In modern Medical Field, gas analyzers have become an indispensable tool in surgery and treatment. These devices are able to monitor and analyze the gas composition of a patient’s body in real time, providing doctors with valuable information to help them make more accurate diagnos and treatment decisions.
Basic principles and working mechanisms of gas analyzers
Gas analyzers use advanced technologies like infrared spectroscopy and mass spectrometry to detect and quantify gases like oxygen and CO₂. In medicine, they are essential for patient monitoring in ICUs, operating rooms, and labs.
if you want learn more about the principles of the gas analyzers, you can read this blog below:
Real-time monitoring during surgery
During surgery, gas analyzers ensure patient safety by monitoring anesthesia, ventilator performance, and the surgical environment in real-time. This data aids in immediate response and postoperative care.
1. Anesthesia Monitoring
Anesthesia monitoring is crucial for surgery, ensuring patient safety by measuring inhaled and exhaled gases like oxygen, CO₂, and anesthetic agents in real time. This helps anesthesiologists maintain the optimal anesthesia depth and prevent complications.
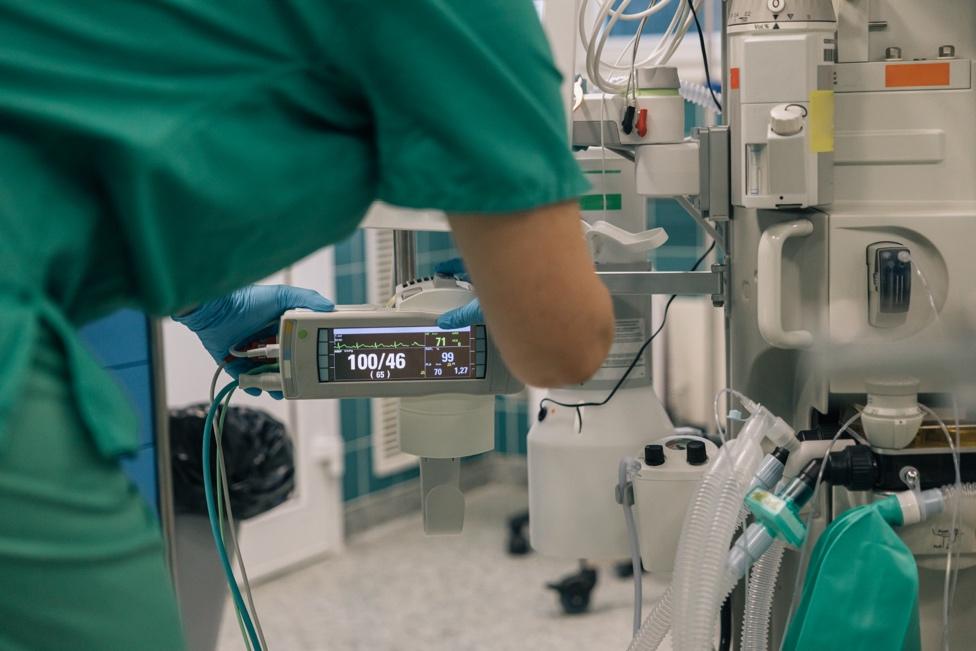

Gas analyzers provide real-time monitoring of anesthetic gas concentration, oxygen, and CO₂ levels, allowing anesthesiologists to adjust anesthesia depth precisely. This ensures patient safety, prevents complications like hypoxemia, and optimizes surgical outcomes.
Advantages of gas analyzers in Anesthesia Monitoring
- High precision and high sensitivity
- Real-time data feedback
- Reduce the misuse of anesthetic drugs
2. Ventilator Management
Gas analyzers play a crucial role in ventilator management during complex surgeries. By ensuring precise ventilation, gas analyzers help prevent complications such as hypoxia and carbon dioxide retention, improving patient safety and surgical outcomes.
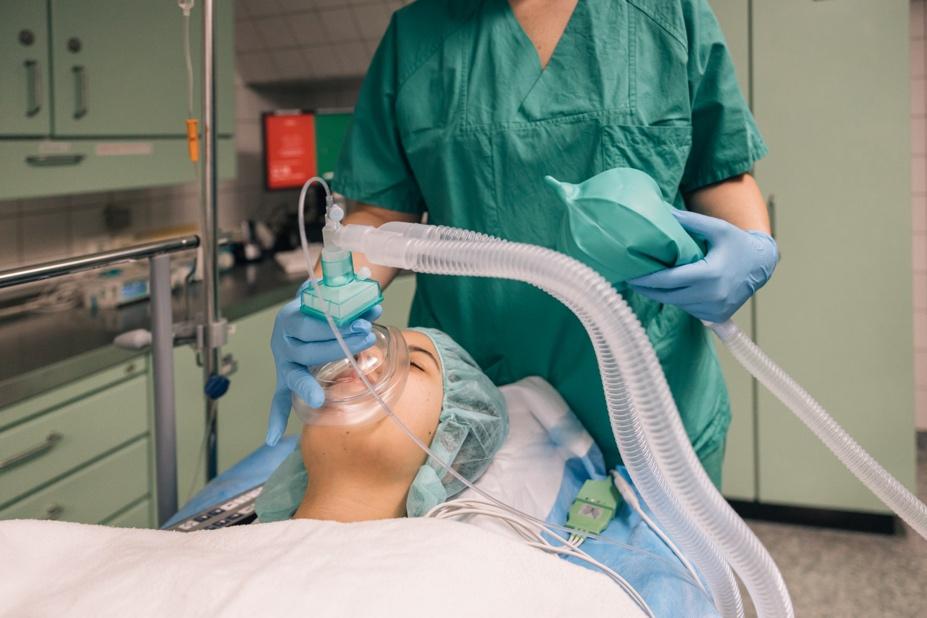
The role of gas analyzers in ventilator management
Gas analyzers play a key monitoring role in ventilator management.Gas analyzers play a vital role in ventilator management by continuously measuring end-tidal CO₂ (EtCO₂), oxygen concentration, and other gases. This allows anesthesiologists to fine-tune ventilator settings, ensuring optimal tidal volume, respiratory rate, and oxygen levels. Real-time monitoring helps prevent hypoxia, hypercapnia, and oxygen toxicity, enabling personalized ventilation management for each patient and enhancing surgical safety.
Specific advantages of gas analyzers in Ventilator Management
- Optimizing breathing management
- Reduce intraoperative complications
- Supporting recovery after surgery
3. Surgical environment monitoring
Various medical gases are usually used in operating rooms, such as oxygen, nitrogen, nitrous oxide, and anesthetic gases. In a closed surgical environment, if the concentration of these gases is not properly controlled, it will not only affect the patient, but also pose a threat to the health of medical staff. In particular, anesthetic gases such as nitrous oxide and isoflurane may have adverse effects on the nervous system of medical staff if they are exposed to high concentrations for a long time.
Protection of the surgical environment by gas analyzers
Gas analyzers play the role of safety guards in monitoring the surgical environment. By continuously monitoring the concentration of various gases in the operating room, the analyzer can detect abnormal conditions in a timely manner. For example, when the oxygen concentration is too high, the analyzer will sound an alarm, prompting medical staff to take measures to avoid potential fire risks. Similarly, if the concentration of anesthetic gas exceeds the standard, the device will immediately warn to protect the health of medical staff.
Advantages of improving operating room safety
- Prevent exposure to hazardous gases:Protect medical staff from the hazards of long-term occupational exposure by real-time monitoring of gas concentrations in the operating room.
- Reduce environmental pollution: Adjust the gas delivery system in real time to avoid unnecessary gas leakage and improve the environmental quality of the operating room.=
- Timely alarm system: When encountering dangerous concentrations of gas, the analyzer can immediately sound an alarm, helping to take emergency measures quickly and ensure the safety of the operation.
Management and monitoring of chronic diseases
Chronic diseases are one of the major public health issues worldwide, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, etc. These diseases usually require long-term management and monitoring. Gas analyzers play an important role in chronic disease management. By analyzing the gas composition of patients’ breath, doctors can better understand the progression of the disease, optimize treatment plans, and thus improve the quality of life of patients. The following will introduce several major applications of gas analyzers in chronic disease management in detail.
1. Chronic respiratory diseases
(1) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
COPD is a common chronic respiratory disease in which the patient’s lung function gradually deteriorates, eventually leading to difficulty breathing. Gas analyzers can help doctors assess a patient’s lung function and gas exchange capacity by measuring the levels of carbon dioxide and oxygen in exhaled air. For example, by measuring end-tidal carbon dioxide (EtCO₂) concentration can be used to understand whether the patient has hypoventilation, thereby guiding whether the treatment plan needs to be adjusted, such as increasing oxygen therapy or adjusting drug dosage.
(2) Asthma
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory respiratory disease characterized by difficulty breathing caused by airway constriction and inflammation. The gas analyzer can assess the degree of airway inflammation in patients by measuring nitric oxide (FeNO) in exhaled gas. FeNO is a biomarker caused by airway inflammation that can help doctors determine the severity of asthma and optimize anti-inflammatory treatments such as inhaled corticosteroids. In addition, by analyzing changes in respiratory gas composition, doctors can identify signs of acute asthma attacks early and intervene in a timely manner. Here are the Advantages of gas analyzers in Chronic respiratory diseases
- Non-invasive monitoring: Gas analyzers can provide a non-invasive and convenient monitoring method, avoiding the discomfort and risks of frequent blood gas analysis.
- Personalized treatment guidance: Based on changes in the composition of a patient’s breathing gases, doctors can tailor a treatment plan for each patient.
- Early warning of changes in condition: By real-time monitoring of gas parameters, the trend of worsening of the disease can be discovered in time and the occurrence of serious complications can be prevented.
2. Cardiovascular disease
Patients with cardiovascular diseases, such as coronary heart disease and heart failure, often suffer from insufficient oxygen supply or limited carbon dioxide excretion. Blood gas analysis with a gas analyzer can provide key physiological indicators such as blood oxygen saturation, carbon dioxide partial pressure, and acid-base status. These parameters are essential for evaluating cardiac function, respiratory efficiency, and systemic oxygen supply.
Gas analyzers aid in heart failure and coronary heart disease management by monitoring oxygen and CO₂ levels, assessing cardiopulmonary function, and guiding treatment decisions. They help adjust medications, oxygen therapy, and mechanical support while providing real-time data for angina assessment and intervention planning.
- Real-time dynamic monitoring: Capable of continuously monitoring blood gas parameters and providing support for the dynamic management of cardiovascular diseases.
- Help optimize treatment options: Combined with the results of blood gas analysis, doctors can adjust drug dosage more accurately and reduce adverse reactions.
- Preventing acute events: Early detection of cardiovascular dysfunction and timely intervention can effectively prevent the occurrence of acute cardiovascular events.
3. Chronic kidney disease
(1) Acid-base balance monitoring
Gas analyzers help chronic kidney disease patients by monitoring CO₂ and bicarbonate levels, assessing acid-base balance, and guiding alkaline drug therapy and diet adjustments to maintain stability and prevent complications.
(2) Renal dyspnea
Gas analyzers assist chronic kidney disease patients by detecting harmful gases in breath, helping diagnose renal dyspnea, and guiding dialysis and treatment adjustments for better respiratory function.
(3) Improving the advantages of chronic kidney disease management
- Accurate acid-base balance monitoring
- Supporting comprehensive treatment decisions
- Convenient long-term monitoring
Summary
Gas analyzers are transforming chronic disease management by providing non-invasive, real-time, and accurate physiological data. They support doctors’ treatment decisions and enhance patients’ self-management, leading to improved quality of life. As personalized medicine and precision treatment advance, gas analyzers will play an increasingly crucial role in future healthcare, optimizing monitoring and treatment strategies for chronic diseases.
| Application Areas | Specific applications | Advantages |
| Real-time monitoring during surgery | Anesthesia monitoring: real-time measurement of anesthetic gases and adjustment of drug dosage; ventilator management: monitoring of respiratory gas composition and optimization of ventilator parameters; surgical environment monitoring: monitoring of gas concentration in the operating room to prevent occupational exposure. | High precision, high sensitivity, and real-time feedback can reduce drug misuse and improve surgical safety. |
| Chronic respiratory diseases | COPD: assess lung function and optimize treatment; asthma: assess airway inflammation and optimize anti-inflammatory treatment. | Non-invasive monitoring, personalized treatment guidance, early warning. |
| Cardiovascular disease | Heart failure: assess cardiopulmonary function and guide the use of drugs and equipment; Coronary artery disease: monitor oxygen and carbon dioxide levels. | Real-time dynamic monitoring, optimization of treatment plans, and prevention of acute events. |
| Chronic kidney disease | Acid-base balance monitoring: assess acid-base status and guide treatment; renal dyspnea: assess harmful substances and guide dialysis. | Accurately monitor acid-base balance, support comprehensive treatment decisions, and facilitate long-term monitoring. |
You can find out more about gas analysers in the medical field through this blog:
Conclusion
Gas analyzers are vital in modern medicine, from real-time surgical monitoring to chronic disease management and personalized treatment. As technology advances, they will enhance precision medicine, improving patient care and medical efficiency.
If you have any questions or would like to know more, please get in touch with us directly! We will get back to you as soon as we can!

























