Discover the secrets to mastering flue gas analysis in this comprehensive guide. Uncover the role of a flue gas analyzer, how to choose the right one, and tips for optimal efficiency and safety. Unlock the benefits and elevate your combustion processes today.
Understanding Flue Gas Analysis!

Flue gas analysis is essential for achieving efficient combustion, reducing emissions, and upholding safety standards. This section explores the meaning, elements, and significance of a flue gas analyzer in the process.
Definition
Flue gas analyzers determine the concentrations of different gases in emissions produced by combustion processes. These devices are found in industrial, commercial, and residential environments, monitoring fuel-consuming equipment.
Precise flue gas analysis helps enhance combustion efficiency, resulting in decreased energy use and reduced harmful emissions. In 2019, the worldwide flue gas analyzer market reached $694 million and continues to expand due to stricter environmental regulations globally.
These analyzers are vital for industries adhering to guidelines like the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulations and the European Union’s Industrial Emissions Directive.
Components Of Flue Gas
Flue gas is made up of various gases and particles produced during combustion processes. The main components are nitrogen (N2), carbon dioxide (CO2), and water vapor (H2O).
Additionally, pollutants such as carbon monoxide (CO), sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter (PM) may be present in trace amounts, posing risks to human health and the environment.
In the United States, the EPA governs six criteria air pollutants, including PM, NOx, and SO2, to protect public health. Worldwide, the World Health Organization estimates that 4.2 million premature deaths annually are due to outdoor air pollution.
Proper flue gas analysis enables the efficient removal of these pollutants, lessening their environmental and public health impacts.
Role Of A Flue Gas Analyzer In The Process
Flue gas analyzers perform several critical tasks in combustion processes:
- Combustion Efficiency Enhancement: By tracking oxygen (O2) and combustible gas levels, such as CO, the analyzer assists in achieving ideal combustion conditions, reducing fuel consumption and lowering costs.
- Emission Management: Assessing flue gas components facilitates pollutant identification and quantification, allowing industries to comply with emission standards and reduce their ecological impact.
- Improved Safety: Detecting hazardous gases, like CO, which can be fatal, even at low concentrations, safeguards workers and nearby communities.
- Equipment Upkeep: Routine flue gas analysis can detect potential combustion equipment problems, enabling prompt maintenance and preventing expensive equipment breakdowns.
- Adherence To Regulations: Flue gas analyzers assist industries in meeting stringent rules set by organizations like the EPA and the European Union, ensuring compliance with environmental and safety guidelines.
Flue gas analyzers are crucial for sustaining efficient combustion processes, managing emissions, and guaranteeing worker and environmental safety. By comprehending flue gas components and the role of these analyzers, industries can refine their processes and contribute to a cleaner, safer planet.
Types Of Flue Gas Analyzers!
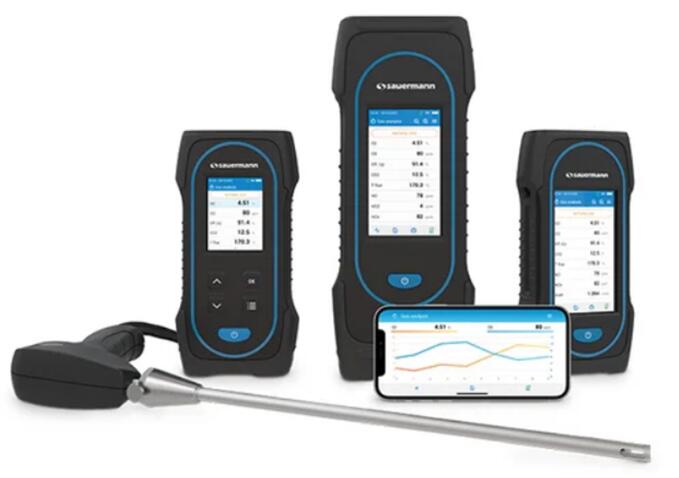

Comprehending flue gas analyzers is vital for enhancing combustion processes and minimizing emissions. These instruments are available in various types, each boasting distinct features and benefits.
- Electrochemical Sensor Analyzers
Electrochemical sensor analyzers provide a dependable method for quantifying gas concentrations in flue gas emissions. Featuring high sensitivity, these analyzers identify particular gases such as oxygen, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides.
The technique hinges on an electrochemical reaction triggered when target gases engage with sensor electrodes. The resulting electrical current corresponds to the gas concentration.
Precision is imperative in flue gas analysis. A study published in ScienceDirect reveals that electrochemical sensors display a low detection threshold, facilitating accurate measurements. Furthermore, these sensors exhibit a swift response time between 5-30 seconds, permitting real-time monitoring.
Nonetheless, potential interference from additional gases can impact the sensor’s efficacy. To tackle this challenge, manufacturers have designed filters and sophisticated algorithms to reduce cross-sensitivity.
In terms of cost, electrochemical sensors are more budget-friendly compared to other variants. MarketsAndMarkets.com’s 2020 market report suggests that the worldwide electrochemical gas sensor market reached $2.3 billion in 2019, with an anticipated compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.4% from 2020 to 2027.
- Infrared (IR) Sensor Analyzers
Infrared sensor analyzers measure gas concentrations by detecting the absorption of specific infrared wavelengths. The non-dispersive infrared (NDIR) technology is commonly used for flue gas analysis, especially for carbon dioxide and hydrocarbon detection.
A key advantage of IR analyzers is their long-term stability and minimal maintenance requirements. The absence of moving parts and consumables contributes to their durability, as confirmed by a 2018 report from the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.
Additionally, IR analyzers can achieve high selectivity and specificity. According to a study in the Journal of Sensors, NDIR sensors provide accurate measurements of carbon dioxide within 1% of the actual concentration.
Despite their higher price compared to electrochemical sensors, IR analyzers offer lower long-term costs. The global NDIR market, valued at $535 million in 2020, is expected to grow at a CAGR of 8.1% from 2021 to 2028, according to a Grand View Research report.
- Paramagnetic Sensor Analyzers
Paramagnetic sensor analyzers rely on the paramagnetic properties of certain gases, such as oxygen, to measure their concentration. This technology uses the attraction of paramagnetic molecules to a magnetic field, creating a measurable force proportional to the gas concentration.
Paramagnetic analyzers boast excellent long-term stability and repeatability. A study published in Analytical Chemistry highlighted that these sensors maintain consistent performance over extended periods without significant drift.
These analyzers also offer fast response times, typically less than 10 seconds, as noted in a 2017 review article in the Journal of Analytical Methods in Chemistry. This rapid response is critical for real-time monitoring of combustion processes.
Paramagnetic analyzers are more expensive than electrochemical and IR sensors, but they remain popular in industries requiring precise oxygen measurements. The global paramagnetic gas sensor market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 6.2% from 2020 to 2025, reaching $124.5 million by the end of the forecast period, as reported by Market Research Future.
How To Choose The Right Analyzer For Your Application?
Selecting the right flue gas analyzer demands careful consideration of multiple factors. The following sections provide expert guidance to help you make an informed decision.
§ Specific Needs And Requirements
Identify your unique application requirements to determine the ideal flue gas analyzer. Different industries, such as power plants, cement production, and waste incineration, demand distinct specifications.
For example, power plants typically require NOx, SO2, and CO monitoring, while waste incinerators necessitate dioxins and furans analysis. Moreover, consider the required measuring range, as analyzers offer various ranges depending on the application.
Flue gas analyzers’ response times also vary, with some models featuring response times as low as 5 seconds, vital in time-sensitive applications.
§ The Type And Concentration Of Gases Present
Understanding the type and concentration of gases in your application is critical. Common flue gas components include CO, CO2, NOx, SO2, and O2. However, other gases like HCl, NH3, and VOCs may be present in specific industries.
The concentration of these gases also impacts analyzer selection. For example, electrochemical sensors excel at detecting low-concentration gases, while non-dispersive infrared (NDIR) sensors are suitable for high-concentration environments.
§ Analysis Of The Environmental Conditions
Environmental factors significantly influence the performance of flue gas analyzers. Temperature, humidity, and dust levels are vital considerations. High temperatures can degrade sensor performance, while humidity can cause condensation, affecting the analyzer’s accuracy.
Ensure the chosen analyzer can withstand your application’s environmental conditions.
For instance, heated sample lines prevent condensation, and proper dust filters maintain analyzer longevity in dusty environments.
§ The Analyzer’s Sensitivity And Accuracy
Accurate and sensitive measurements are crucial for compliance and process optimization. Analyzers’ accuracy varies, with some models offering an error rate as low as ±0.5%. Furthermore, sensitivity is essential for detecting trace concentrations.
For example, tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy (TDLAS) analyzers can detect gas concentrations down to parts per billion (ppb) levels.
§ Ease Of Use And Maintenance
User-friendly and low-maintenance analyzers improve efficiency and reduce downtime. Look for features such as clear user interfaces, remote access capabilities, and onboard diagnostics. Moreover, opt for analyzers with extended calibration intervals and easy-to-replace sensors, which minimize maintenance requirements.
§ Durability And Lifespan Of The Analyzer
The analyzer’s longevity and durability directly impact the return on investment. High-quality materials and robust designs ensure the analyzer can withstand harsh conditions, extending its lifespan. Furthermore, reputable manufacturers often provide warranties, guaranteeing the analyzer’s performance for a specified period.
§ Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Weigh the initial investment against long-term benefits when selecting a flue gas analyzer. While low-cost options may seem attractive, they may not offer the durability, accuracy, or maintenance benefits of higher-priced models.
Consider the total cost of ownership, including maintenance, calibration, and replacement parts, to make an informed decision. Ultimately, a cost-effective flue gas analyzer will strike a balance between initial cost and long-term value.
Tips For Optimal Efficiency And Safety!

Unlock the full potential of flue gas analyzers by following these expert tips. Focus on proper installation, regular maintenance, and accurate interpretation of readings, combustion efficiency, and emission standard compliance.
§ Proper Installation And Placement Of The Flue Gas Analyzer
Position the probe in the flue, ensuring a temperature range of 150-250°C for optimal performance. Correct placement results in reliable readings, increasing the analyzer’s lifespan and minimizing measurement errors.
§ Regular Maintenance And Calibration
You must schedule calibrations at least once a year or according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Clean and replace sensors, filters, and other parts as needed. Consistent upkeep ensures accurate readings and prolongs the equipment’s service life.
§ Accurate Interpretation Of Flue Gas Analyzer Readings
Understand key parameters such as oxygen, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxide concentrations. Knowledge of these values helps diagnose combustion inefficiencies and identify necessary adjustments for optimal performance, reducing energy costs and emissions.
§ Monitoring And Optimizing Combustion Efficiency
Flue gas analyzers enable real-time tracking of combustion performance. Regularly analyze readings to optimize fuel-to-air ratios, minimize heat loss, and maximize energy efficiency. Optimal combustion reduces operational expenses and environmental impact.
§ Ensuring Compliance With Emission Standards
Flue gas analyzers provide essential data for regulatory compliance. Continuous monitoring of emission levels helps identify and mitigate potential breaches. Adhering to regulations protects your business from penalties, contributes to a cleaner environment, and supports sustainable practices.
How To Troubleshoot Common Flue Gas Analyzer Issues?
Addressing flue gas analyzer issues requires understanding potential problems and their solutions.
o Sensor Drift or Failure
When sensors in a flue gas analyzer drift or fail, accuracy suffers. Sensor drift may occur over time due to continuous exposure to high concentrations of gases or prolonged use. Regular calibration and timely sensor replacement ensure optimal performance.
o Incorrect Calibration
Calibration errors lead to inaccurate measurements, affecting critical processes. Follow manufacturer guidelines for proper calibration frequency and procedure. Utilize calibration gases with known concentrations to maintain analyzer accuracy.
o Interference From Other Gases
Cross-interference from other gases can compromise readings. Employing analyzers with selective sensors mitigates interference issues. Be aware of the gases present in your application and choose appropriate sensors for accurate measurements.
o Failure To Start Or Unexpected Shutdown
Power supply issues or internal malfunctions can cause startup failure or unexpected shutdowns. Check power sources and wiring for faults. Consult the manufacturer’s manual for troubleshooting steps and reach out to technical support if necessary.
o Inconsistent Or Erratic Readings
Erratic readings may stem from sensor contamination, aging, or damage. Maintain a clean environment for your analyzer, avoiding dust or moisture buildup. Regularly inspect and clean sensors and replace them as needed for consistent results.
o Difficulty In Interpreting The Results
Clear interpretation of results is crucial for decision-making. Familiarize yourself with the analyzer’s manual, focusing on understanding the display and data output. Seek training or assistance from the manufacturer for proper data interpretation and informed decision-making.
Conclusion
Mastering flue gas analysis is essential for achieving efficient combustion, reducing emissions, and upholding safety standards. By understanding the role of flue gas analyzers, selecting the right type for your application, and following best practices for optimal efficiency and safety, industries can contribute to a cleaner, safer planet. For reliable and cost-effective flue gas analyzers, we recommend visiting ESEGas.com.