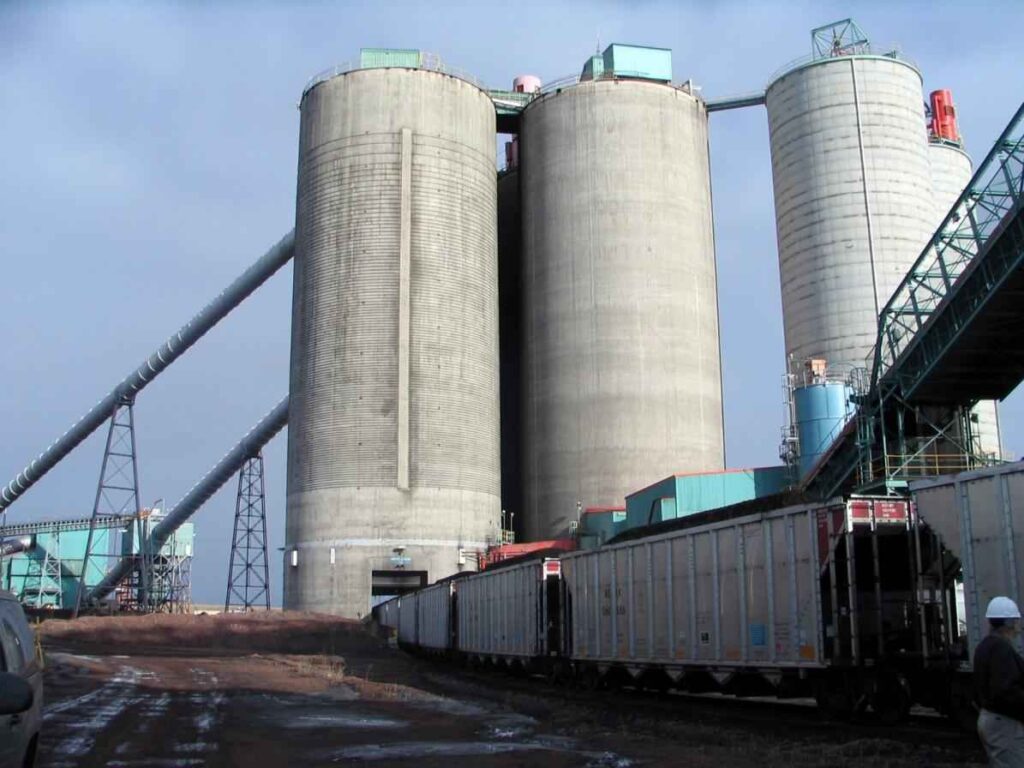

Coal silo poses serious fire and explosion risks from self-heating coal dust. Continuous monitoring of carbon monoxide (CO) and oxygen (O₂) levels is critical for early warning. An NDIR (Non-Dispersive Infrared) Process Gas Analyzer like ESEGAS’s IR–GAS series delivers rapid, real-time CO and O₂ readings. Its high-stability infrared detectors measure CO (and other gases) continuously. When CO spikes or O₂ drifts, operators see hidden smoldering before flames appear.
NDIR-based process gas analyzers provide proactive, data-driven safety by catching combustion precursors early. Coal silo gains a critical safety edge — proactive control instead of reactive damage control.
Why Is Continuous CO and O₂ Monitoring Essential in Coal Silo?

Coal silos, common in power plants and cement facilities, are susceptible to spontaneous combustion due to the oxidation of coal dust. This oxidation releases carbon monoxide (CO) and consumes oxygen (O₂), serving as early indicators of potential fire hazards. Coal dust can self-ignite if it oxidizes or if inerting fails. Even low-temperature oxidation produces CO and consumes O₂.
The Significance of CO Monitoring
CO is a colorless, odorless gas produced during the early stages of coal oxidation. Even at low temperatures, coal can oxidize, leading to a gradual increase in CO levels. Monitoring CO concentrations provides a reliable method for detecting self-heating within the silo before visible signs, such as smoke or elevated temperatures, become apparent. This early detection is crucial for implementing preventive measures to avert fires or explosions.
The Role of O₂ Monitoring
In inerted coal silos, maintaining low O₂ levels is vital to prevent combustion. A rise in O₂ concentration may indicate a leak or failure in the inerting system, compromising the safety of the storage environment. Continuous O₂ monitoring ensures that the inert atmosphere remains effective, reducing the risk of spontaneous combustion.
Integrated Monitoring for Enhanced Safety
Combining CO and O₂ monitoring offers a comprehensive approach to silo safety. Together, CO and O₂ sensors give EHS teams a clear window into hidden hot spots and inerting status in silos, enabling action before conditions become dangerous. Detecting unusual CO or O₂ trends is only the first step—understanding why they happen is what turns data into action.
What Causes Abnormal CO and O₂ Levels in a Coal Silo?
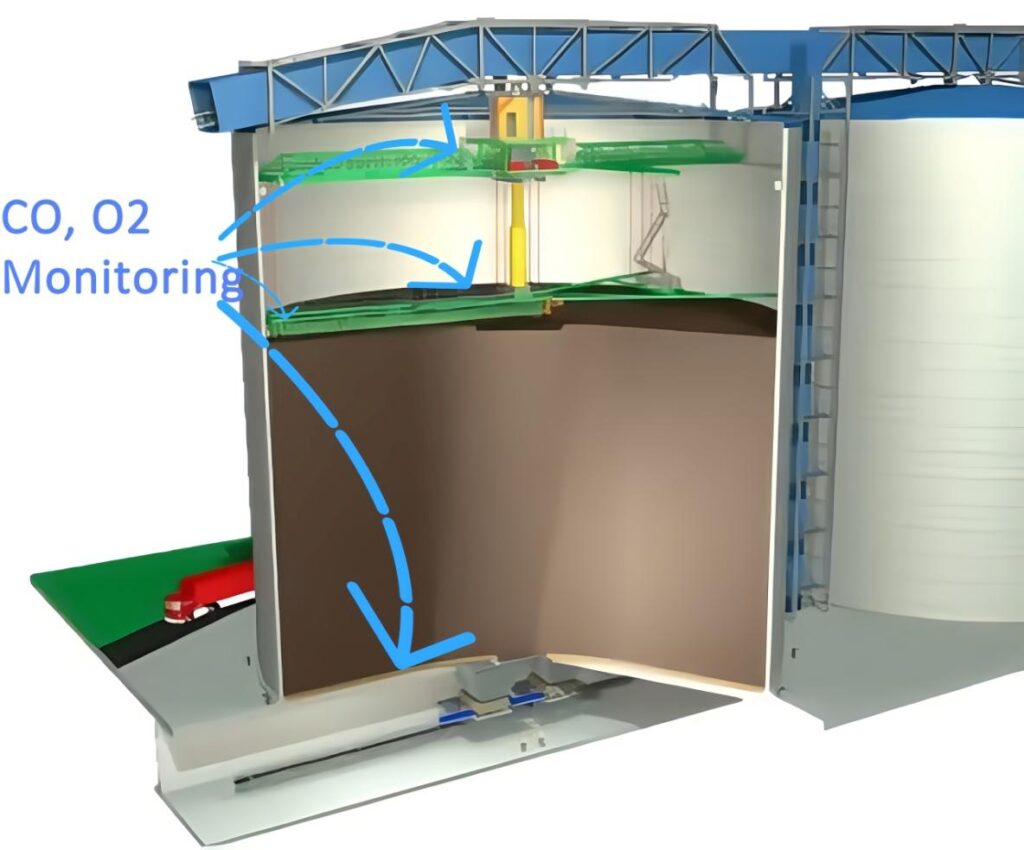
In coal silos, several root causes can trigger dangerous shifts. Here’s what to watch for:
1. Self-Heating and Oxidation
Coal can slowly oxidize during storage, even at low temperatures. This process consumes O₂ and produces CO and CO₂. If CO rises while O₂ drops, that’s a clear sign of internal oxidation or smoldering. Often, it’s invisible—but the process gas analyzer catches it early.
Wet or tightly packed coal restricts airflow, traps heat, and accelerates gas buildup. If oxygen remains present, CO levels can surge. This makes moisture control and consistent monitoring critical, especially after refills or shutdowns.
3. Mechanical Friction or Equipment Heat
Malfunctions—like a jammed auger or overheated bearing—can create localized hot spots. These pockets may not spread immediately but will generate detectable CO spikes. Spotting them fast helps avoid escalation.
4. Inerting System or Ventilation Failures
Many plants use nitrogen or CO₂ to keep O₂ levels below the coal dust’s LOC (Limiting Oxygen Concentration), which can be as low as 8%. If O₂ rises, it might mean a leaking seal, stuck valve, or stopped fan. These failures quietly undo the silo’s protection—until the gas analyzer sounds the alarm.
Leaks from boilers, flue gas ducts, or other process lines can feed extra CO or O₂ into the silo. The result? Confusing readings unless the analyzer captures both gases at once.
The ESEGAS process gas analyzer helps cut through this complexity. With real-time dual-gas readout, it shows both CO and O₂ trends side by side. For example, rising CO with falling O₂ points to oxidation inside the coal bed. But if both gases rise, you’re likely seeing outside air intrusion. That insight helps teams respond fast—whether it means injecting more inert gas, cooling down the silo, or halting operations. Implementing NDIR-based process gas analyzer can provide early warnings, allowing for timely interventions that prevent catastrophic events.
How Does NDIR Process Gas Analyzer Prevent Fires and Explosions in Coal Silo?
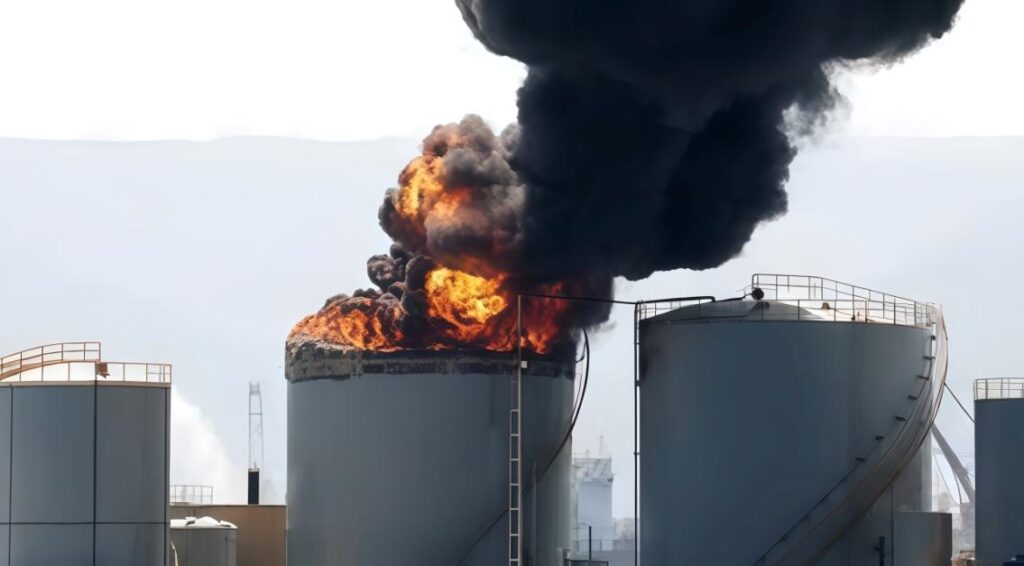

Coal storage isn’t just about capacity — it’s about control. To keep operations safe, plants need more than just alarms. They need fast, intelligent gas detection systems that can think and act before people even realize there’s a problem.
1. Accurate CO Detection: reliable in low-oxygen environment
NDIR (non-dispersive infrared) process gas analyzers detect gases like CO by measuring their unique infrared absorption. Each gas absorbs light at specific wavelengths. The process gas analyzer shines an IR beam through the sample and measures how much light is absorbed at CO’s signature band. A reference detector ensures accuracy by comparing signal loss.
Unlike catalytic sensors, NDIR doesn’t need oxygen to work. That’s a major advantage in coal silos, where inerting reduces O₂ to prevent combustion. NDIR still delivers reliable data in low-oxygen or fully inert environments. Moreover, ESEGAS’s process gas analyzer is able to monitor Oxygen (O₂) with Electrochemical Detector.
2. Continuous, Real-Time Monitoring: No Blind Spots
Speed also matters. NDIR systems offer real-time feedback with fast response times. This ensures they capture sudden CO spikes or O₂ increases — events that point sensors or spot checks might miss. In a silo fire scenario, seconds of warning can make all the difference.
When CO climbs or O₂ drifts past safe limits, the process gas analyzer can trigger automatic responses: inerting, venting, or shutting off the feed. This tight feedback loop turns risk into control.
3. Rugged Sample Conditioning: Built for Coal Dust Realities
Coal environments are harsh — hot, dusty, and full of sticky tars. Advanced analyzers overcome these challenges with heated sample probes (typically 160–180 °C), inline sintered filters, and self-cleaning blowback systems. These components keep the flow steady and prevent blockages. Integrated flow sensors detect any drop in performance and alert operators instantly. This ensures reliable, long-term measurements with minimal maintenance disruption.
4. Built-in Diagnostics: Smart from the Inside Out
Today’s analyzers don’t just measure gases — they monitor themselves. ESEGAS’s NDIR process gas analyzers—like the IR-Gas model—use temperature-stabilized detectors and factory calibration to ensure drift-free performance. Automatic calibration checks using internal references or gas loops help maintain accuracy without manual effort. This enhances measurement stability, even with fluctuating ambient conditions.
5. Modular Design: Scalable and Future-Proof
One of the biggest advantages is modularity. For example, systems like ESEGAS’s process gas analyzers support multiple sensors in one cabinet. Plants can start with a NDIR process gas analyzer, then add industrial computer, or even dust monitors as needed. Each module shares the same housing, wiring, and interface, which simplifies training and cuts installation costs. Remote heads can also be placed at different silo points, offering a wider safety net. And as gas detection technology evolves, users can upgrade modules without replacing the whole system.
With these features, modern process gas analyzers don’t just measure — they protect, automate, and future-proof your coal handling systems. To ensure a process gas analyzer effectively safeguards coal silo operations, meticulous attention to installation details is essential.
What Are the Best Practices for Installing and Running the NDIR Process Gas Analyzer in a Coal Silo?
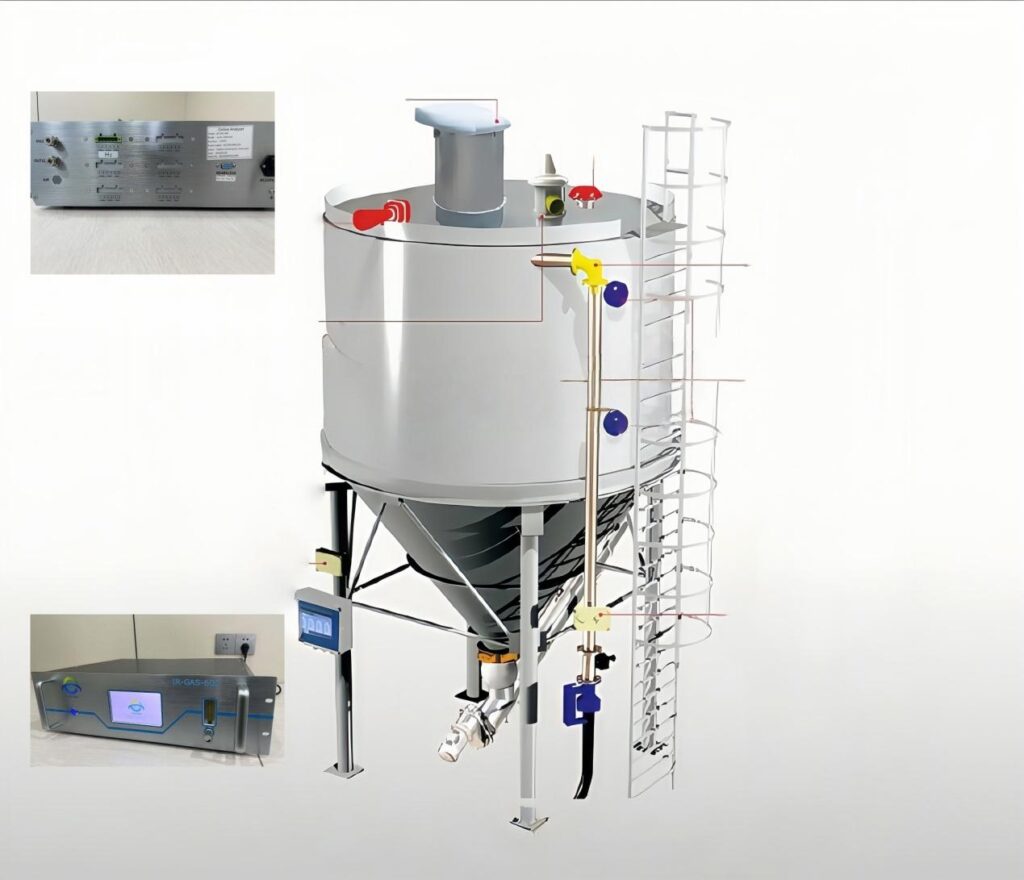

Implementing a non-dispersive infrared (NDIR) process gas analyzer like the ESEGAS IR-GAS series requires both precision and planning. Below are key practices to ensure accurate, reliable CO and O₂ monitoring.
1. Choose the Right Probe Location
Place the sampling probe where gas mixing is most representative—usually near the top-center of the silo. Heat the probe above the dew point to prevent condensation. Add a 2–5 μm dust filter to protect the optics and maintain signal clarity.
2. Condition the Sample Properly
Use a heated, corrosion-resistant sample line and a thermal conditioning unit to dry and clean the gas. Keep the tubing short and insulated. Install auto-blowback or filter-cleaning functions to reduce maintenance in dusty environments.
3. Maintain and Calibrate Consistently
Stick to a fixed calibration routine—every two months is a good start. Use certified span gases. Many ESEGAS process gas analyzers support dual-sensor cross-checks, making it easier to verify accuracy without interrupting measurements. Always keep spare filters and sensor heads in stock.
4. Set Sensible Alarm Thresholds
Don’t wait for values to become dangerous. Set CO alarms slightly above baseline to catch early trends. For O₂, keep alarm points well below the coal dust’s Limiting Oxygen Concentration (LOC), typically 8–11%. Trigger alerts at 5–6% O₂ for added safety margin.
5. Integrate with Plant Controls
Connect the analyzer to the plant’s DCS or safety PLC via digital outputs. This enables automatic responses—like nitrogen purging or emergency shutdowns. Log data for EHS reviews, compliance reporting, and root cause analysis.
6. Build Awareness Across Teams
Train operators on reading gas trends and interpreting alarms. Include gas-monitoring reviews in toolbox talks. Position the analyzer not just as a sensor, but as a smart, predictive tool that enhances safety and operational insight.
When installed correctly, the ESEGAS process gas analyzers don’t just detect danger—it prevents it. It turns invisible gas data into real-time decisions that protect lives, equipment, and compliance. Proper setup ensures you get every second of warning that technology can offer.
For technical specifications, you can refer to the ESEGAS process gas analyzers product page.
How Does the Process Gas Analyzer Shape Operations and Safety Culture?

Installing an NDIR process gas analyzer like the ESEGAS IR-GAS series brings both immediate and long-term gains:
- Short term: plant teams gain early warning capabilities. As soon as CO levels begin to rise or O₂ drifts upward, alarms trigger. This allows prompt actions like boosting inert gas flow, cooling the silo, or initiating controlled unloading—before the situation escalates.
- Longer term: the process gas analyzer supports a proactive, data-driven safety culture. Continuous gas logging helps teams detect recurring trends, such as seasonal self-heating or ventilation imbalance. Engineers can fine-tune interlocks or ventilation sequences. EHS managers gain valuable documentation for audits and compliance.
Moreover, the process gas analyzer acts as part of the plant’s digital backbone. It integrates with dashboards and IoT platforms to enable predictive maintenance. With ESEGAS’s features like auto-zero, dual sensor redundancy, and temperature-controlled optics, the data stays reliable for months. And when measurements stay trustworthy, risk becomes manageable.
Conclusion
Coal dust hazards demand more than guesswork—they require speed, precision, and insight. The ESEGAS process gas analyzer delivers all three.
It detects the invisible signs of danger before flames ever appear. It works in inert conditions where catalytic sensors fail. It transforms silo monitoring from a passive checklist into a real-time safety decision system.
Whether you’re trying to prevent fires, improve operational continuity, or build a stronger safety culture, this technology offers a clear path forward. In today’s high-stakes industrial world, early detection isn’t a luxury—it’s a responsibility.
Explore the full technical specs at ESEGAS IR-GAS Series.
If you want to know more details, contact with us please!























