Environmental protection has become an important issue in modern industrial production. With the acceleration of industrialization, harmful emissions from factories have a serious impact on the environment and human health. Cement factories, as an important industrial production base, are particularly important for emission control. Among them, HCl (hydrochloric acid) gas, as one of the common harmful gases, needs to be effectively controlled. In this paper, we will introduce the application of gas analyzers in the control of HCl gas emissions from cement plants, and discuss their principles, functions, and importance in environmental protection.
Gas Analyzer Introduction
A gas analyzer is an instrument used to detect and analyze the composition of gases. It measures gas concentration, pressure, temperature, and other parameters to help plants monitor and control harmful gas emissions. A gas analyzer typically includes components such as sensors, sampling systems, and data processing units that analyze collected gas samples to provide accurate data to support plant operations and environmental management.
HCl Gas Emissions from Cement Plants
During cement production, the main raw materials, limestone and clay, contain chlorides. And in the clinker firing process, chloride will be combined with calcium in limestone to form calcium chloride, which is then released as HCl gas HCl is released as HCl gas. HCl gas is contained in the chimney emissions from cement factories, which, if not effectively controlled, can be potentially harmful to the surrounding environment and population, for example, leading to the generation of acid rain, damaging vegetation and soil, and posing a threat to the health of the surrounding population.
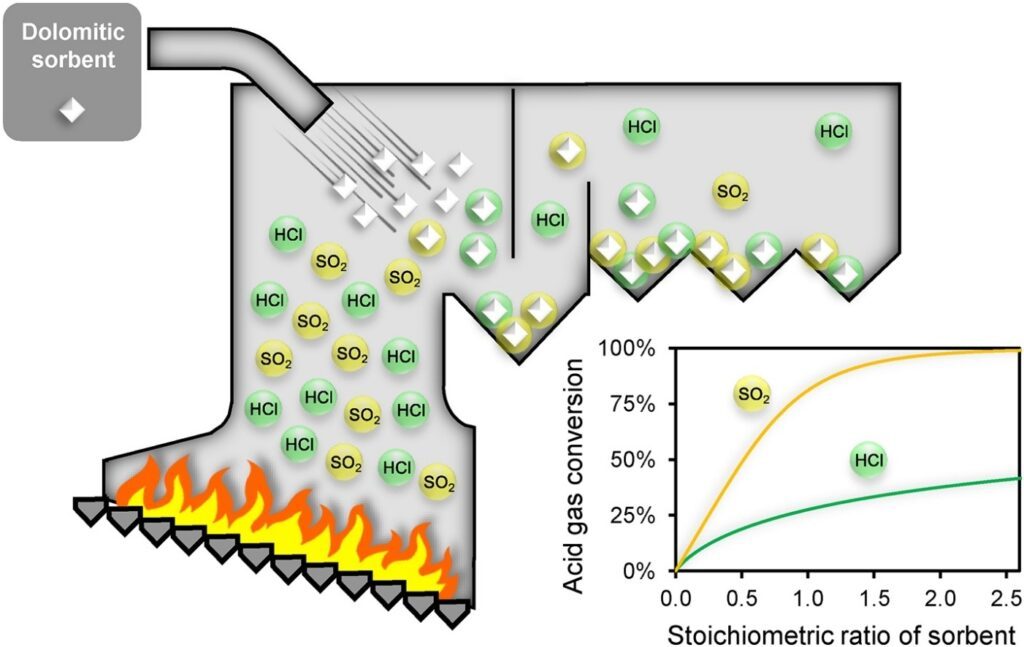
Therefore, cement plants must take effective measures to control and minimize HCl gas emissions in order to protect the environment and the health of employees. The following are the main problems faced by HCl gas emissions in cement plants:

- Sources and processes: The main raw materials used in cement production are limestone and clay, etc., which release a large amount of gas during calcination at high temperatures. Among them, limestone contains chlorides, such as sodium chloride and calcium chloride, which release HCl gas when these chlorides are decomposed by heat. Therefore, the firing process in cement plants is a major source of HCl gas emissions.
- Impact on the environment: HCl is a strongly corrosive and toxic gas, long-term exposure to high concentrations of HCl will have a serious impact on the surrounding ecological environment.HCl gas emissions will not only cause atmospheric pollution, but also reduce the pH value of the soil and water, causing harm to soil and aquatic organisms.
- Health effects: HCl gas is an irritant gas that has a strong irritating effect on the human respiratory tract and skin. Long-term exposure to high concentrations of HCl gas can cause respiratory diseases such as asthma and chronic bronchitis, posing a threat to the health of employees and surrounding residents.
- Regulatory Compliance Requirements: As environmental protection regulations continue to be strengthened, cement plants must comply with strict emission standards and regulatory requirements to control and monitor harmful emissions such as HCl. Otherwise, companies will face severe penalties such as fines and suspension of production.
- Social responsibility and corporate image: As an important industrial producer, cement factories bear social responsibility and must take active measures to reduce pollution to the environment. Increased awareness of environmental protection has also made the environmental image of enterprises increasingly important to external evaluation, therefore, effective control of HCl gas emissions is not only a regulatory requirement, but also a reflection of corporate social responsibility.
In summary, the problem of HCl gas emissions from cement plants not only has serious impacts on the environment and health, but also challenges companies’ regulatory compliance and social responsibility. Therefore, cement plants must take effective measures to control and reduce HCl gas emissions to protect the environment and human health.
Application of Gas Analyzers in HCl Emission Control
Real-time monitoring and data collection: The gas analyzer can monitor the gas composition, especially the concentration of HCl gas, at the emission outlet of the cement plant in real time. By collecting and transmitting data in time, the plant can understand the emission situation and adjust the production process in time to keep the emission within a reasonable range. Gas analyzers play a vital role in the control of HCl gas emissions in cement plants. The following is a detailed description of the application of gas analyzers in HCl emission control:

- Real-time monitoring and data acquisition: The gas analyzer can be installed at the emission outlet or related equipment in a cement plant to monitor the concentration of HCl gas in real time. By collecting gas samples through sensors and transmitting the data to a data processing unit, the gas analyzer is able to provide accurate HCl concentration data.
- Automatic Alarm and Control: The gas analyzer can be set with a warning threshold that will automatically signal an alarm once the HCl concentration is detected above the set value. In this way, the factory can take timely measures, such as stopping the relevant production equipment, to reduce the emission of HCl gas and protect the environment and the safety of employees.
- Data Analysis and Optimization: The data collected by the gas analyzer can be analyzed in depth to help the plant understand the patterns and influencing factors of HCl emissions during the production process. By analyzing these data, the production process can be optimized to reduce the generation and emission of HCl and improve production efficiency and environmental protection.
- Environmental Monitoring and Reporting: The gas analyzer not only monitors the gas condition at the vent, but also sets up monitoring points around the plant to monitor the concentration of HCl gas in the environment in real time. The monitoring data can be used to prepare environmental reports to be released to regulators and the public to ensure environmental compliance of the plant.
- Remote monitoring and management: Some of the advanced gas analyzers have remote monitoring and management functions, which allow the factory to remotely monitor the gas conditions at the emission outlets and monitoring points through the Internet, realizing remote control and management, and improving production efficiency and response speed.
- Quantitative Measurement and Precision Control: The gas analyzer can quantitatively measure HCl gas with high precision and stability. By accurately measuring the concentration of HCl gas, the plant can control the emission within a reasonable range, avoid over-emission and reduce the risk of environmental pollution.
- Versatility and adaptability: Gas analyzers are often multi-functional, capable of detecting a wide range of gas components, and suitable for different industrial environments and conditions. Cement plants can therefore choose the right gas analyzer for their actual needs and achieve comprehensive emission monitoring and control.
Gas Analyzer Selection and Maintenance
When selecting a gas analyzer and performing maintenance, several factors need to be considered, including accuracy, stability, suitability, ease of use, maintenance costs, after-sales service and technical support. These aspects are described in more detail below:,
Selecting a Gas Analyzer
- Accuracy and Stability:
The accuracy of a gas analyzer is critical, especially when monitoring HCl gas emissions, where even small errors can lead to violations of environmental standards. Therefore, it is critical to select a gas analyzer with high accuracy and stability.
- Applicability and flexibility:
Ensure that the selected gas analyzer is suitable for the high temperature and high humidity working environment of the cement plant. In addition, consider whether the installation method and interface of the equipment are flexible enough to meet the needs of the actual situation in the cement plant.
- Ease of use and maintenance costs:
Choosing a gas analyzer that is simple to operate and easy to maintain will reduce labor costs and maintenance expenses. At the same time, make sure that the maintenance cost of the selected equipment does not exceed your budget.
- After-sales service and technical support:
Choose a gas analyzer brand with good after-sales service and technical support to ensure that the equipment can solve problems during operation, and carry out maintenance and upgrading in a timely manner.
Maintaining gas analyzers
- Periodic inspection and calibration:
Regularly check the parameters of the gas analyzer to ensure its proper operation. Also, calibrate regularly to ensure the accuracy of the measurement results.
- Cleaning and maintenance:
Clean the sensors and instrument surfaces of the gas analyzer regularly to prevent dust and dirt from accumulating and affecting measurement accuracy. Especially in working environments such as cement plants, where the air may contain large amounts of dust, cleaning needs to be intensified.
- Replace parts in a timely manner:
For wearing parts, such as sensors, check them regularly and replace them in time to ensure the normal operation of the equipment. Timely replacement of aging or damaged parts can effectively extend the service life of the equipment.
- Software updates and upgrades:
Regularly update the software of your gas analyzer for the latest features and performance optimization. Software updates typically improve the stability and accuracy of the device.
- Training of operators:
Train operators in the use of gas analyzers and maintenance techniques to reduce the likelihood of human error and equipment failure.
Through the above maintenance measures, the normal operation of the gas analyzer can be ensured and its stability and reliability can be improved, so as to effectively control the HCl gas emission from the cement plant and protect the environment and human health.
How Our HCl Gas Analyzers Respond
HCl TDLAS (Tunable Diode Laser Absorption Spectroscopy) gas analyzers offer several advantages for the analysis of hydrogen chloride (HCl) gas.
Some of the key advantages of HCl TDLAS gas analyzers include:
- High Sensitivity and Selectivity: HCl TDLAS analyzers provide high sensitivity and selectivity for detecting and measuring HCl gas. The tunable diode laser emits light at specific wavelengths that correspond to the absorption lines of HCl, allowing for precise and accurate measurements even at low concentrations.
- Real-time Monitoring: TDLAS gas analyzers offer real-time monitoring capabilities, providing continuous and instantaneous measurements of HCl concentrations. This is particularly useful for applications where rapid response and timely detection of HCl gas are essential, such as industrial process control or safety monitoring.
- Wide Dynamic Range: HCl TDLAS analyzers can cover a wide dynamic range, allowing them to measure HCl concentrations across a broad span, from low parts-per-billion (ppb) levels to higher parts-per-million (ppm) concentrations. This flexibility makes them suitable for various applications with different concentration ranges.
- Non-contact Measurement: TDLAS gas analyzers perform non-contact measurements, meaning that they do not require direct contact with the gas sample. This eliminates the need for complex sample conditioning systems and reduces maintenance requirements.
- Minimal Interference: TDLAS technology is relatively immune to interference from other gases, dust, or humidity present in the gas sample. This ensures accurate and reliable measurements of HCl gas, even in complex gas mixtures or challenging environmental conditions.
- Low Maintenance: TDLAS gas analyzers generally have a robust design and require minimal maintenance. They are less prone to drift or degradation over time, resulting in reduced calibration and service intervals.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: Many HCl TDLAS analyzers are equipped with advanced features such as remote monitoring and control capabilities. This allows users to access and manage the analyzer from a central control room or remotely, enhancing operational convenience and efficiency.
- Compliance with Regulations: HCl TDLAS gas analyzers often meet regulatory requirements and industry standards for HCl gas monitoring, making them suitable for compliance monitoring applications.
These advantages make HCl TDLAS gas analyzers a preferred choice for HCl gas analysis in various industries, including
- chemical manufacturing,
- semiconductor fabrication
- waste incineration
- environmental monitoring.
What are the main technologies for monitoring HCL
Two main technologies are used to monitor HCl gas:
☑ Tunable Diode Laser Absorption Spectroscopy (TDLAS)
☑ Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy
TDLAS is a laser-based technique that uses tunable lasers to measure the absorption of light at specific wavelengths, allowing the targeted measurement of HCl gas. FTIR spectroscopy is a technique that measures the absorption of infrared light, which means it can measure a wide range of compounds including HCl gas.
We can offer
ESE-LASER-HCL-200 online TDL HCL gas analysis system
ESE-LASER-HCL-200P Portable TDL HCL gas analyzer
ESE-LASER-HCL-500 online TDL HCL gas analyzer
ESE-LASER-HCL-700 Trace HCL gas analyzer (ppb range)
Advantages and Importance of Gas Analyzers in Cement Plants

- High Accuracy and Reliability: The gas analyzer adopts advanced sensing technology with high accuracy and reliability, capable of accurately measuring the concentration of harmful gases such as HCl, providing reliable data support for emission control.
- Real-time monitoring and rapid response: Gas analyzers can monitor gas emissions in real time, detect problems and take measures in time to effectively avoid environmental pollution and safety accidents.
- Automated control and intelligent management: Gas analyzers can be integrated with automated control systems to achieve automated emission control, reduce human intervention and improve management efficiency and accuracy.
- Compliance monitoring and environmental management: Gas analyzers help cement plants monitor emissions and ensure compliance with environmental regulations, as well as provide data support for environmental management, enhancing corporate image and sustainability.
Conclusion
In today’s context of increasing environmental awareness, cement plants and other industrial enterprises must pay attention to the control of HCl and other harmful gas emissions. As an important monitoring and control equipment, gas analyzer plays a key role in HCl emission control in cement plants. Through real-time monitoring, automatic alarm and intelligent management, the gas analyzer can help cement plants reduce HCl emissions, protect the environment and human health, and promote sustainable industrial development.

























