Continuous Emission Monitoring Systems (CEMS) are crucial in industrial settings, ensuring gas emissions comply with environmental regulations. However, many companies struggle with understanding the components of CEMS systems and how to install them effectively. Are you looking to install a CEMS system but unsure about its components or the installation process?

CEMS systems comprise several key components, including gas sampling equipment, sensors, analyzers, and data acquisition systems. Installing a CEMS system requires careful consideration of various factors such as environmental conditions, instrument configuration, and calibration processes.
Understanding the components of a CEMS system is the first step in its successful installation and operation. In this article, we will walk you through the main elements of a CEMS gas system and explain the installation steps to ensure optimal performance.
1. What are the Main Components of a Continuous Emission Monitoring Systems (CEMS)?
The CEMS gas system comprises several critical components, each designed to perform a specific function in measuring and recording emission data. These components work together to provide accurate, real-time monitoring of pollutants in the gas stream.
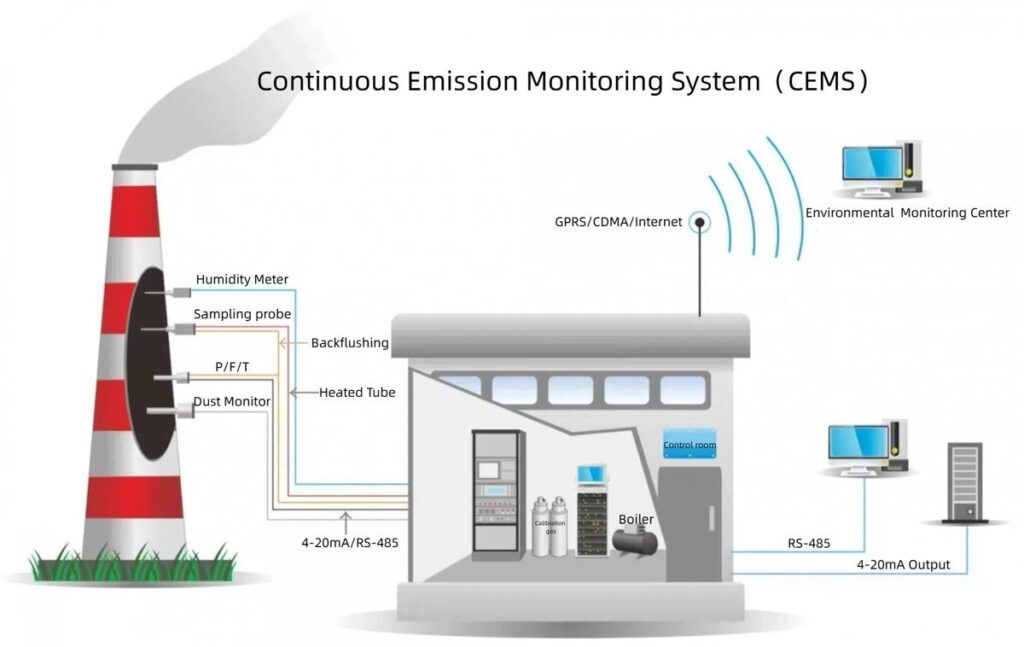
Gas Sampling System
The gas sampling system is one of the most crucial parts of a CEMS setup. Its primary function is to collect representative gas samples from the emission source, typically a stack or chimney. The sampling system includes several subcomponents such as the sampling probe, cooling system, filters, and gas transport lines.
- Sampling Probe: This is inserted into the gas stream to draw in the gas sample. The probe must be positioned in a place that ensures a representative sample is collected, avoiding areas with turbulence or significant stratification.
- Cooling System: Since gas samples can be at high temperatures, the cooling system ensures the sample cools to an optimal temperature before analysis to prevent condensation and damage to the analyzers.
- Filters: Filters remove particulate matter and water vapor from the gas sample, ensuring that only gases are sent to the analyzer.
Gas Analyzers
Gas analyzers are at the heart of the CEMS system. They measure the concentration of specific gases, such as CO2, SO2, NOx, and O2. Different types of analyzers are used depending on the gas being measured:
- Infrared Absorption Analyzers: These are commonly used to measure gases like CO2 and CO. They work by passing infrared light through the gas sample and detecting how much light is absorbed at specific wavelengths.
- UV-DOAS Analyzers: These are often used for measuring SO2,NOx emissions. They rely on a chemical reaction that produces light, which is detected and quantified.
- Electrochemical Analyzers: Used for gases like oxygen, these devices use the principle of electrochemical reactions to measure gas concentration.
Each analyzer has to be chosen carefully based on the specific gases that need to be measured in a given industrial setting.
Data Acquisition System (DAS)
The Data Acquisition System (DAS) is responsible for collecting data from the gas analyzers and processing it in real time. It ensures that data is logged continuously and in a format that can be stored for reporting purposes.
- Data Logging and Reporting: The DAS stores emission data over time, which can be retrieved for compliance reporting, performance assessments, or audits. It is crucial for meeting regulatory standards, as CEMS is often used for compliance with environmental laws.
- Alarm System: The DAS is also responsible for triggering alarms if the emissions exceed the regulatory thresholds, which allows plant operators to take corrective action immediately.
Calibration Equipment
Calibration is vital for ensuring the accuracy of the CEMS system,it used to test and adjust the system’s sensors and analyzers to ensure they provide accurate readings. This equipment typically includes reference gases, gas calibration cylinders, and check standards.
2. How to Install Continuous Emission Monitoring Systems (CEMS)?
Installing a CEMS gas system is a technical process that requires proper planning, expertise, and adherence to regulatory guidelines. The installation process is divided into several stages: environmental assessment, equipment setup, and system testing.

Environmental Assessment and Site Preparation
Before the installation of the CEMS system, a thorough environmental assessment must be conducted. This step ensures that the installation site is suitable and complies with the system’s requirements.
- Site Selection: The location of the system installation is critical to its efficiency. The sampling probe should be placed at a point where the gas is homogenous and free of disturbances. This ensures that the sample drawn is representative of the entire emission stream.
- Space and Accessibility: Adequate space should be allocated for installing the system components, especially the analyzers, cooling system, and data logging equipment. The location should also be accessible for routine maintenance and calibration.
Installing the Gas Sampling System
The gas sampling system is installed first, as it is the primary method for drawing gas samples from the emission stream. The sampling probe needs to be securely attached to the stack or chimney and should be positioned to minimize sample distortion. Special care should be taken to install the cooling system and filtration devices correctly to prevent clogging and condensation.
Setting Up the Analyzers and DAS
Once the sampling system is in place, the gas analyzers and the Data Acquisition System (DAS) are installed. The analyzers should be positioned in a controlled environment to avoid temperature extremes and contaminants, which could affect their performance.
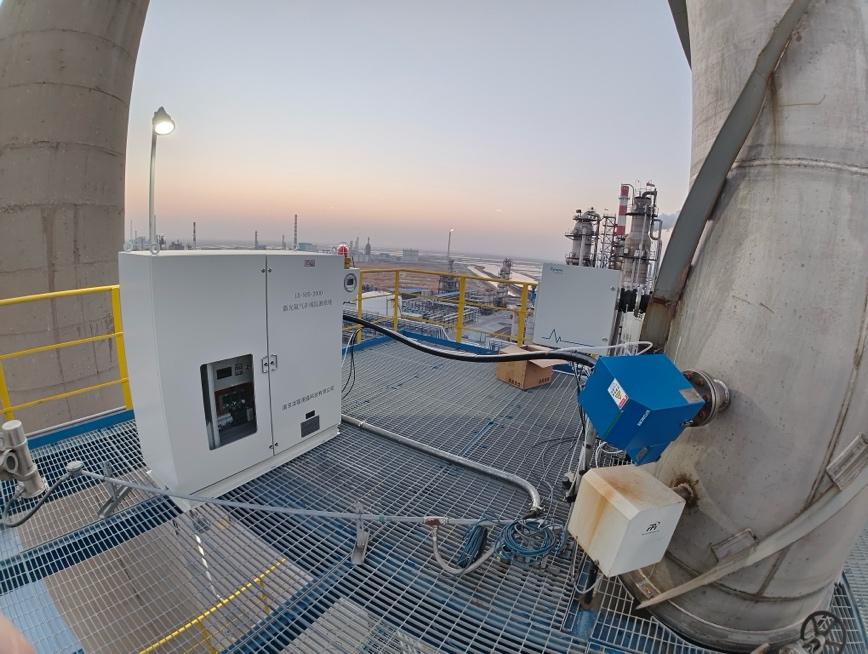

- Connecting the Sensors: The analyzers are calibrated to the gas sampling system to measure the relevant gases. Each analyzer must be properly calibrated using reference gases to ensure accurate readings.
- DAS Integration: The Data Acquisition System is connected to all the analyzers, allowing it to receive data from each unit. The system must be configured to log data, trigger alarms, and generate reports automatically.
Electrical and Data Connections
Proper electrical wiring and data connections are essential for the smooth operation of a CEMS. Power supply lines need to be securely installed, and data cables should be shielded to prevent electrical interference. The system must also be connected to the plant’s central control room for remote monitoring.
3. How is a Continuous Emission Monitoring Systems Calibrated and Tested Post-Installation?
Once the system has been physically installed, it is crucial to perform calibration and testing to ensure that all components are functioning as expected.

Zero and Span Calibration
Zero and span calibration are the first steps in the calibration process. Zero calibration ensures that the analyzer reads zero when no gas is present, while span calibration involves exposing the analyzer to a known concentration of gas to ensure its readings are accurate.
- Zero Calibration: This is done by introducing zero gas (typically nitrogen or synthetic air) into the system to verify that the instrument’s baseline is accurate.
- Span Calibration: The analyzer is exposed to a gas with a known concentration (calibration gas) to adjust the system to provide accurate readings for the gases being measured.
Field Testing and Performance Validation
After the initial calibration, the system undergoes field testing. This involves running the Continuous Emission Monitoring Systems (CEMS) at full capacity and comparing the emission readings to those from other certified instruments, such as reference monitors or manual sampling methods.
- Verification Against Standards: The test results must match regulatory standards and industry benchmarks. If discrepancies are found, further adjustments and recalibrations are required.
- Continuous Monitoring: Once the Continuous Emission Monitoring Systems (CEMS) passes the field tests, it enters regular operation, with continuous monitoring and routine maintenance to ensure ongoing compliance.
Conclusion
Installing and maintaining a Continuous Emission Monitoring Systems involves more than just setting up the equipment—it requires careful planning, accurate calibration, and regular testing to ensure compliance with environmental regulations. By understanding the components of a CEMS system and following the proper installation and calibration steps, businesses can ensure the system operates efficiently and meets regulatory standards.
If you have any questions, don’t hesitate to contact us; we will respond as soon as possible!

























