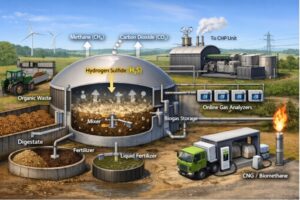
Flue gas analyzers are essential tools in combustion processes and air quality control. These devices measure the composition of gases emitted from industrial processes, ensuring that emissions meet regulatory standards and contribute to environmental protection. By analyzing components such as carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2), oxygen (O2), and nitrogen oxides (NOx), they provide critical data for optimizing fuel use and reducing pollution.
This article explores various aspects of Guidance on selecting the right analyzer for your needs!

What Aspects Can We Learn about Flue Gas Analyzers
Definition of Flue Gas Analyzers
It is a device used to measure the gases produced during combustion. It helps evaluate how well combustion systems work and ensures that they meet environmental standards.
How Flue Gas Analyzers Work
They work by taking samples of exhaust gases from sources like boilers, furnaces, and engines. They use specialized sensors to identify and measure different gas components. The most common gases measured include:
- Oxygen (O2): This indicates how efficiently combustion is taking place.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): High levels of this gas suggest that combustion is incomplete.
- Nitrogen Oxides (NOx): These gases are important for meeting regulations because of their harmful effects on the environment.
Importance of Flue Gas Analyzers
Flue gas analyzers are crucial in monitoring combustion and protecting the environment. They assess the performance of heating systems by identifying areas of inefficient fuel use, enabling optimization of fuel consumption while enhancing safety through early detection of hazardous gas levels. These devices also help industries meet emissions standards set by regulatory bodies, reduce harmful emissions contributing to air pollution, and provide detailed analyses that aid in the development of cleaner technologies. By linking industrial processes with environmental responsibility, flue gas analyzers support sustainable management practices across various sectors.
What are the Types of Flue Gas Analysers?
1. Portable Flue Gas Analyzers
Portable flue gas analyzers are designed for mobility and flexibility, making them highly suitable for various applications across different environments. These compact devices are particularly advantageous when performing periodic checks and maintenance tasks on-site. By offering ease of transportation and setup, they allow technicians to conduct thorough flue gas analysis without the constraints of a fixed location.

Features and Advantages:
- Mobility: With their lightweight design, portable analyzers can be easily carried to different locations, making them ideal for fieldwork.
- Versatility: Equipped with multiple sensors, these devices can measure various gases such as O2, CO, and NOx simultaneously, providing comprehensive data on combustion efficiency.
- Ease of Use: Many models feature intuitive interfaces that simplify operation, allowing users to quickly obtain accurate readings with minimal training.
- Real-Time Data Collection: Portable analyzers often provide instant readings, enabling immediate assessment and decision-making on-site.
- Cost-Efficiency: Compared to stationary options, portable units typically require lower initial investments and operational costs.
Typical use cases for portable analyzers include:
- Maintenance Checks: Technicians frequently use these devices for routine inspections of boilers, heaters, and other combustion systems. Regular checks ensure optimal performance and early detection of potential issues.
- Compliance Verification: In industries where emission standards are strict, portable analyzers help verify compliance by providing precise measurements that can be documented for regulatory purposes.
- Troubleshooting: When unexpected issues arise in combustion systems, portable analyzers allow technicians to quickly diagnose problems by analyzing the composition of exhaust gases.
Incorporating these versatile tools into routine operations enhances both environmental protection efforts and system efficiency. Embracing the portability of these analyzers allows businesses to maintain high standards in flue gas monitoring across diverse settings.
2. Continuously Emission Monitoring System
Continuously Emission Monitoring System are crucial for industrial applications, especially when continuous monitoring is necessary. Unlike portable analyzers that are great for moving around and doing occasional checks, Continuously Emission Monitoring System are built for long-term use, providing steady and dependable data collection.

Importance of Continuous Monitoring
In industries like power generation, chemical manufacturing, and waste management, it’s vital to continuously monitor flue gases to meet environmental regulations and improve operational efficiency.
These systems offer immediate data that helps maintain emissions standards set by government agencies, preventing organizations from facing large fines and promoting environmental sustainability.
Key Features of Stationary Analyzers
- Designed to endure tough industrial conditions, stationary analyzers are more durable and reliable over long periods.
- Using advanced sensors such as O2, CO, NOx, these devices accurately measure gas levels, offering a precise understanding of combustion processes.
- Equipped with complex software for data collection and analysis, these systems easily integrate with existing plant control systems.
Deciding between portable and stationary options largely depends on the specific needs of your operations. While mobility benefits maintenance checks, the sturdiness and accuracy of stationary analyzers make them essential for ongoing industrial applications.
What are the Key Components and Working Principles of a Flue Gas Analyzer?
Flue gas analyzers are equipped with essential sensors that play a crucial role in accurately measuring various gas concentrations during combustion processes. The most common sensors include those for oxygen (O2), carbon monoxide (CO), and nitrogen oxides (NOx). These sensors are integral to determining the efficiency of combustion and ensuring compliance with environmental standards.
Essential Sensors
- Oxygen (O2) Sensor: Measures the amount of oxygen in the flue gas, providing insights into combustion efficiency.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO) Sensor: Detects CO levels to prevent incomplete combustion, which can lead to hazardous emissions.
- Nitrogen Oxides (NOx) Sensors: Includes separate measurements for NO and NO2, crucial for monitoring pollutants that contribute to air quality issues.
Measurement Range
Each sensor has a specific measurement range tailored to detect even trace amounts of gases, ensuring precise monitoring. For instance, O2 sensors typically have a range from 0% to 25%, while CO sensors may measure from 0 ppm to several thousand ppm, depending on the application.
Measurement Process
- Gas Sampling: The analyzer draws a sample of flue gas from the exhaust stream.
- Sensor Analysis: The collected sample is passed over the sensors, where chemical reactions occur to produce measurable electrical signals.
- Data Logging: These signals are converted into digital data, providing real-time readings displayed on the analyzer’s interface.
- Data Interpretation: Advanced software within the analyzer processes these readings to deliver actionable insights about combustion efficiency and emissions levels.
Understanding these components and their functions allows you to appreciate how flue gas analyzers contribute significantly to both environmental protection and operational efficiency in various industries.
What are the Significance and Applications of Flue Gas Monitoring Systems?
Flue gas monitoring systems play a crucial role in ensuring regulatory compliance with emissions standards. Governments and environmental agencies worldwide set strict limits on the allowable emissions from industrial processes to protect air quality and public health. By continuously measuring and analyzing the composition of flue gases, these systems help industries adhere to legal requirements by providing accurate data on pollutants such as SO2, NOx, and CO2.

The significance of flue gas analyzers goes beyond compliance. They are essential tools for efficiency optimization in various sectors. Through precise monitoring, industries can fine-tune combustion processes, reducing fuel consumption and minimizing emissions. This not only leads to cost savings but also contributes to environmental sustainability.
These flue gas analyzers are used across various industries which rely heavily on it:
- Manufacturing: Ensures that production processes align with environmental regulations while optimizing fuel usage.
- Power Generation: Vital for maintaining efficient combustion in power plants, reducing operational costs, and meeting emission targets.
- Chemical Industries: Helps in managing complex chemical reactions while keeping emissions within permissible levels.
- Cement Production: Monitors emissions during the high-temperature kiln operations to ensure compliance with pollution control norms.
Flue gas monitoring systems are essential for both regulatory adherence and operational efficiency across various industrial sectors. By enabling real-time data analysis, they provide industries with the insights needed to improve energy efficiency while minimizing their environmental impact. These systems highlight the importance of integrating technological solutions like IoT for enhanced performance and reliability in emission management.
How to Select the Right Flue Gas Analyzer for Your Needs?
It is essential for both accuracy and user satisfaction. Key features to evaluate include:
Measurement Range: The analyzer should cover the specific range of gases relevant to your application, such as SO2, NOx, CO, and O2. A broad measurement range ensures versatility in different industrial scenarios.
- Response Time: Quick response times are critical in dynamic environments where conditions change rapidly. Faster response times allow for real-time monitoring and immediate adjustments.
- User Interface Clarity: A clear and intuitive user interface enhances usability, enabling operators to easily navigate through settings and view data without extensive training.
- Ease of Calibration: Regular calibration is necessary for maintaining accuracy. An analyzer that simplifies the calibration process can save time and reduce errors, making it a preferred choice for routine checks.
Consider these factors alongside your specific needs to ensure you select a flue gas analyzer that optimizes performance while providing a seamless user experience.
Evaluating these elements helps align the technical capabilities of the analyzer with the operational demands of your environment, ensuring efficient monitoring and compliance with emissions standards.
Conclusion
Understanding flue gas analyzers and their comprehensive functions are crucial for industries committed to environmental protection and efficiency optimization. These devices serve as essential tools in monitoring emissions, ensuring compliance with stringent environmental regulations, and improving combustion efficiency.
FAQs
A: Flue gas analyzers are instruments used to measure the concentration of various gases emitted during combustion processes. They play a crucial role in monitoring air quality and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
A: The primary functions of flue gas analyzers include monitoring combustion efficiency, detecting harmful emissions, and providing data for regulatory compliance. They help in optimizing combustion processes and improving overall air quality.
A: Portable flue gas analyzers are designed for mobility and are typically used for maintenance checks in various locations. In contrast, stationary flue gas analyzers are fixed installations that provide continuous monitoring, particularly in industrial applications such as power generation.
A: Essential components of flue gas analyzers include sensors for measuring gases like O2, CO, and NOx, data logging capabilities, and measurement types to ensure accurate readings during combustion processes.
A: Flue gas monitoring systems play a vital role in ensuring compliance with emissions standards set by regulatory bodies. They provide real-time data on emissions levels, helping industries maintain adherence to environmental regulations.
A: Common challenges include sensor degradation over time, technical issues related to calibration and maintenance, and the need for regular updates to keep up with emerging technologies like IoT integration in flue gas analysis.