In modern industrial production, environmental protection and industrial safety have become important issues that cannot be ignored. Especially in controlling air pollution, dust monitoring and management is one of the core contents of environmental monitoring. The dust monitor in the Continuous Emission Monitoring System (CEMS) is a device specially designed to monitor and record the concentration of dust in industrial emissions, and its accuracy and real-time performance are of great significance to environmental protection. In this blog, we will introduce in detail the working principle of CEMS dust monitor, selection guidance, and use cases in different application scenarios.
Principle of Operation of CEMS Dust Monitors
CEMS dust monitors work on the basis of three main technologies: optical, electrochemical and beta-ray absorption. Each technology has its own unique monitoring mechanism and is suitable for different industrial environments and requirements. These three principles are described in detail below:
1. Optical principles
Optical principles are one of the most widely used techniques in dust monitors. It mainly includes laser scattering and light scattering techniques.
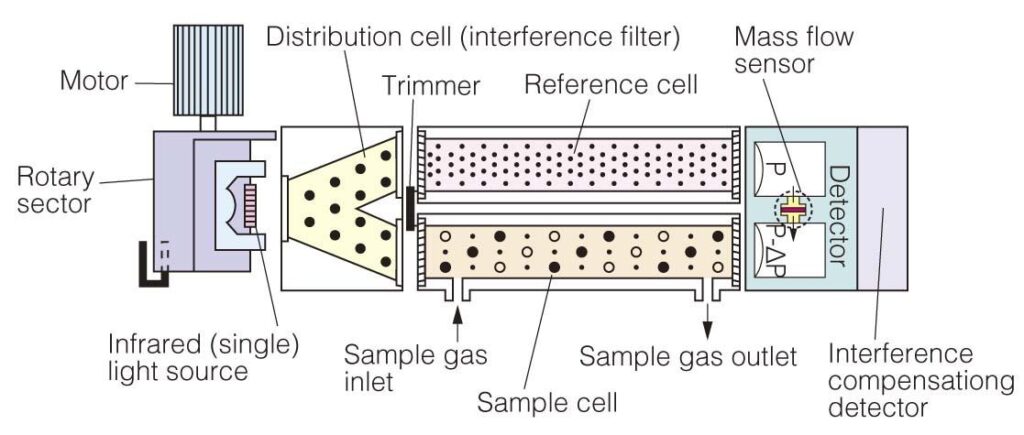
- Laser Scattering Technology
In laser scattering technology, a laser light source emits a laser beam that passes through a sample of gas containing dust. When the laser beam encounters dust particles, the beam is scattered. The monitoring instrument is equipped with one or more detectors to capture this scattered light. Based on the intensity and angular distribution of the scattered light, the size, concentration, and other relevant characteristics of the dust particles can be calculated. This technique is particularly effective for fine particle-size dust, providing real-time data on particle size distribution and concentration.
- Light scattering techniques
Similar to laser scattering, light scattering techniques use a light source to irradiate passing dust samples but typically use a broadband light source rather than a single wavelength laser. When the light source illuminates the dust particles, the particles scatter the light in different directions. A detector measures the dust concentration based on the intensity of the scattered light. This method is simple and low-cost and is suitable for large-scale or continuous environmental monitoring.
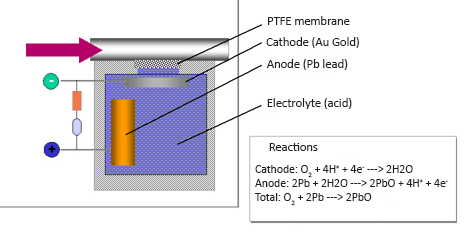
2. Electrochemical principles
Electrochemical dust monitors use the behavior of dust particles in an electric field to determine their concentration. The monitor is equipped with electrically charged electrodes inside the monitor, and when dust-laden gases flow through the electrodes, the dust particles affect the current or resistance between the electrodes. By measuring the change in current or resistance, the concentration of dust can be inferred. This method is particularly suitable for application scenarios where the dust particles are electrically charged or are able to exhibit a specific behavior in an electric field. ( Image source: flsmidth )
3. Beta-ray absorption
The beta-ray absorption method is an accurate dust monitoring technique particularly suited to high-concentration dust environments. In this method, a beta-ray source (usually a radioisotope) emits beta rays that pass through a sample of dusty gas. The dust particles absorb some of the beta rays and the remaining rays are captured by a detector. By measuring the attenuation rate of the rays (i.e. the intensity of the rays after they have penetrated the gas), the dust concentration can be calculated. Due to its high accuracy and adaptability to high dust concentrations, this method is widely used in industrial emissions and environmental monitoring.
Each of these three monitoring principles has its advantages and limitations, and the selection of an appropriate monitoring technique requires consideration of the specific application environment, the purpose of the monitoring, and the cost-effectiveness. In practice, one or a combination of techniques is often chosen to achieve the best monitoring results based on specific needs. Below is a detailed table comparing the three main techniques used in CEMS dust monitors: optical, electrochemical, and beta-ray absorption, covering their principles, advantages, costs, technical parameters, application scenarios, and limitations:
| Type of technology | principle | dominance | (manufacturing, production, etc) costs | Technical Parameters | application scenario | limitations |
| Principles of optics (laser scattering/light scattering) | A light source (laser or broadband light) is utilized to irradiate the dust sample and the dust concentration is calculated by measuring the intensity and distribution of the scattered light. | Accurate measurement of particle size distribution and concentration, real-time data, good effect on tiny particle size dust. | middle to high | Wide measuring range and high accuracy with real-time data and particle size analysis. | Plant emissions, indoor air quality monitoring, environmental monitoring | Sensitive to environmental conditions such as light and air cleanliness, with high equipment maintenance and calibration needs. |
| electrochemical principle | Dust concentration is monitored by measuring the change in current as the gas passes through the charged electrode. | Simple, low cost, and suitable for continuous monitoring. | low to medium | Well adapted to measure mainly concentration rather than particle size. | Chemical plants, mining, and other environments where hazardous dust needs to be monitored. | Lower accuracy, possible chemical interference, and limited access to particle size information. |
| beta-ray absorption | A beta ray source is used to pass through the dust sample and the dust concentration is calculated based on the degree of ray absorption. | High precision, suitable for high concentration dust, stable results. | your (honorific) | Highly accurate measurements, capable of handling highly concentrated dust samples. | Monitoring of emissions from heavy industry, e.g. steel mills, and cement plants. | The equipment is expensive, requires handling of radioactive material, and is complicated to maintain. |
The Selection of CEMS Dust Monitors
Selecting a CEMS dust monitor is a complex process involving several considerations. Selecting the right dust monitor requires consideration of the characteristics of the monitoring object, the conditions of the monitoring environment, and the accuracy of the monitoring objectives. Below is a detailed selection guide covering the main factors that should be considered when selecting a dust monitor:
1. Characteristics of the object to be monitored
- Dust types
Combustible Dust: Equipment needs to be selected that is capable of safely monitoring flammable and explosive dust and may require additional safety certifications.
Chemical Dust: For corrosive or other chemically active dust, the materials and construction of the monitor must be chemically resistant.
- Dust particle size
Particle size affects the type of monitoring technology chosen. For example, laser scattering techniques are suitable for monitoring fine particle-size dust.
- Dust concentration
The concentration level determines the measurement range of the monitor required, and high-concentration environments may be more suited to using beta-ray absorption.
2. Accuracy and measuring range
- Measurement accuracy
Higher accuracy requirements usually mean higher equipment costs. Select the appropriate level of accuracy based on the purpose of the monitoring and regulatory requirements.
- Measurement range
Ensure that the measurement range of the selected monitor covers the expected range of variation in dust concentration.
3. Environmental factors
- Temperature and humidity
The equipment must be able to operate stably under the temperature and humidity conditions found in the actual working environment.
- Gas background
Gas composition may affect the performance of some types of monitors, e.g. optical monitors may be affected by scattered light from background gases.
4. Economic considerations
- Cost-effectiveness
Consider the acquisition cost of the equipment, operation, and maintenance costs, and potential calibration costs.
- Maintenance requirements
The ease and frequency of maintenance of the equipment is also part of the cost, and equipment that is easy to maintain and less expensive to run over time should be selected.
5. Compliance and certification
- Environmental regulations
Ensure that the selected equipment complies with relevant environmental regulations and emission standards.
- Security certification
For specific environments, such as flammable and explosive environments, the equipment also needs to have the appropriate safety approvals.
6. Manufacturers and technical support
- Manufacturer reputation
Choose a well-known and well-reviewed manufacturer to ensure the quality of the equipment and subsequent technical support. esegas is a well-known manufacturer specializing in CMES equipment and can provide customized CMES products and solutions according to your needs.
- Technical support and services
Consider the technical support and services provided by the manufacturer, including installation, commissioning, troubleshooting and regular calibration services. esegas has professional engineers as well as an after-sales service team to take care of your worries.
By taking all of these factors into consideration, the CEMS dust monitor that best suits the needs of a particular application can be effectively selected. This process ensures that the equipment can provide accurate and reliable data in the specific monitoring environment, thus helping organizations comply with environmental regulations while protecting public health and safety.
The Various Applications of CEMS Dust Monitors
CEMS dust monitors are used in a wide range of applications, covering everything from industrial emissions monitoring to environmental protection to indoor air quality assessment. Not only do these devices play an important role in maintaining environmental standards and regulatory compliance, but they also play a key role in improving productivity and safeguarding public health. The following are details of specific applications of CEMS dust monitors in various fields:
1. Industrial Emission Monitoring
Industrial emissions are one of the most traditional and critical application areas for dust monitors. In industries such as steel manufacturing, chemical production, power generation, and cement manufacturing, monitoring and controlling the amount of dust emitted is critical to maintaining air quality.
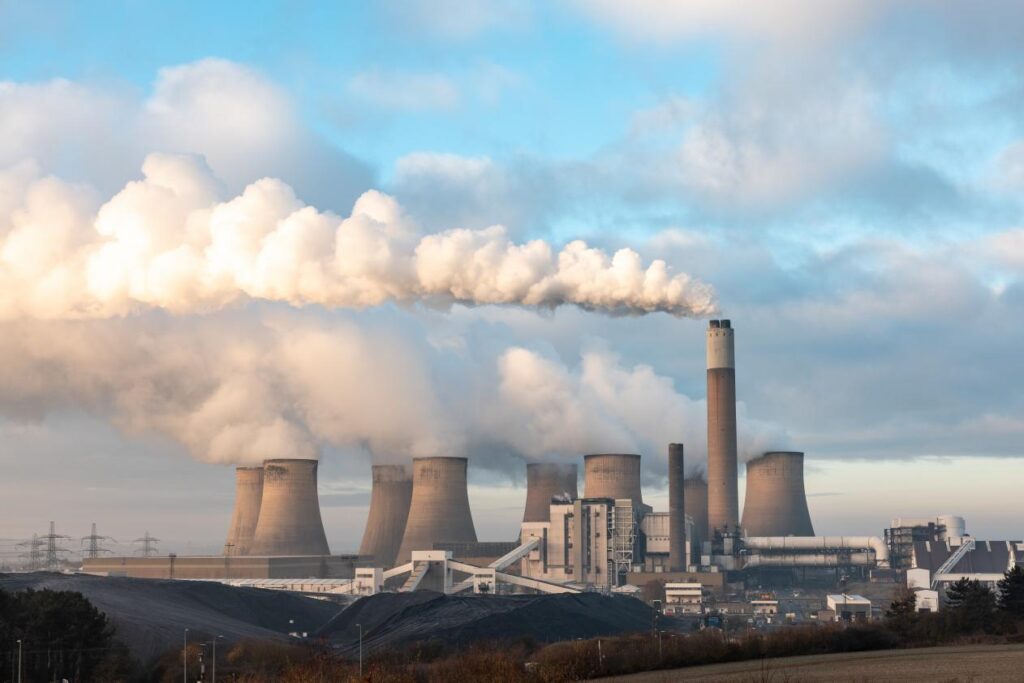

- Steel manufacturing
The coking, ironmaking, and steelmaking stages of the steel production process generate large amounts of dust and fumes. Using CEMS dust monitors allows you to monitor dust emissions from these processes in real-time to ensure that they do not exceed legal standards. This not only helps companies comply with environmental regulations but also helps to improve production processes and reduce raw material waste.
- Cement plants
Cement production is a high dust emission process, especially in the crushing, grinding, and clinker calcination stages. The installation of dust monitors in these stages can effectively control and reduce dust pollution in the surrounding environment.
2. Environmental quality monitoring
Dust monitors are widely deployed at environmental monitoring stations to assess and manage air quality. These devices continuously monitor suspended particulate matter (PM10 and PM2.5) in the air and provide accurate data support for environmental protection departments to develop appropriate air quality improvement measures.

- Urban air quality monitoring
Air quality monitoring stations in cities utilize dust monitors to track and record dust concentrations, and this data is used in public health early warning systems and environmental policy development.
- Special area surveillance
Dust monitoring is especially important in special areas such as mines and construction sites. Dust in these areas may rise dramatically due to increased operational activities, and the use of CEMS dust monitors allows for timely adjustments to operational schedules and reduces the impact on the surrounding environment.
3. Indoor air quality assessment
In places such as hospitals, schools, offices, and public buildings, indoor air quality directly affects people’s health and work efficiency. Dust monitors are used in these environments to help managers assess and improve indoor air quality.

- Medical environment
In critical areas such as operating rooms and intensive care units, air quality needs to be strictly controlled. Dust monitors can monitor airborne particles in real-time to ensure that the standards of the healthcare environment are met.
- Office and educational institutions
Offices and schools are crowded places where airborne dust is associated with several respiratory diseases. Monitoring dust concentrations in these environments can help to improve indoor air quality through appropriate ventilation and cleaning measures.
4. Research and development
Dust monitors also play an important role in the field of scientific research and technology development. By monitoring changes in dust concentrations in different environments and conditions, researchers can better understand the impact of dust on the environment and health, leading to the development of new abatement technologies and improvements in existing monitoring methods.
- Environmental scientific research
Environmental scientists use dust monitors to study the sources and pathways of air pollution and its impact on ecosystems as a basis for developing more effective environmental protection strategies.
- New technology development
Technology developers use dust monitoring data to design and test new air purification and dust control equipment designed to improve the environmental friendliness and economic efficiency of industrial production.
Through these applications, CEMS dust monitors not only play a key role in the industrial and environmental fields, but are also valuable in improving public health, promoting scientific research, and fostering technological innovation. With the advancement of monitoring technology and the strengthening of environmental regulations, the applications of dust monitors will be further expanded and their contribution to social development and environmental protection will become more significant.
How to Do Maintenance Work on CEMS Dust Monitors
Proper maintenance of CEMS dust monitors is key to ensuring their long-term stable operation and data accuracy. Regular and proper maintenance not only extends the life of the equipment but also reduces the risk of sudden breakdowns and ensures the continuity and reliability of the monitoring data. Below are a few important steps for performing CEMS dust monitor maintenance:
1. Routine inspection and cleaning
Surface Cleaning: Periodically clean the exterior of the instrument with a soft cloth or appropriate cleaner to avoid dust accumulation affecting the performance of the equipment.
Sensor Cleaning: The dust sensor is the most critical part of the monitor and should be cleaned according to the manufacturer’s instruction manual. Some sensors may require the use of specific cleaners or tools to remove accumulated dust and contaminants.
Vents and filters: Check and clean the air inlet and outlet ports to make sure they are not clogged. Replace or clean air filters regularly to prevent dust and other particles from entering the interior of the instrument.
2. Calibration and performance verification
Periodic calibration: Calibration is performed at regular intervals based on the frequency of use of the equipment and the manufacturer’s recommendations. Calibration ensures the accuracy of the instrument’s measurements and usually requires the use of a standard known concentration of calibration gas or particulate matter.
Performance verification: Periodic performance tests are performed to check that all operating parameters meet the specified criteria. This includes testing response times, detection limits, and measurement accuracy.
3. Software updates and technical support
Software updates: Regularly check for and install software updates. These updates may contain important performance improvements, new features, and security patches that can help improve the efficiency and data processing capabilities of your device.
Technical Support: Contact the supplier’s technical support team in case of technical problems or operational queries. Maintain good communication about the latest maintenance techniques and industry standards.
4. Records and reports
Maintenance Records: Detailed records of the date, content, and results of each maintenance and calibration operation. These records are important for tracking the historical performance of the equipment and help when troubleshooting is required.
Performance reports: Regularly generate and review performance reports, which should contain equipment operating data, test results and any anomalies. Use this information to assess the overall condition of the equipment and make adjustments or repairs as necessary.
By implementing these maintenance measures, operators of CEMS dust monitors can ensure that the equipment is always performing at its best while minimizing the occurrence of data interruptions or inaccuracies due to equipment failure. Maintenance is not just about taking care of your equipment, it is a necessary step in ensuring that your environmental monitoring data is accurate and reliable.
Q&A
In order to better understand and utilize CEMS dust monitors, here are some Q&A’s on common questions about this equipment that can help users resolve doubts and effectively apply these monitoring tools.
Q1: How does a CEMS dust monitor work?
A1: CEMS dust monitors measure the concentration of dust in the air by means of different monitoring techniques such as optical scattering, electrochemical analysis, or beta-ray absorption. The device collects data continuously and can provide readings of dust concentration to the operator in real-time to help monitor and adjust production processes or environmental control measures.
Q2: What are the factors to consider when choosing a CEMS dust monitor?
A2: The following factors should be considered when selecting a CEMS dust monitor:
Monitoring needs: The selection of the appropriate monitoring technology is based on the purpose of the monitoring and the characteristics of the monitoring object (e.g., dust type and concentration).
Environmental conditions: Consider the effect of the operating environment (e.g., temperature, humidity, gas background, etc.) on the performance of the equipment.
Accuracy and Measurement Range: Select a device that meets the required measurement accuracy and range.
Economical: Consider the acquisition cost of the equipment, the operation and maintenance costs, and possible calibration costs.
Q3: What is included in the maintenance of a CEMS dust monitor?
A3: Maintaining a CEMS dust monitor typically involves regular calibration, cleaning and software updates. Calibration is key to ensuring data accuracy and usually needs to be done according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Cleaning sensors and changing filters prevents dust buildup and equipment deterioration. Software updates ensure that the device is running the latest monitoring programs and algorithms.
Q4: How to solve the common faults of the CEMS dust monitor?
A4: When confronted with a device failure, you should first check that the power supply and connections to the device are normal. Next, check to see if the sensor has been contaminated by dust or other material buildup. If the problem persists, refer to the user manual for troubleshooting or contact technical support for assistance. Regular professional maintenance and inspection is also an effective way to prevent malfunctions.
Q5: Can CEMS dust monitors be integrated with other environmental monitoring systems?
A5: Yes, CEMS dust monitors are usually designed with good compatibility and interfaces to integrate with other environmental monitoring systems. This allows for more comprehensive data collection and analysis, helping users to better understand and control environmental conditions. Integration is usually achieved through software platforms that can collect and analyze data from different monitoring devices.
Conclusion
CEMS dust monitor is an indispensable part of modern environmental monitoring systems. Through a correct understanding of the principle, precise selection guidance, and practical application demonstration, we can better utilize these advanced equipment to provide strong technical support for environmental protection and industrial production safety. Through continuous technology updates and application optimization, dust monitoring in the future will be more efficient and precise, creating a cleaner and safer living and working environment for human beings. If you have any questions, please get in touch with us!

























