Gas Chromatographs | Uses gas-solid interaction | High | Slow | Industry, research |
| UV-DOAS Analyzers | Ultraviolet differential optical absorption spectroscopy | High | Moderate | Industrial emissions |
The Science Behind HCL Measurement!
– Spectrophotometry
It’s a reliable method for HCL detection. Light beams pass through the gas. Distinct colors are absorbed by HCL, telling us about its presence.
– Gas Chromatography
It separates the gas mixture. The HCL in the gas gets detected because each gas behaves differently.
– Electrochemical Detection
In this method, HCL causes a chemical reaction. The reaction produces an electrical signal. That signal is measured.
– Infrared Absorption
HCL absorbs certain infrared light. By measuring this absorption, one can find out the amount of HCL present.
– Ion Selectivity
It looks at the charge of the particles. HCL has a certain charge, so this method can find it.
– Flame Ionization
In this case, HCL is turned into ions using a flame. The ions are then measured.
– Tunable Diode Lasers
These lasers can ‘tune’ into HCL. They send a signal which tells us about the amount of HCL.
– Mass Spectrometry
It separates ions by their mass. Since HCL ions have a certain mass, they can be found with this method.
– Ultraviolet Absorption
It is similar to infrared absorption. But, in this case, ultraviolet light is used instead.
Installation and Operation of Hydrogen Chloride Analyzers!

– Site Selection
The first step in the setup is site selection. The right site ensures the analyzer works at its best.
– Unpacking
Careful unpacking protects the sensitive parts of the analyzer.
– Installation
Proper setup of the analyzer is vital. It affects its performance and longevity.
– Power Setup
The analyzer needs the right power source. This step includes setting up that source.
– System Calibration
It ensures the analyzer readings are accurate. Calibration should be done at regular intervals.
– Test Run
It checks if the analyzer is working as expected. It’s done before the analyzer starts its full operation.
– Maintenance Schedule
Regular upkeep keeps the analyzer in good shape. It prevents sudden breakdowns.
– Filter Replacement
Filters need to be changed regularly. They help keep the gas clean.
– Sensor Cleaning
It ensures the sensors can detect HCL properly.
– Data Download
The readings of the analyzer need to be saved for later use.
– Alarm Setting
It warns users if the HCL levels get too high.
– Power Management
It ensures the analyzer uses power efficiently.
– System Update
It includes upgrading the analyzer software. Updates keep the analyzer up to date.
– Troubleshooting
When problems arise, they need to be solved swiftly. This step deals with those problems.
Performance Evaluation of Hydrogen Chloride Analyzers!
- Sensitivity defines an analyzer’s ability to detect slight changes. Greater sensitivity in a Hydrogen Chloride Analyzer means better performance, more reliable data.
- Accuracy matters significantly. With higher accuracy, an analyzer ensures correct measurements. Less room for errors helps in critical decisions.
- Precision is vital too. Greater precision indicates consistency. Consistent readings bolster confidence in an analyzer’s results.
- Resolution is the smallest change a device can measure. High resolution means an analyzer can track even minute variations in Hydrogen Chloride levels.
- Linearity signifies that a unit can give reliable readings across its entire range. More linearity ensures equal performance at all measurement levels.
- Response Time plays a significant role. Fast response time allows quick data collection, essential for monitoring real-time changes.
- Zero Drift and Span Drift refer to an analyzer’s stability. Low drift rates suggest stable, reliable readings over time, crucial for long-term monitoring.
- Longevity matters in the lifespan of an analyzer. Longer-lasting devices reduce replacement costs, promoting cost-effective operations.
- Maintenance Frequency impacts operating costs. Fewer maintenance requirements indicate less downtime, higher productivity.
Software Solutions for Hydrogen Chloride Analyzers!
- Data Management helps handle large volumes of information. Efficient data management results in easy access, quick retrieval, aiding informed decisions.
- Calibration Scheduling is essential. Regular calibration ensures the analyzer’s accuracy remains top-notch, promoting reliable data collection.
- Alarm Notifications are crucial for immediate action. Timely alerts can prevent hazardous conditions, promoting safety.
- Remote Monitoring enables tracking operations from afar. Remote access provides flexibility, making the analyzer more user-friendly.
- Data Analysis provides insights. Deep data analysis helps identify trends, facilitates proactive measures.
- Reporting Tools assist in documenting findings. Effective reporting aids communication, fosters transparency in processes.
- User Interface is a key factor. User-friendly interface improves operator efficiency, reduces chances of errors.
- Network Integration broadens accessibility. Integration with a network enables data sharing, promotes collaborative work environment.
- Device Syncing enhances operational efficiency. Synchronized devices ensure data consistency across multiple platforms.
- Software Updates are critical for maintaining performance. Regular updates bring improvements, enhance features, and boost analyzer’s functionality.
Conclusion
The blog walked you through the world of Hydrogen Chloride Analyzers. They help measure HCL and keep industry processes safe. Take action now! Visit ESEGAS for the best Hydrogen Chloride Analyzers and to meet your safety needs. Stay informed, stay safe!