In steelmaking, syngas refers to a mixed gas stream made up of carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H₂), carbon dioxide (CO₂), methane (CH₄), and other trace gases. It forms during processes like coke oven off-gas, blast furnace gas, and direct reduction gas streams. These gases serve as reducing agents and fuel in key steelmaking stages, including blast furnaces, direct reduced iron (DRI) plants, and electric arc furnace (EAF) operations. Controlling the balance of these components influences heat, reduction reactions, and energy input across the plant.
Plant engineers and operations managers often search “Syngas for Quick Monitoring” because rapid insights into syngas composition help them make better decisions in real time. Quick monitoring reduces guesswork around fuel quality, prevents inefficient combustion, and ensures that reducing gases are used effectively. This leads to lower energy waste, improved throughput, and fewer off-spec batches.

Moreover, modern steel plants operate under tight safety and environmental standards. Real-time syngas data supports compliance by identifying hazardous spikes in CO or CH₄ and by helping control emissions. In short, quick syngas analysis helps reduce energy costs, improve process control, and protect both people and the environment.
So the central question becomes clear: Can real-time syngas monitoring actually enhance operational efficiency in steel plants? In the sections that follow, we’ll explore how fast, accurate syngas analysis delivers measurable gains in performance, safety, and cost control
How Does Syngas for Quick Monitoring Support Key Steelmaking Stages?
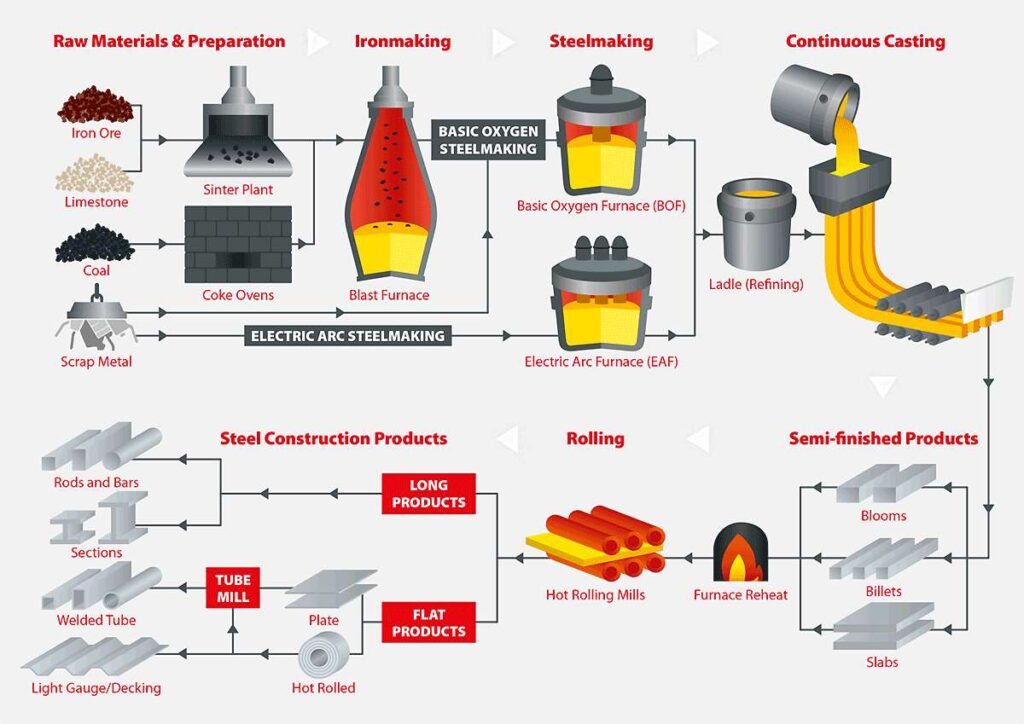
In steel plants, syngas plays a vital role across major production routes, from blast furnaces to modern low-carbon processes. It mainly consists of carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H₂), carbon dioxide (CO₂), and small amounts of methane (CH₄). These components serve as reducing agents and fuel sources during iron extraction and steelmaking.
Blast Furnace Operations
In a traditional blast furnace, iron ore is reduced to molten iron using coke, which also generates a reducing gas stream rich in CO and H₂. This syngas supplements the coke, providing both heat and chemical energy to drive reduction reactions. When the gas mix is balanced correctly, the blast furnace operates more efficiently and uses less coke overall. An imbalanced gas composition, however, can slow reduction reactions and increase fuel consumption.
Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) Production
In the DRI process, iron ore is turned into solid sponge iron without melting it. Syngas—primarily CO and H₂—acts as the reducing agent in this solid-state reaction. Precise control of the syngas H₂/CO ratio boosts reduction efficiency and lowers energy use. This process also reduces reliance on coke and decreases carbon emissions compared to conventional blast furnaces.
Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) Steelmaking
Electric arc furnaces mainly melt scrap steel using electrical energy. However, auxiliary syngas is often used to support combustion control and maintain stable thermal conditions in the furnace. Proper syngas balance enhances combustion efficiency and helps avoid energy waste or unstable furnace atmospheres, especially when melting sponge iron produced by DRI.
Across all these stages, real-time insights into syngas composition help operators fine-tune reactions. That leads to reduced fuel waste, optimized heat distribution, and more consistent steel quality across processes.
What Composition Challenges Make Syngas for Quick Monitoring Essential?
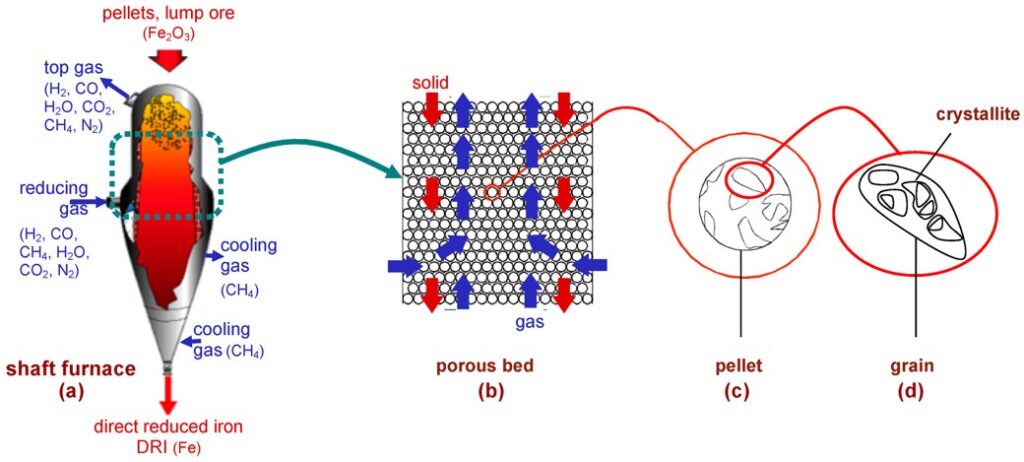
In steelmaking, syngas composition can drift quickly due to changing feedstocks, process heat, or reaction conditions. For example, the balance between hydrogen and carbon monoxide (H₂/CO) varies with raw material and gasifier conditions. Likewise, trace oxygen, carbon dioxide, and hydrocarbons can appear unexpectedly in the gas stream. These small shifts may seem minor, but they can have outsized effects on combustion quality, reduction reactions, and emissions control.
When the H₂/CO ratio moves outside its ideal range, combustion efficiency drops. That means furnaces burn fuel less completely, which wastes energy and can slow reduction reactions in blast furnaces or DRI units. Even small amounts of oxygen or light hydrocarbons can change flame stability or combustion stoichiometry, leading to inconsistent heat delivery and higher fuel costs.
Without real-time syngas analysis, plant operators can only guess at gas quality between slow, offline lab tests. These delays make it hard to adjust process controls fast enough to prevent energy waste or off-spec output. Worse still, poor gas balance can increase emissions or trigger safety alarms, forcing unplanned downtimes. In contrast, quick monitoring gives engineers immediate insight into changing gas chemistry, enabling tight control over efficiency and stability across the steelmaking workflow.
How Can Syngas for Quick Monitoring Drive Efficiency Gains in Steel Plants?
Modern steel plants demand precise control over gas composition to improve performance and cut costs. Real-time syngas monitoring delivers actionable data that operators can use directly to optimize key processes like combustion, reduction reactions, and furnace control. Quick monitoring helps plants run more smoothly and efficiently by reducing guesswork and tightening process control.
A. Operational Efficiency Gains
Accurate, real-time syngas data allows operators to maintain the ideal fuel-to-air ratio in blast furnaces and reheating units. As a result, combustion becomes more complete, which lowers consumption of coke and auxiliary fuels and reduces soot formation.
Moreover, quick gas feedback supports faster process adjustments during key stages like ironmaking and EAF melting. When syngas chemistry shifts, operators can respond immediately to cut cycle times, stabilize throughput, and keep production running without delays.
B. Cost and Energy Savings
Better syngas control also drives energy and cost savings. When plants track syngas composition in real time, they minimize fuel waste and optimize energy use across gasifiers, burners, and heat exchangers. This lowers overall energy consumption and decreases refractory wear from inefficient firing.
In addition, real-time monitoring helps prevent abnormal operational events that lead to unplanned stoppages, which saves maintenance costs and protects throughput continuity.
C. Quality & Yield Improvements
Stable syngas composition delivers consistent metallurgical reactions in ironmaking and steel refining steps. When CO and H₂ are kept within target ranges, reduction and combustion reactions proceed as designed, reducing scrap rates and improving final steel quality.
Overall, syngas for quick monitoring doesn’t just track gas quality—it enables operators to act on data in real time, helping steel plants improve efficiency, cut expenses, and deliver higher-quality products with greater consistency.
What Syngas Analyzer Technologies Enable Effective Syngas for Quick Monitoring?
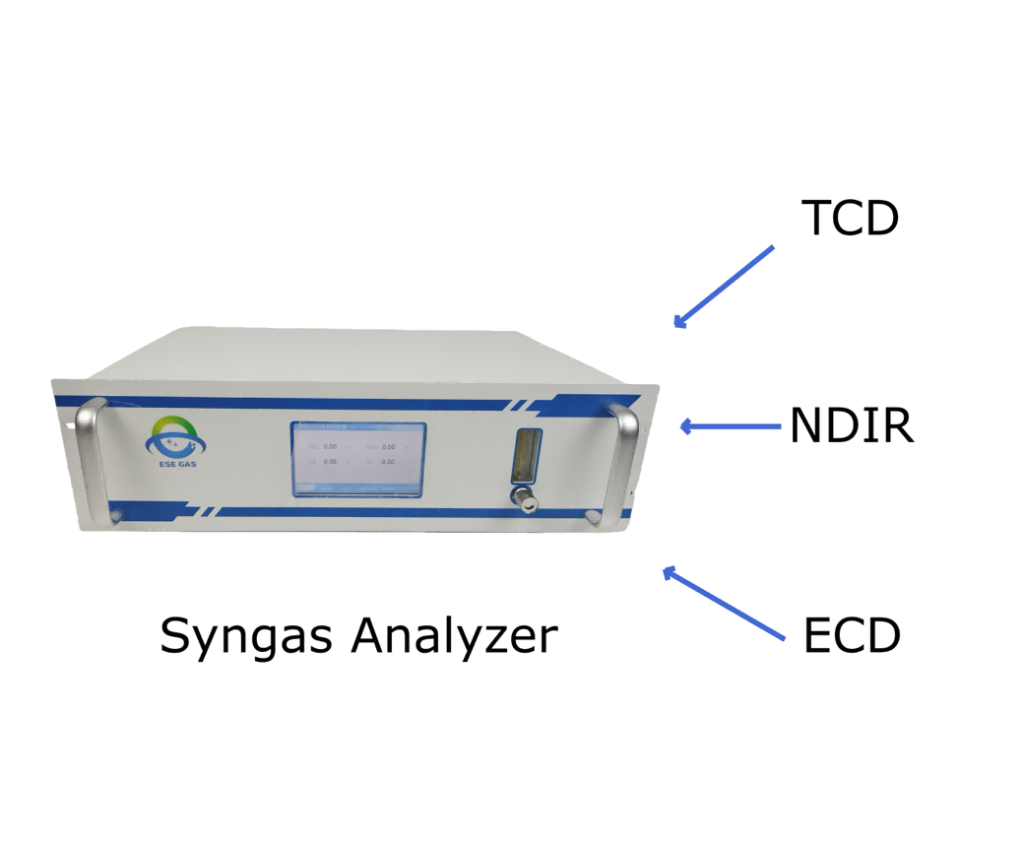
Accurate syngas monitoring depends on reliable sensing technologies that respond quickly to changes in gas composition. Today’s industrial syngas analyzers combine several measurement methods to capture key syngas components like CO, CO₂, CH₄, H₂, and O₂. Each technology has a clear role in delivering precise, real-time data for process control and automation.
A. Key Measurement Technologies
Non-Dispersive Infrared (NDIR) Sensors
NDIR sensing uses targeted infrared absorption to detect IR-active gases like carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and methane. Because it measures specific wavelengths absorbed by these molecules, it delivers fast, repeatable readings even in mixed gas streams. This makes NDIR ideal for monitoring combustion and reduction reactions in steel production.
Thermal Conductivity & Electrochemical Sensors
Hydrogen (H₂) doesn’t absorb IR like CO or CO₂, so thermal conductivity detectors (TCD) are used instead. TCDs measure how gas thermal conductivity changes with composition, enabling accurate H₂ quantification. Meanwhile, electrochemical cells measure oxygen levels by tracking electrical currents generated during gas reactions at electrodes. Together, these technologies give a broader view of syngas chemistry.
Multi-Gas Integration & Real-Time Output
Modern analyzers integrate these sensors into a single system that reports CO, CO₂, CH₄, H₂, O₂, and other components simultaneously. They deliver real-time outputs via digital interfaces like 4-20 mA, RS-485, or PLC links so plants can automate control loops and react instantly to gas shifts.
B. How Technology Affects Decision-Making
Quick syngas analysis transforms data into decision-ready insights. When an analyzer feeds high-frequency gas data into a Distributed Control System (DCS) or PLC, the plant can adjust fuel valves, air flows, or burner settings without waiting for lab tests. This real-time feedback reduces operator guesswork and shortens response times, which improves combustion efficiency and stabilizes throughput across blast furnaces, DRI units, and EAF operations.
In brief, combining NDIR, TCD, and electrochemical gas sensing with real-time automation creates a robust foundation for syngas for quick monitoring in steel plants and other industrial settings. These technologies enable faster, smarter decisions that cut fuel waste, enhance product quality, and support smooth process control.
Conclusion
As we’ve seen, real-time syngas monitoring delivers measurable benefits across efficiency, safety, and compliance in steelmaking. Quick access to accurate gas composition data helps operators fine-tune combustion, reduce unnecessary fuel use, and keep reactions within optimal parameters. This not only cuts energy waste, but also supports smoother production, lowers emissions, and boosts overall throughput. These gains go far beyond buzzwords — they have real impact on plant performance and profitability. Continuous gas analysis helps reduce off-spec batches and keeps energy use stable in blast furnaces, DRI units, and EAF operations.
Moreover, real-time syngas data enhances process safety and environmental compliance. Monitoring key components like CO, H₂, CO₂, and O₂ allows plants to detect imbalances that could lead to unsafe conditions or elevated emissions. This capability helps operations meet tightening regulatory standards while protecting workers and equipment from hazardous gas upsets. With real-time syngas insights, operators can respond quickly to deviations rather than reacting after the fact, which reduces risk and downtime.
Given these advantages, syngas for quick monitoring has become a core element of responsible, high-performance steel manufacturing. Exploring advanced syngas analyzer solutions can help you turn data into action — improving operations from the furnace to the final mill. Let’s explore tailored syngas monitoring solution together!
FAQs:
1. What does syngas mean in steelmaking and why monitor it?
Syngas stands for synthesis gas, a mixture of hydrogen (H₂), carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO₂), methane (CH₄), and other trace gases. In steel plants, it acts as a reducing agent and fuel in blast furnaces, direct reduced iron (DRI) units, and electric arc furnaces. Monitoring syngas’s composition helps operators control combustion and reduction reactions more precisely, which leads to better process efficiency and fuel use.
2. Why is Syngas for Quick Monitoring important in steel production?
Syngas composition can change quickly due to feedstock shifts, heat variation, or pressure changes. Quick monitoring delivers near-real-time data that allows engineers to adjust operations instantly, reducing energy waste and preventing inefficiencies. Without rapid feedback, operators may miss critical gas shifts that affect combustion efficiency and product quality.
3. How does syngas variability affect steel plant performance?
Variations in key components like CO and H₂ alter how well the gas burns and how efficient reduction reactions are. Imbalanced syngas can lead to incomplete reactions, higher fuel use, unstable furnace conditions, and greater emissions. Real-time syngas monitoring helps spot these issues early and correct them before they impact production.
4. What operational benefits come from syngas quick monitoring?
Quick syngas insights help plants:
- Maintain optimal fuel-to-air ratios for cleaner combustion
- Reduce coke and auxiliary fuel consumption
- Adjust processes promptly to prevent cycles that waste energy
- Stabilize throughput across steelmaking stages
These benefits support lower costs, better quality, and higher uptime.
5. Does syngas quick monitoring help reduce production costs?
Absolutely. Precise syngas analysis supports better combustion control and energy use, which in turn cuts fuel consumption and refractory wear. It also helps prevent unplanned stoppages, lowers maintenance costs, and enhances overall energy efficiency.
6. Is syngas monitoring only useful in blast furnaces?
No. While blast furnaces benefit greatly, syngas monitoring is also crucial in DRI operations and electric arc furnaces (EAF). In DRI, it ensures the H₂/CO ratio is suitable for efficient reduction. In EAF, it helps control auxiliary fuel combustion, stabilizing furnace temperatures and improving melting efficiency.