Industrial emissions are under stricter scrutiny than ever before. Manual reporting and outdated sampling methods leave companies vulnerable to fines, compliance breaches, and environmental criticism. The solution lies in a continuous emission monitoring system (CEMS) — a technology designed to provide real-time, precise, and automated emissions data directly from the source.

A CEMS gas analyzer is part of a continuous emission monitoring system that continuously measures gases like SO₂, NOₓ, CO, CO₂, O₂, and more from industrial exhaust streams. These systems ensure compliance, optimize combustion efficiency, and enable transparent environmental reporting in real time.
While the purpose of CEMS seems clear — to monitor emissions continuously — the real value lies in how these systems function, where they are applied, and what makes advanced solutions such as the ESEGAS CEMS LX-4000stand out among competitors. Let’s explore each aspect in detail.
What Is a CEMS Gas Analyzer?
Industries face growing pressure to control and document emissions in accordance with strict national and international regulations.
Conventional testing methods are slow, error-prone, and lack continuous data, creating blind spots that can lead to costly non-compliance.
The CEMS gas analyzer offers continuous, automated measurement of multiple gases in flue emissions, ensuring accuracy, traceability, and compliance.
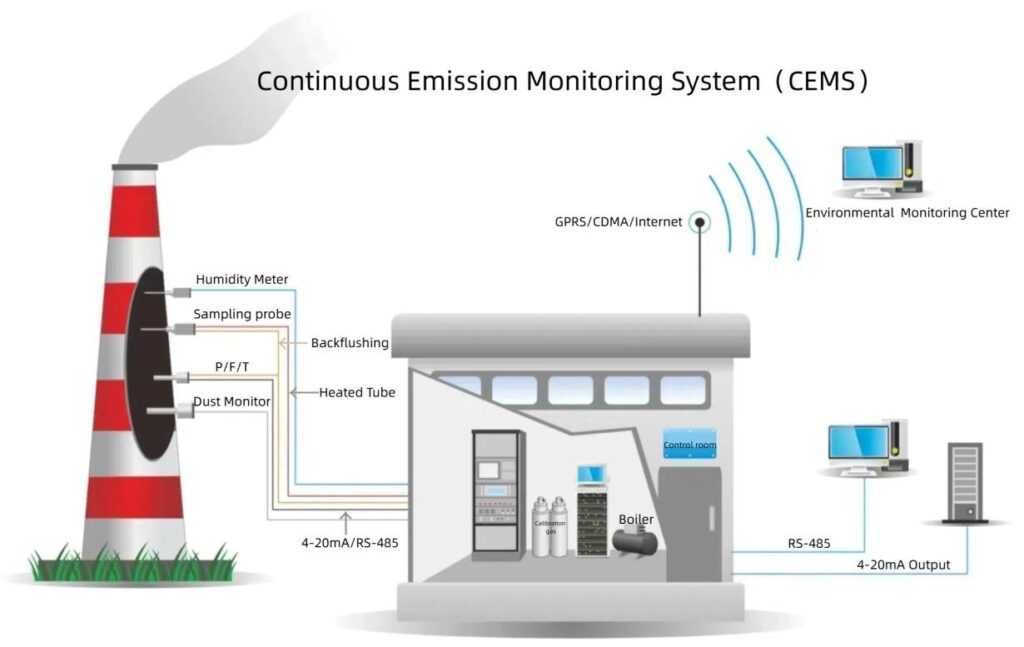
A CEMS gas analyzer is the heart of a continuous emission monitoring system (CEMS), designed to analyze the concentration of target gases in the exhaust flow of combustion processes. These analyzers use advanced detection principles such as non-dispersive infrared (NDIR), ultraviolet (UV), flame ionization detection (FID), and electrochemical sensors to quantify gases like SO₂, NOₓ, CO, CO₂, O₂, HCl, and HF. Combined with a sampling probe, conditioning system, and data acquisition unit, the analyzer continuously measures and records emissions data — transforming compliance monitoring from a reactive task into a proactive management tool.
How Does the ESEGAS CEMS LX-4000 System Work?
Managing multi-gas measurement across varying flow rates, temperatures, and humidity levels can compromise data accuracy.
Without an integrated monitoring architecture, plants risk inconsistent readings and data loss.
The ESEGAS CEMS LX-4000 provides a fully integrated solution that ensures reliability, precision, and compliance through advanced design.

The ESEGAS CEMS LX-4000 is an intelligent, modular, and fully automatic system that measures multiple gas components simultaneously — including SO₂, NO, NO₂, O₂, CO, CO₂, HCl, HF, and even water vapor. Built for continuous operation in harsh industrial environments, it integrates every key subsystem: gas sampling and conditioning, multi-gas analyzers, automatic calibration, and a data acquisition and handling system (DAHS).
One of its defining strengths lies in the precision of its sampling system — engineered to prevent condensation, particle interference, and cross-contamination. The CEMS LX-4000 also incorporates automatic zero and span calibration routines, ensuring data accuracy without manual intervention. Its industrial control computer manages all process data, providing real-time visualization, trend analysis, and remote access capabilities. By linking directly with regulatory platforms, the system enables automatic emission reporting that meets requirements such as the EU IED, China GB standards, and US EPA 40 CFR Part 60/75.
Where Are CEMS Gas Analyzers Used?
Without accurate, continuous, and traceable emission data, facilities risk regulatory violations, unexpected plant shutdowns, environmental penalties, and public criticism. Intermittent testing or manual sampling fails to capture the true variability of emissions—especially during load changes or process upsets—making compliance verification nearly impossible.
The CEMS gas analyzer, integrated within a continuous emission monitoring system (CEMS), provides round-the-clock measurement and reporting of key pollutants. It enables real-time insights into plant performance, ensuring compliance, transparency, and process optimization across multiple industries.
CEMS in Power Generation
Power plants—whether coal-fired, gas-fired, or biomass—are among the largest sources of stack emissions. They require CEMS gas analyzers to continuously monitor flue gases such as SO₂, NOₓ, CO, CO₂, and O₂ to comply with air-quality permits and emission trading schemes.

In coal-fired power plants, CEMS are typically installed downstream of desulfurization (FGD) and denitrification (SCR/SNCR) units to verify the efficiency of these emission control systems. For natural gas combined-cycle (NGCC) units, CEMS ensure low-NOₓ combustion and verify turbine performance under varying loads.
The ESEGAS CEMS LX-4000 system offers industry-grade reliability with automatic calibration, temperature-compensated sensors, and rugged sample handling. Its modular architecture allows integration with flue gas flowmeters, dust monitors, and opacity sensors—making it a comprehensive solution for emission compliance under US EPA 40 CFR Parts 60 & 75 and EU IED 2010/75/EU frameworks.
CEMS in Petrochemical and Refining Industries
Refineries and petrochemical complexes operate dozens of combustion sources—heaters, reformers, boilers, and incinerators—each requiring emission monitoring. Here, CEMS systems measure gases like NOₓ, CO, CO₂, and O₂ to optimize combustion efficiency and track emissions from sulfur recovery units (SRU) and flares.
In such corrosive, high-temperature environments, ESEGAS CEMS systems excel thanks to their heated sample lines, acid-resistant components, and anti-condensation design, ensuring stable measurement of acid gases such as H₂S, HCl, and HF. The LX-4000 model also supports networked data handling—allowing central emission reporting from multiple process units to the plant’s environmental management system (EMS).
CEMS in Cement and Lime Production
Cement kilns and lime furnaces produce emissions with high dust loading, fluctuating temperature, and moisture content—conditions that challenge traditional analyzers. CEMS gas analyzers in this sector must measure SO₂, NOₓ, CO, CO₂, O₂, and sometimes total hydrocarbons to verify compliance and monitor combustion control.

The ESEGAS CEMS LX-4000 uses high-temperature extraction probes, efficient particle filtration, and heated linesto deliver accurate readings even in dust-rich environments. With integrated flow measurement and automatic data logging, it ensures reliable reporting aligned with EN 15267-3 (QAL1 certification) and local environmental standards.
CEMS in Steel, Metallurgy, and Non-Ferrous Industries
Blast furnaces, sintering plants, coke ovens, and foundries emit complex gas streams containing CO, NOₓ, SO₂, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Continuous monitoring is essential not only for compliance but also for process optimization—such as controlling furnace efficiency and gas recycling.
ESEGAS provides rugged CEMS solutions with reinforced sampling systems capable of handling high-temperature, high-particulate exhaust. The LX-4000 integrates advanced diagnostics and self-cleaning functions to maintain measurement stability even in severe industrial atmospheres.
CEMS in Waste Incineration and Waste-to-Energy (WtE)
Municipal and hazardous waste incinerators face some of the world’s strictest emission regulations. They must monitor up to 10–12 parameters simultaneously—SO₂, NO, NO₂, CO, CO₂, O₂, HCl, HF, NH₃, TOC, and sometimes Hg or dioxins—under continuous operation.
The ESEGAS CEMS LX-4000 is engineered specifically for these challenges. It supports multi-gas detection, automated calibration sequences, and real-time transmission of data to supervisory control systems or government portals. By maintaining continuous records of emission concentration and total pollutant load, operators can demonstrate full compliance with directives like EU Waste Incineration Directive 2000/76/EC and corresponding EPA MACT standards.
CEMS in Chemical and Fertilizer Production
Ammonia, nitric acid, and urea plants emit NOₓ and N₂O, while sulfuric acid units release SO₂. For these processes, real-time measurement is critical to maintain catalyst performance and prevent environmental exceedances. The ESEGAS CEMS LX-4000 provides precise NOₓ and SO₂ quantification using UV and NDIR detection, enabling fine-tuned process control.

In fertilizer plants, emission data from CEMS gas analyzers also feeds into sustainability reporting frameworks like ISO 14064 and corporate ESG dashboards, demonstrating the plant’s commitment to clean manufacturing.
Emerging Applications: Hydrogen, Biomass, and Carbon Capture
As industries transition to low-carbon operations, CEMS gas analyzers are evolving to support hydrogen combustion, biomass co-firing, and carbon capture utilization and storage (CCUS) facilities. These new processes demand analyzers capable of measuring very low NOₓ and CO concentrations and validating CO₂ capture efficiency.
In these sectors, emissions such as SO₂, NOₓ, and CO₂ are continuously monitored to ensure compliance with environmental standards. The ESEGAS CEMS LX-4000, for example, is particularly suited for facilities that require high-accuracy flue gas monitoring and long-term stability. Its modular setup allows for easy integration with existing plant automation systems (PLC/DCS) and adapts to varied process conditions — from low-temperature exhausts to high-moisture flue gas.
What Are the Key Benefits of Using a CEMS Gas Analyzer?
Problem: Traditional emission monitoring often requires high maintenance and frequent calibration, resulting in downtime and additional costs.
Agitation: These inefficiencies reduce plant productivity and risk inaccurate reporting.
Solution: Modern systems like ESEGAS CEMS offer advanced automation, self-diagnostics, and reliable data accuracy that optimize both compliance and performance.
The benefits of deploying a continuous emission monitoring system such as the ESEGAS CEMS LX-4000 extend beyond regulatory compliance. Its high-precision sensors and automated calibration ensure long-term stability with minimal maintenance. The system’s integrated architecture — encompassing gas sampling, conditioning, analyzers, and data management — eliminates compatibility issues found in fragmented setups.
Additionally, remote monitoring capabilities allow operators to supervise multiple plants simultaneously, enabling predictive maintenance and faster response to anomalies. The result is a system that not only ensures environmental responsibility but also supports operational efficiency and data transparency — both crucial for modern industries focused on sustainability and ESG performance.
Conclusion
In a world moving toward stricter environmental standards, CEMS gas analyzers represent the technological backbone of industrial emission control. Solutions like the ESEGAS CEMS LX-4000 deliver precise, real-time data that empower facilities to operate cleanly, efficiently, and confidently within compliance frameworks. As industries evolve, continuous emission monitoring will remain not just a regulatory necessity but a symbol of corporate responsibility and sustainable innovation.
If you have any questions, please contact us directly!
























