As industrial production continues to increase its environmental protection requirements, the monitoring of flue gas emissions has become increasingly important. To ensure that flue gas emissions meet environmental protection standards, the Continuous Emission Monitoring System (CEMS) is widely used in various industrial sites. CEMS provides a reliable basis for environmental compliance by monitoring flue gas emission data in real-time. However, to ensure the monitoring accuracy and stability of CEMS, daily maintenance of the system is essential. This blog will introduce the maintenance method of the extraction method CEMS flue gas online monitoring system to help operators better understand and perform maintenance work.

Introduction to the Extraction CEMS System
The extraction CEMS system is an online monitoring system that extracts flue gas samples and analyzes them in an analyzer. Its working principle is to extract gas samples from the flue into the analyzer, measure the concentration of gas components such as SO₂, NOx, CO, CO₂, O₂ through optical, electrochemical, and other analytical techniques, and finally transmit the monitoring results to the data processing system. The system has high monitoring accuracy and reliability, so it is widely used in emission monitoring in industries such as power, petrochemical, and cement.
Composition of the Extraction CEMS System
The extraction CEMS system mainly includes the following parts:
The extraction CEMS (Continuous Emission Monitoring System) is a system used to monitor industrial flue gas emissions in real-time. The system extracts gas samples from the flue and analyzes them to measure the concentrations of gas components such as SO₂, NOx, CO, CO₂, and O₂. The extraction CEMS system mainly consists of the following parts: sampling unit, pretreatment unit, analysis unit, data processing unit, and calibration unit. Each part plays a key role in the operation of the system. The following is a detailed description of these components.
- Sampling unit

- Sampling probe
The sampling probe is the front-end device of the extraction CEMS system, which is used to extract gas samples from the flue. It is usually installed at the sampling point of the flue. Through its specific structure and materials, it can withstand high temperatures, high humidity, and highly corrosive flue gas environments. The design of the sampling probe also needs to ensure the flow state of the airflow in the probe to avoid sample gas retention, concentration, and other phenomena that affect the measurement accuracy.
- Sampling pipeline
The sampling pipeline is used to transport the flue gas sample from the sampling probe to the pretreatment unit. It needs to keep the composition of the sample gas unchanged, avoid adsorption, leakage or chemical reaction, and ensure the integrity and representativeness of the sample gas.
- Preprocessing unit
The pretreatment unit is used to perform necessary pretreatment on the sample gas transmitted from the sampling unit to remove interfering substances such as dust, moisture, acidic gas, etc. in the sample, ensuring that the gas meets the measurement conditions when entering the analysis unit.


- Dust Collector: The dust collector is used to remove particulate matter from the sample gas to prevent the particulate matter from clogging subsequent equipment or affecting measurement accuracy.
- Dehumidifier: Dehumidifiers are used to remove moisture from sample gases to prevent condensation from corroding analytical instruments or affecting measurement results.
- Cooler: The cooler is used to reduce the temperature of the sample gas to adapt it to the working conditions of the analytical instrument and remove some of the moisture.
- Chemical absorption device: The chemical absorption device is used to remove specific interfering components (such as acidic gas, alkaline gas, etc.) in the sample gas to ensure the accuracy of the analysis results.
- Analysis Unit
The analysis unit is the core part of the CEMS system, responsible for analyzing the components of the pre-treated sample gas. Different gas components usually use different analysis methods and instruments.
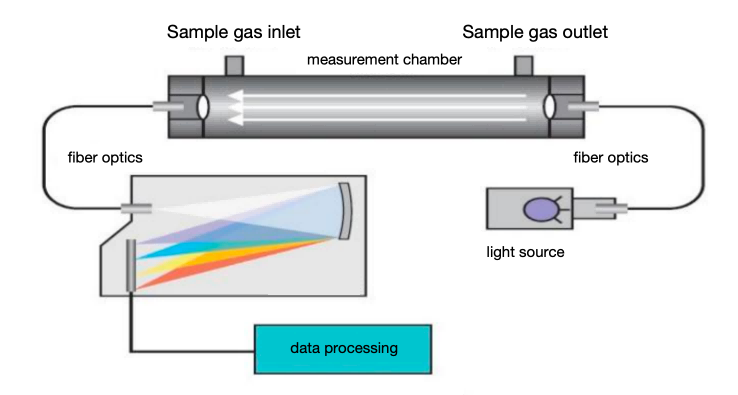
- Gas Analyzer: Gas analyzers are used to measure the concentration of target components (such as SO₂, NOx, CO, CO₂, O₂, etc.) in sample gases.
- Moisture Analyzer: Humidity analyzers are used to measure the humidity of sample gas to compensate for the interference of humidity on the measurement of other gas components.
- Data processing unit
The data processing unit is used to receive the signal output by the analysis unit and process, record and transmit the data.
- Data Collector: The data logger is used to receive and collect signals from analytical instruments and convert analog signals into digital signals for subsequent processing.
- Data processing software: Data processing software is used to calculate, analyze and process the collected data.
- Calibration unit
The calibration unit is used to regularly calibrate the gas analyzers in the CEMS system to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the monitoring data.
- Calibration gas: Calibration gases are standard gases of known concentration used to calibrate the zero and span of analytical instruments.
- Automatic calibration device: The automatic calibration device is a device that can automatically perform calibration. Through the built-in gas switching device and calibration program, the calibration process is automatically performed at set time intervals.
Daily maintenance method of CEMS system based on extraction method

Maintenance of sampling unit
Sampling probe cleaning: The sampling probe is a component that is in direct contact with flue gas and is easily blocked by smoke and particulate matter, resulting in inaccurate sampling. Clean the probe regularly, usually at least once a week, and more frequently if necessary. Clean the probe with a cleaning tool or cleaning fluid and check for signs of corrosion or damage.
Sampling pipeline inspection: The sampling pipeline is the channel connecting the sampling probe and the pretreatment unit, which is prone to blockage, aging, or leakage. The integrity of the pipeline should be checked regularly, especially whether the connection parts are firm and leak-free, and whether the pipe wall has cracks or aging. Once an abnormality is found, the pipeline should be replaced immediately.
Filter replacement: In the sampling unit, filters are usually set to prevent particulate matter from entering the analytical instrument. The filter needs to be checked and replaced regularly, usually once a month, depending on the dust concentration of the flue gas and its usage. When replacing, make sure that the specifications and models of the new filter meet the original manufacturer’s requirements.
Maintenance of the pre-processing unit
Dust collector cleaning: The dust collector is used to remove large dust particles in the flue gas to prevent clogging of the sampling pipeline and damage to the analytical instrument. Clean the dust in the dust collector regularly to ensure its normal operation.
Cooler maintenance: The cooler is used to reduce the temperature of the sample gas to prevent high temperatures from damaging the analytical instrument. The heat dissipation performance of the cooler should be checked regularly, and the dust and dirt on the surface of the cooler should be cleaned to ensure a good cooling effect.
Dehumidifier maintenance: Dehumidifiers are used to remove moisture from flue gas to prevent moisture from corroding analytical instruments or affecting measurement accuracy. The operating status of the dehumidifier should be checked regularly, and the desiccant or dehumidification membrane should be cleaned or replaced to ensure its dehumidification effect.
Maintenance of the analysis unit
Calibration of gas analyzer: The gas analyzer is the core component of the CEMS system, and its measurement accuracy directly affects the reliability of monitoring results. The gas analyzer should be calibrated regularly according to the use requirements and the provisions in the equipment manual. It is usually recommended to perform zero and span calibration once a month to ensure the accuracy of measurement.
Cleaning and maintenance of the analyzer: Clean the optical components, electrodes, and gas path of the analyzer regularly to avoid damage caused by smoke or corrosive gases. Check whether there is the foreign matter or scaling inside the analyzer and clean it in time to prevent blockage.
Replacement of detection sensors: The detection sensors inside the gas analyzer have a certain service life, usually 1-2 years. According to the aging and use of the sensors, the sensors should be replaced regularly to ensure the accuracy of the analyzer.
Maintenance of Data Processing Unit
Data backup and storage: Monitoring data is an important basis for environmental compliance. Data should be backed up and stored regularly to prevent data loss or damage. It is recommended to perform a complete data backup once a week and store the backup files safely.
Software update and maintenance: The data processing software in the CEMS system should be regularly checked and updated to fix known vulnerabilities and errors and add new functions to ensure that the system always runs in the best condition.
Maintenance of the calibration unit
Checking of calibration gas: Calibration gas is used to calibrate the analytical instruments of the CEMS system regularly. Its concentration and purity have a direct impact on the calibration results. The validity period and cylinder pressure of calibration gas should be checked regularly to ensure that they meet the use requirements.
Automatic calibration function test: Many CEMS systems have an automatic calibration function that automatically calibrates at set intervals. This function should be checked and tested regularly to ensure that the automatic calibration function is working properly.
Common CEMS system failures and solutions

1. Check the data: Mainly check whether the oxygen is normal. If it is higher than 10%, it means there may be a leak. The leak is mainly checked on the gas path on the negative pressure side of the sampling pump. If the value feels inaccurate, contact the operator for verification. The analyzer needs to be calibrated. If it is still the same as the initial value after calibration, it means that the value is accurate.
2. Check all gas lines: observe whether the drainage is smooth, water accumulation in the pipeline, water vapor in the filter, and whether the sampling pump is working properly. The water in the glass condenser should be emptied every day. The indication of the float flowmeter should be between 1.5 and 1.7. If it is too large or too small, it should be adjusted in time. Is there water in the float flowmeter? If there is water, it means that the peristaltic pump is not draining smoothly and needs maintenance. Blow the water in the pipeline dry with back-blowing air. Use compressed air to purge the sampling pipeline every day to prevent blockage. (Open the compressed air valve and press the back-blowing button on the cabinet door.)
3. The main reasons for poor drainage of peristaltic pumps:
(1) Drainage pipe is blocked
(2) The roller part of the pump axis cannot press the hose tightly. As a result, a vacuum cannot be formed and the water cannot be sucked out of the refrigeration tank. If it is the second reason, you need to loosen the tube compression spring screw inside the pump so that the roller presses the hose tightly. If the axis of the peristaltic pump is too loose, you need to replace the peristaltic pump.
4. Check whether the heating pipeline is heated normally. Touch the sampling pipeline with your hand to see if it is warm. Check whether the thermostat that controls the temperature of the heating pipeline is working properly. Adjust the temperature (generally set to 120 degrees). Turn up the temperature to see if it heats (test whether the power supply is 220V). Turn down the temperature to see if it does not heat up.
Conclusion
The extraction method CEMS flue gas online monitoring system is an important tool for modern industrial flue gas emission monitoring. Its daily maintenance is essential to ensure the normal operation of the system and the accuracy of the data. By regularly checking and maintaining the sampling unit, pretreatment unit, analysis unit, data processing unit, and calibration unit, system failures can be effectively reduced and the reliability and accuracy of monitoring data can be improved. Industrial enterprises should formulate detailed maintenance plans and perform maintenance in strict accordance with operating procedures to ensure the long-term stable operation of the flue gas emission monitoring system, to better meet the requirements of environmental protection regulations.
If you have any questions, please leave a message or contact us!