
The continuous real-time multi-gas analyzer gives waste-to-energy plants real-time insight into emission monitoring. And it ensures they meet strict limits and enables smarter operations. With continuous data, plants can immediately detect problems and adjust processes, improving efficiency and protecting the environment.
In this article, we will to help you choose the right multi-gas analyzers and systems for your waste incineration step-by-step.
Why Real-Time Emission Monitoring Matters in Waste Incineration?

Regulatory Drivers
Waste incineration is heavily regulated. For example, all European waste incinerators must meet the EU Industrial Emissions Directive (IED 2010/75/EU), which mandates continuous stack monitoring and strict pollutant limits. Similar rules exist worldwide (e.g., US NSPS/NESHAP for waste combustors).
Operational & Safety Benefits
Real-time multi-gas analyzer in CEMS improves plant control and safety. Continuous gas data instantly alerts operators to abnormalities, allowing rapid corrections. For example, a sudden rise in CO or HCl can prompt immediate burner or feed adjustments to avoid an upset. Live feedback lets you fine-tune combustion: real-time air/fuel adjustments cut CO and NOₓ emissions and ensure complete burning.
Environmental & Community Impact
Beyond compliance, real-time monitoring benefits local air quality and public health. Waste incinerators can emit pollutants like SO₂, NOₓ, HCl, fine particulates, and even mercury if not well controlled. Communities also demand transparency; disclosing real-time emissions builds trust. For example, one incinerator’s public sharing of CEMS data “boosted its environmental protection image” and gained community support.
Which Gases Must Be Monitored in Waste Incineration Emissions?
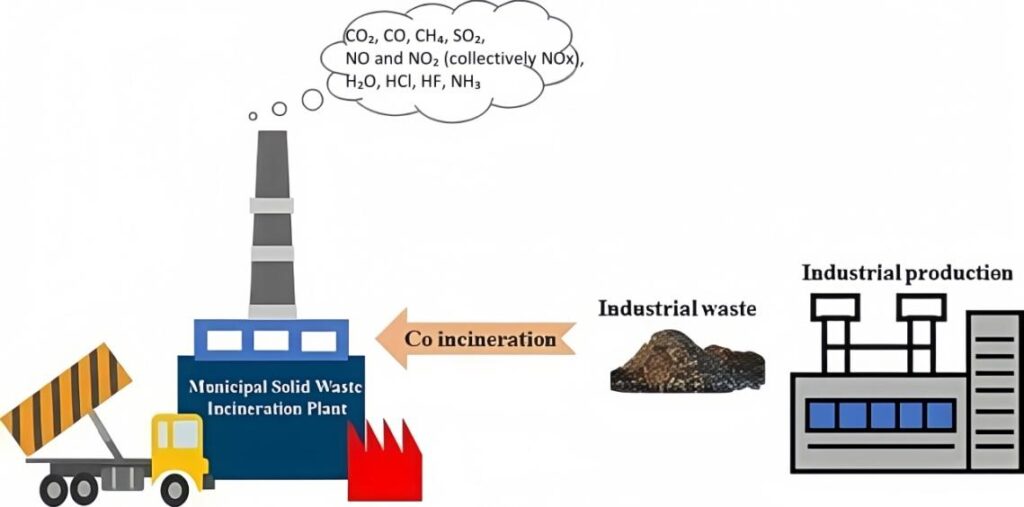
(Emission from waste incineration)
Waste incineration produces a complex mix of gases, and environmental standards regulate many of them. Real-time monitoring is critical for compliance and safety. The typical target gases include:
- CO₂ (carbon dioxide)
- CO (carbon monoxide)
- CH₄ (methane)
- SO₂ (sulfur dioxide)
- NO and NO₂ (collectively NOx)
- H₂O (water vapor)
- HCl (hydrogen chloride)
- HF (hydrogen fluoride)
- NH₃ (ammonia)
These compounds are byproducts of combustion and can vary with feedstock composition and burner efficiency. Failing to monitor them properly can lead to permit violations, community health complaints, and unsafe plant conditions.
How Do You Choose the Right Multi-Gas Analyzer for Waste Incineration Emission Monitoring?
Multi-gas analyzer is able to make real-time emission monitoring happen. Most of time, multi-gas analyzer will operate as a CEMS for industrial emission monitoring. When selecting a multi-gas analyzer or continuous emission monitoring system, start by assessing the condition of the gas stream. If the sample is clean and dry, a standalone multi-gas analyzer is usually sufficient. These systems work well when there’s minimal particulate matter, no oil mist, and low water content.
If the gas stream runs hot, wet, or dusty, you must add more to the multi-gas analyzer. Deploy a CEMS (Continuous Emissions Monitoring System) with the sample conditioning in these situations. This typically involves removing moisture, particulates, and oil droplets before the gas reaches the multi-gas analyzer. Without proper pretreatment, sensor accuracy and system lifespan can both suffer.
So, the rule of thumb is simple:
- Clean and dry gas? Select multi-gas analyzers.
- Is the gas stream dirty, wet, or hot? Choose a full CEMS with pretreatment modules.
This decision lays the groundwork for reliable and compliant monitoring.
Matching Sensor Technology to Target Gases
Modern multi-gas analyzers are not one-size-fits-all. Each target gas requires a specific sensor technology. ESEGAS’s multi-gas analyzers combine multiple detection methods into one integrated platform. Here’s how they break down:
Ideal for stable, infrared-absorbing gases like CO, CO₂, and CH₄. These sensors are rugged and respond quickly. Facilities often use CEMS in harsh environments.
Best for SO₂, H₂S, NO, NO₂, and overall NOx levels. UV-DOAS offers excellent selectivity in gas mixtures and handles low concentrations well.
Designed for HCl, HF, and NH₃. This method excels at detecting gases with strong absorption lines and low cross-sensitivity. It also works well in hot and corrosive environments. However, it only can monitor one gas with one machine.
The all-rounder. FTIR detects dozens of gases at once, including SO₂, NOx, HCl, HF, CO, CO₂, CH₄, H₂O, and various VOCs. It delivers a complete emissions profile in a single reading.
Using the right sensor for each gas not only ensures accurate data but also prevents false alarms and missed thresholds.
How Can ESEGAS Customize Multi-Gas Analyzer Solutions for Waste Incineration Emissions?

While individual sensors can be powerful, integration is where real impact happens. Multi-gas analyzer in CEMS is the consequence by combining NDIR, UV-DOAS in one unified system. Moreover, TDLAS and FTIR technologies have their own target gases and advantages. ESEGAS multi-gas analyzers in CEMS deliver:
- Comprehensive gas coverage in a single cabinet
- Fewer sampling points and simpler installations
- Streamlined maintenance and calibration routines
- Centralized data logging and alarms via SCADA or DCS systems
For plant engineers, this means fewer headaches. For EHS and ESG professionals, it means higher confidence in reported data. And for system integrators, it means smoother deployment with fewer compatibility issues. Discover how ESEGAS delivers tailored solutions.
ESEGAS designs emission monitoring packages to match your plant’s needs. Waste incinerator flue gas often carries dust, moisture, and oil residues. Thus, we pair multi-gas analyzers with the right sample conditioning.
Common configurations include:
- Single CEMS(NDIR+UV-DOAS): For well-conditioned, low-dust streams.
- FTIR-CEMS: To capture a full suite of gases in one unit.
- CEMS + TDL gas analysis system: When you need both broad coverage and targeted HCl/HF/NH3 detection.
For example:
- SO₂, NOx, CO monitoring: We integrate NDIR and UV-DOAS into your CEMS. You get a five-gas analyzer that continuously reads SO₂, NOx, CO₂, CO, and CH₄ in CEMS.
- SO₂, NOx, HCl/HF/NH3 monitoring: We pair a TDL gas analysis system and CEMS.
- Full gas profile (SO₂, NOx, CO₂, CO, CH₄, H₂O, HCl, HF, NH₃): We recommend FTIR-CEMS for its comprehensive scope and cost-effective performance.
By choosing the right mix of technologies, you ensure accurate, reliable, and compliant emissions data. Ultimately, ESEGAS balances performance and budget to deliver the smartest, most cost-effective emissions monitoring solution.
Conclusion

The choice between a multi-gas analyzer and a full CEMS depends on one thing: the nature of the gas stream. Clean gases with gas flow velocity allow for direct measurement in laboratory. But dirty, wet, or chemically reactive gases require pretreatment and careful sensor selection in industry.
Matching each target gas with the right detection method is critical. Integrating multiple technologies into one system prevents data gaps, lowers costs, and makes your reports audit-ready.
Ultimately, waste incineration is a high-stakes environment. The gases aren’t just numbers—they’re operational risk indicators, compliance requirements, and community concerns rolled into one. Real-time data is your most valuable tool. Use it wisely to help you gain community support.
Want to learn more about integrating multi-gas analyzers into your waste-to-energy plant?
Stay tuned for our next post on calibration, maintenance, and data integration best practices of multi-gas CEMS.

























