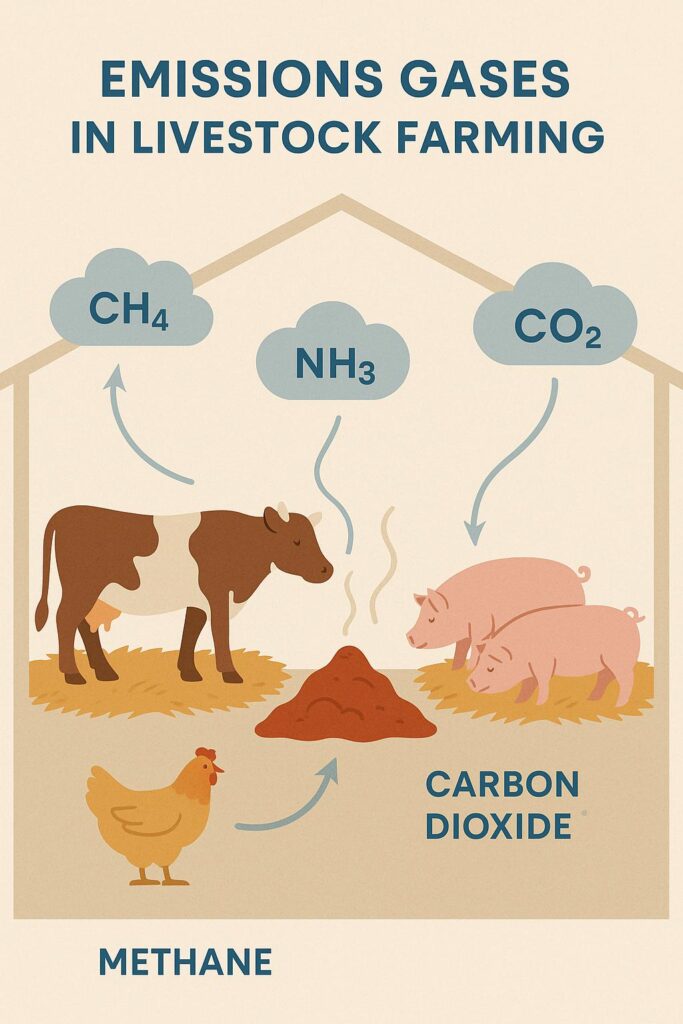
The livestock industry is under increasing pressure to meet both animal welfare standards and environmental regulations. Poor air quality inside barns—caused by the accumulation of ammonia (NH₃), methane (CH₄), hydrogen sulfide (H₂S), and carbon dioxide (CO₂)—can lead to serious health problems for animals and workers alike. If left unmanaged, these gases not only reduce productivity but also increase mortality and operational costs. Addressing this silent yet impactful threat requires precise and reliable monitoring tools.

Pic resource:WIKIFARMER LIBRARY
Gas analyzers have become indispensable tools in modern livestock farming, offering real-time insights into environmental gas concentrations that affect animal health and productivity. By detecting harmful gases early, farm operators can take proactive measures to ventilate, neutralize, or otherwise manage indoor air quality, ensuring a healthier and more profitable farming environment.

But knowing that gas analyzers help isn’t enough. How exactly do they work in agricultural contexts? What measurable benefits do they bring, and which models are best suited for different livestock operations?
How do gas analyzers improve air quality in livestock housing?
In intensive livestock environments, the air isn’t just filled with the sounds and smells of animals—it’s often loaded with invisible threats. Ammonia from decomposing manure, carbon dioxide from animal respiration, and methane from fermentation processes build up quickly, especially in enclosed housing. The longer these gases remain undetected, the more damage they can cause to both animal health and structural infrastructure.
Gas Analyzers are revolutionizing how farms tackle air pollution by offering continuous, precise measurements of key harmful gases inside barns and enclosures. Rather than relying on manual inspection or reactive maintenance, farms can now act proactively based on real-time environmental data. This shift in monitoring transforms air quality management from a reactive task into a strategic advantage.
Here’s how they work and why they matter:
1. Real-Time Detection of Harmful Gases
Gas analyzers provide immediate feedback on concentrations of NH₃, CO₂, CH₄, and other volatile compounds. For instance:
- Ammonia (NH₃), even at low levels (~25 ppm), irritates the respiratory tract of poultry and swine.
- Carbon dioxide (CO₂) buildup signals inadequate ventilation, particularly during winter when barns are sealed.
- Methane (CH₄), though less directly harmful to animals, is a fire hazard and a climate concern.
With instruments like the ESEGAS ESE-LASER-100 Ammonia Analyzer, farmers can set alarms or triggers for automatic ventilation once NH₃ reaches a dangerous threshold. Similarly, IR-GAS-600 monitors CO₂ levels, ensuring animals don’t suffer from hypoxia or related stress.
2. Intelligent Ventilation and Automation
The data from gas analyzers can be integrated into ventilation control systems. Instead of relying on fixed schedules, barns can now ventilate only when necessary, conserving energy while protecting animal welfare.
- For example, a spike in ammonia detected during night hours—when temperatures are lower—can activate minimum ventilation fans without exposing animals to cold drafts.
- In summer, analyzers help balance between heat and gas concentration, avoiding heat stress.
This intelligent response enhances both comfort and safety, especially in large-scale operations.
3. Early Warning System for Systemic Failures
Gas analyzers act as “canaries in the coal mine.” When waste management systems underperform or ventilation ducts become clogged, gas levels change before visible signs of deterioration appear.
- A sudden CO₂ increase might indicate a broken fan.
- Gradual CH₄ buildup might suggest that a composting unit is overloaded or malfunctioning.
This predictive insight helps reduce maintenance costs and avoid emergencies.
4. Long-Term Data for Air Quality Optimization
ESEGAS analyzers are not just spot-check tools—they record and transmit long-term trends. This data can be used to:
- Evaluate the effectiveness of bedding materials in absorbing ammonia.
- Compare gas buildup between different barn layouts.
- Identify seasonal air quality variations that affect animal growth rates.
With the ESE-GH-2080 Greenhouse Gas Analyzer, farms can also monitor CH₄ and CO₂ simultaneously, enabling comprehensive strategies for both health and climate compliance.
5. Preventing Structural Corrosion and Equipment Degradation
High ammonia and hydrogen sulfide levels corrode metal fixtures, electrical panels, and even concrete. Over time, this leads to costly repairs and downtime. Continuous gas monitoring helps detect these corrosive conditions early, extending the lifespan of infrastructure and reducing replacement costs.
What specific health benefits do animals gain from improved air monitoring?
Poor air quality leads to chronic stress in animals, weakening immune response and making them more susceptible to infections like respiratory diseases and footpad dermatitis in poultry. Stress also disrupts feeding behavior, reducing growth rates and increasing feed conversion ratios.
By maintaining a stable and clean air environment, Gas Analyzers indirectly improve animal welfare. Healthy animals grow faster, require fewer antibiotics, and yield higher-quality meat, milk, or eggs. In effect, the use of gas monitoring tools like ESEGAS’s Greenhouse Gas Analyzer ESE-GH-2080 translates directly into improved animal outcomes.
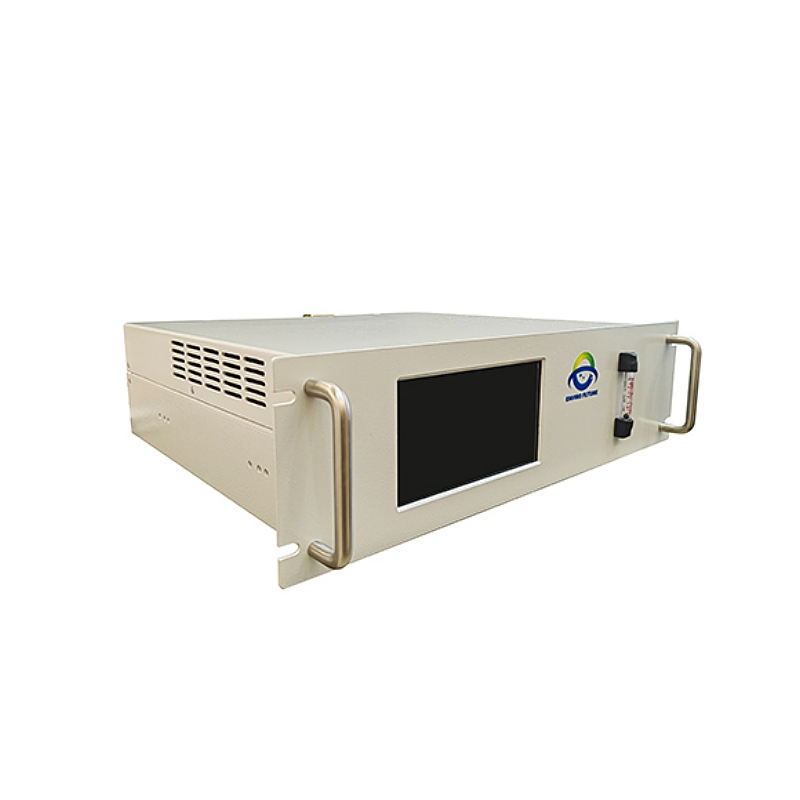

How does gas analysis data enhance farm management decisions?
Beyond animal health, gas monitoring data can transform how a farm is managed. It provides concrete evidence of the effectiveness of ventilation systems, manure management, and housing design.
For example:
- If H₂S spikes after manure removal, it signals a need for better waste handling procedures.
- Elevated CO₂ levels may indicate insufficient airflow in winter settings.
- Trends in CH₄ could help assess bedding degradation or composting effectiveness.
Such insights allow farm managers to adjust operational protocols in real time, improving energy efficiency and reducing environmental emissions. These benefits become especially critical in larger operations or during periods of extreme weather.
What are the economic advantages of using gas analyzers in livestock farming?
Investing in Gas Analyzers brings measurable returns. Reduced disease incidence means lower veterinary costs. Stable air quality improves feed efficiency, so animals grow faster on less input.
Additionally, by preventing equipment corrosion caused by high levels of NH₃ or H₂S, the lifespan of fans, sensors, and metal structures is extended. Regulatory compliance is another benefit: farms that document air quality data are better positioned to meet national or international environmental standards, avoiding fines or penalties.
Which gas analyzers are best suited for livestock environments?
Choosing the right gas analyzer depends on your farm size, species, and housing design.
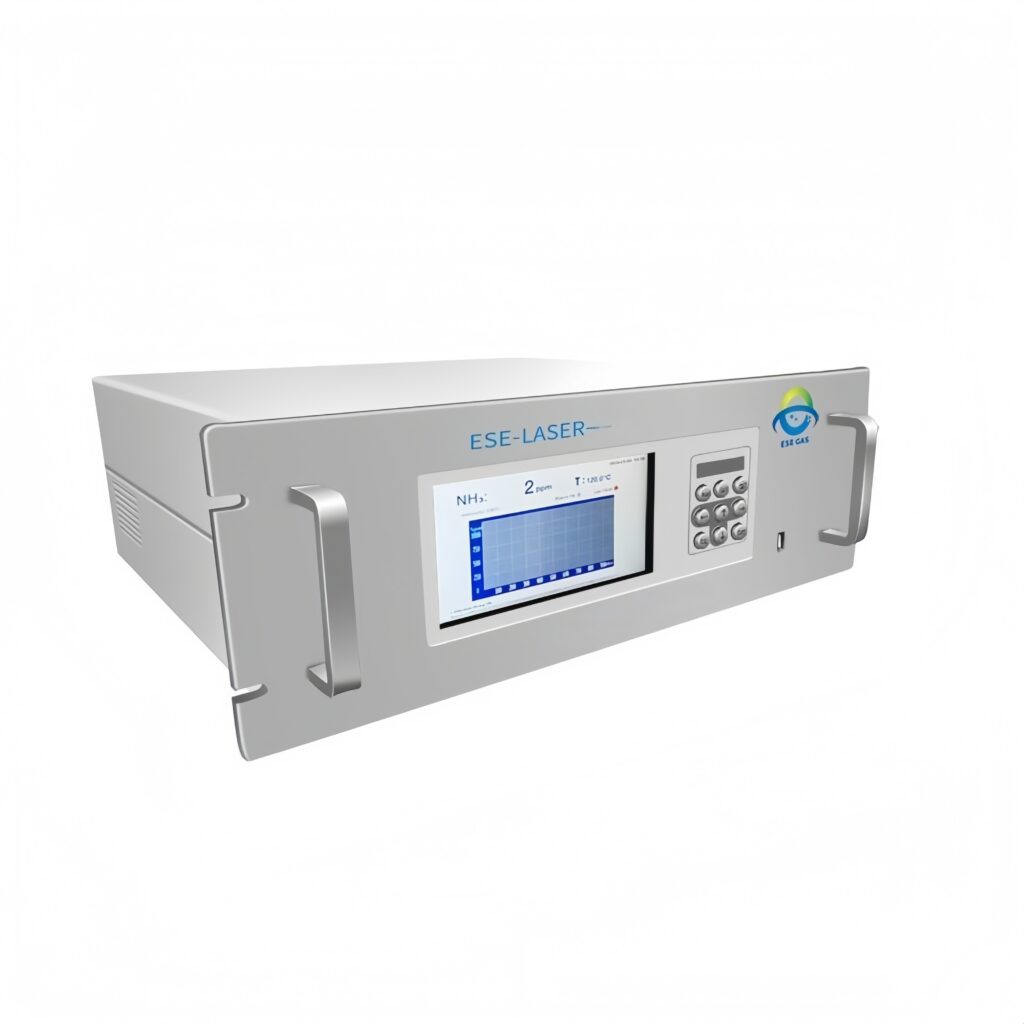

| Product | Gas Monitored | Ideal Use Case |
| ESE-LASER-100 | Ammonia (NH₃) | Poultry, swine facilities with manure accumulation |
| IR-GAS-600 | Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) | All housing types to assess ventilation efficiency |
| ESE-GH-2080 | CH₄, CO₂ | Integrated farms with manure management systems |
Portable analyzers are great for spot-checking problem areas, while continuous online systems are better suited for permanent installations. ESEGAS offers customizable options to fit both needs.
Conclusion
Gas analyzers have evolved from optional accessories to essential tools in responsible livestock farming. By precisely monitoring toxic and climate-active gases, they not only safeguard animal health but also optimize farm performance and reduce operational costs. With solutions from trusted manufacturers like ESEGAS, livestock producers can confidently meet the dual demands of profitability and environmental stewardship.