For decades, steel mills relied on “paper math” to report carbon footprints. Engineers used fuel consumption and emission factors to estimate their output. Those days are over. As we approach 2026, the industry is hitting a massive turning point. New global mandates, such as the EU Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM), now demand “primary data.” This means you must measure actual molecules in the stack, not just guess from a spreadsheet.
This shift creates a tough technical challenge for EHS managers. You need Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions testing equipment that is sensitive enough for strict EPA or ETS compliance. However, it must also survive the brutal heat and dust of a blast furnace. How do you balance lab-grade precision with industrial-grade durability? This guide solves that puzzle by focusing on high-uptime solutions for the harshest environments.

Beyond simple compliance, look at the bigger picture. In a “Green Steel” economy, carbon is a currency. If your sensors over-report emissions by even 5%, you lose money on carbon taxes. Conversely, accurate data lets you prove your efficiency to high-value buyers. Investing in top-tier emissions testing equipment isn’t just a regulatory chore. It is a tool for carbon-competitive pricing that protects your bottom line in a low-carbon market.
Where Should You Install Greenhouse Gas Emissions Testing Equipment Across Your Steel Mill?

Before buying Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions testing equipment, you must map your facility. Not every stack is the same. Each production area has its own “personality” and technical hurdles. If you use the same tool everywhere, your data will suffer. You must match the equipment to the specific environment.
The Heavy Lifters: Blast Furnaces and Coke Ovens
Blast furnaces and coke ovens are the most demanding spots. They vent high concentrations of CO2 and methane. However, the air is thick with abrasive dust and moisture. Standard sensors will fail here within weeks. You need heavy-duty Greenhouse Gas emissions testing equipment featuring heated sampling probes. Look for systems with multi-stage filtration. These filters catch particulates before they reach the delicate analyzer, ensuring your uptime stays high.
The Speed Demons: Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF)
Electric Arc Furnaces operate differently. They run in cycles, meaning gas levels spike and drop rapidly. To capture these “bursts,” you need speed. Slow sensors will miss the peak emissions during the melting phase. Aim for analyzers with a T90 response time of less than 3 seconds. This speed ensures you capture every ton of carbon for accurate ESG reporting.
The Silent Contributors: Captive Power Plants
Many mills overlook their on-site power plants. However, these stacks are vital for your Scope 1 totals. Since these plants burn coal or waste gas, they emit a steady stream of CO2. Use a Continuous Emissions Monitoring System (CEMS) here. It provides the reliable, 24/7 data stream required by tax auditors.
Which Sensing Technologies Power the Best Greenhouse Gas Emissions Testing Equipment?
Before selecting your hardware, you must identify your targets. In a steel mill, CO2 is the main culprit. However, methane (CH4) from coke ovens and nitrous oxide (N2O) also impact your carbon footprint. To track these accurately, you need the right “brain” inside your Greenhouse Gas emissions testing equipment.
The Reliable Workhorse: NDIR Technology
Non-Dispersive Infrared (NDIR) is the go-to choice for most steel mills. It excels at measuring CO2 and methane with proven long-term stability. Because it is robust, it handles the vibration and dust of a mill floor better than most. If you need a cost-effective solution for standard stacks, NDIR is your best bet.
The Precision Expert: TDLAS and FTIR
For more complex tasks, consider TDLAS. This laser-based tech offers sub-second accuracy. It ignores “interference gases,” making it perfect for high-moisture areas. If you need to track multiple gases like N2O and CO at once, FTIR is the winner. It acts like a “multi-tool,” analyzing several greenhouse gases through one single beam.
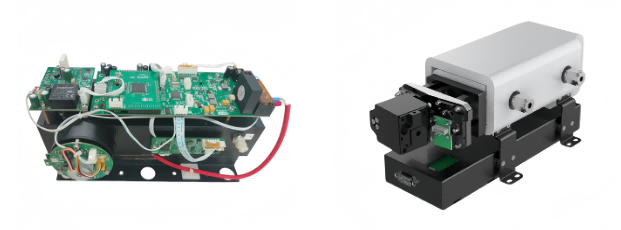
The High-Performance Choice: ESE-GH-2080
When global auditors knock, you need data they can trust. This is where the ESE-GH-2080 Greenhouse Gas Analyzer shines. It combines NDIR and UV-DOAS technologies to eliminate measuring errors. In fact, it hits a 0.1% error margin, which is the “Gold Standard” for international carbon verification. It gives you the precision of a lab with the toughness of a factory.
What Technical Features Define Top-Tier Greenhouse Gas Emissions Testing Equipment?

Buying a greenhouse gas analyzer is only the first step. To build a world-class Greenhouse Gas emissions monitoring system, you must look at how the hardware handles real-world stress. Your equipment must do more than just “read” gases. It must provide auditable, high-accuracy data that stands up to global scrutiny.
Your system is essentially a financial reporting tool. Therefore, the Greenhouse Gas emissions testing equipment must support ISO 14064 or EPA-compliant data logging. Look for analyzers that record raw data alongside calibration logs. This transparency is vital during a carbon audit. It proves your numbers are real and haven’t been altered.
Raw stack gas is often too hot or wet for direct testing. You must choose between “Hot/Wet” and “Cold/Dry” setups. Most steel mills prefer Cold/Dry systems. These use high-performance gas coolers to strip away moisture instantly. By removing water vapor, you protect the analyzer from corrosion. This choice significantly extends the life of your sensors and keeps your readings stable.
Maintenance costs often exceed the initial purchase price. To save money, select a modular design. Some modern systems feature “SimpleClick” sensor elements. These allow your technicians to swap parts in minutes without specialized tools. Reducing downtime during calibration keeps your monitoring system active 24/7, ensuring you never miss an emission spike.
Which Mistakes Should You Avoid When Buying Greenhouse Gas Emissions Testing Equipment?

Even with a big budget, a few simple oversights can ruin your monitoring project. Steel mills are notoriously “dirty” environments that eat sensitive electronics for breakfast. To keep your system running, you must avoid these three common traps:
1.The Dust Trap: Forgetting Particulate Management
Dust is the number one killer of sensors in a steel mill. Standard sampling probes will clog within days in a sinter plant or blast furnace. To prevent this, always choose Greenhouse Gas emissions testing equipment with automatic back-purge ports. These systems use high-pressure air to “blow out” dust from the filters automatically. This simple feature saves your team from climbing stacks for manual cleaning every week.
2.The Gold-Plated Trap: Over-Specifying Sensitivity
Many managers mistakenly buy lab-grade gear with “parts-per-billion” (ppb) sensitivity. However, most carbon regulations only require accuracy in the parts-per-million (ppm) range. Buying excessive sensitivity just makes the equipment more fragile and expensive to calibrate. Stick to industrial-grade ppm sensors that offer the ruggedness your facility actually needs.
3.The Data Silo: Ignoring Digital Integration
Don’t buy a “dumb” analyzer that only shows numbers on a screen. Modern ESG reporting requires seamless data flow. Ensure your equipment supports digital interfaces like Modbus or Profibus. This allows the hardware to talk directly to your centralized ESG software. Automated data transfer eliminates human error and makes your next carbon audit a breeze.
Conclusion
The global steel industry is entering a new era of accountability. Deciding on the right monitoring strategy today determines your competitiveness tomorrow. Whether you operate a traditional BF-BOF plant or a modern EAF facility, your data must be bulletproof. One size does not fit all. You must tailor your hardware to your specific production route and the strict requirements of your target export markets.
Choosing the right Greenhouse Gas emissions testing equipment protects you from rising carbon taxes and regulatory fines. Accurate, real-time measurement allows you to prove your “Green Steel” credentials to premium buyers worldwide. As standards evolve, having a flexible and digitally integrated system ensures you won’t have to replace your entire setup every few years.
Don’t leave your compliance to chance. Before you sign a procurement contract, take a professional first step. We recommend consulting with technical specialists to perform a site-specific “Gap Analysis.” Contact an expert today to design a rugged, high-precision monitoring solution that secures your mill’s future in a low-carbon world.
FAQs:
1. Why should steel mills move from estimated calculations to direct GHG measurement in 2026?
New global regulations like EU CBAM and updated EPA reporting rules now prioritize “primary data.” Direct measurement using Greenhouse Gas emissions testing equipment provides a more accurate carbon footprint than paper-based estimates. This precision prevents over-paying on carbon taxes and helps mills qualify for “Green Steel” certifications by proving lower emission intensity.
2. What is the best sensing technology for CO2 monitoring in a blast furnace?
NDIR (Non-Dispersive Infrared) is the industry standard for CO2 and CH4 due to its ruggedness and long-term stability. However, for environments with high moisture or rapid fluctuations, TDLAS technology is often the “Gold Standard” as it offers sub-second response times and zero cross-interference from other gases.
3. How does a Cold/Dry sample conditioning system reduce maintenance costs?
A Cold/Dry system uses a high-performance gas cooler to remove moisture from the sample gas immediately after it leaves the stack. By “drying” the gas, you prevent acid condensation and water droplets from damaging the delicate sensors inside your Greenhouse Gas emissions testing equipment. This leads to fewer sensor failures and longer calibration intervals.
4. What equipment is needed for a complete GHG monitoring system besides the analyzer?
A robust monitoring system requires several integrated components:
- A gas sampling probe with back-purge for dust removal.
- A dust monitor to track particulate matter.
- Integrated temperature, pressure, and flow meters to calculate the total mass of emissions.
- A data acquisition system (DAS) for ISO 14064 compliant reporting.
5. How can I avoid probe clogging in high-dust steel mill environments?
Always specify Greenhouse Gas emissions testing equipment that includes automatic back-purge ports. This feature uses compressed air to periodically blow dust off the probe filter, preventing clogs in sinter plants or blast furnaces and reducing the need for manual cleaning at dangerous heights.
6. Does the ESE-GH-2080 Greenhouse Gas Analyzer meet international audit standards?
Yes. The Greenhouse Gas Analyzer ESE-GH-2080 utilizes advanced NDIR and UV-DOAS technology to achieve a 0.1% error margin. This level of precision meets the strict verification requirements for global carbon markets, providing the “audit-ready” data needed for international trade.