Industrial processes face challenges in efficiency, regulatory compliance, and environmental sustainability. Monitoring emission gases provides a clear pathway to overcome these challenges, ensuring cleaner, more optimized operations.
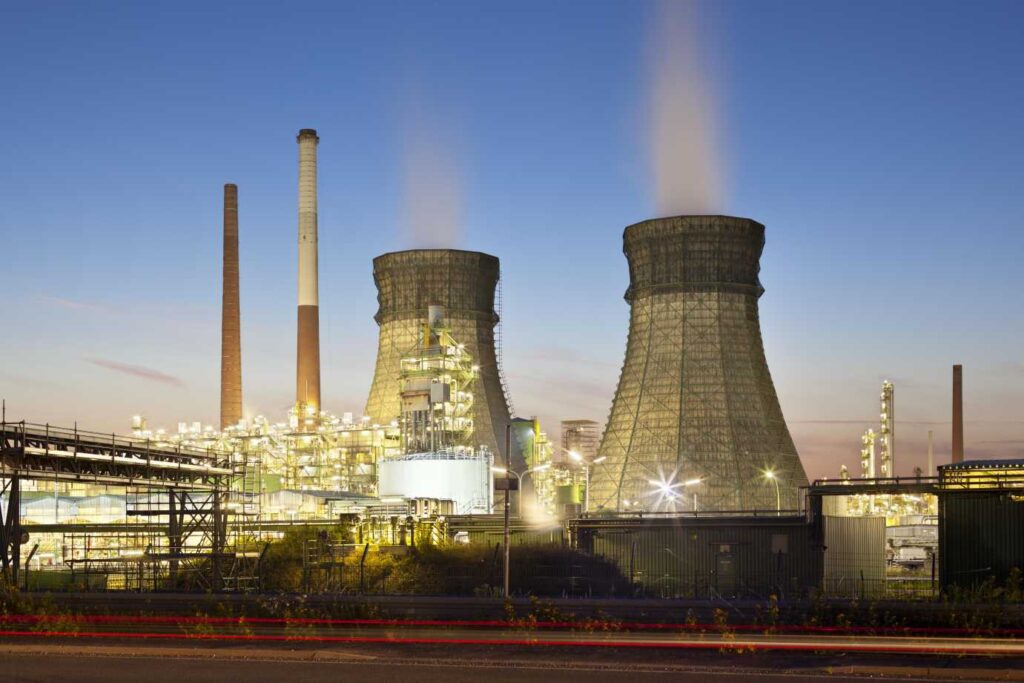

Emission gas monitoring plays a critical role in improving industrial efficiency by identifying inefficiencies, ensuring regulatory compliance, and reducing environmental impact. This enables industries to enhance operations, minimize waste, and align with sustainability goals.
Effective emission gas monitoring is not just about meeting regulations; it’s a tool for businesses to innovate and refine processes. This article explores the importance of emission monitoring, the tools involved, and how the data drives operational improvements.
Why Is Emission Gas Monitoring Critical for Industrial Optimization?
Without clear data on emissions, industrial processes face inefficiencies, regulatory risks, and environmental harm. Emission gas monitoring provides actionable insights to overcome these challenges.

Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
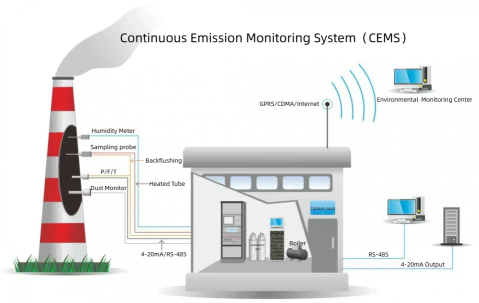
Industries worldwide are subject to stringent environmental regulations, requiring them to control emissions of harmful gases like CO₂, NOx, and SOx. Non-compliance can lead to significant penalties, operational restrictions, or even legal actions. Emission gas monitoring systems (e.g., Continuous Emission Monitoring Systems, or CEMS) allow real-time tracking and reporting, ensuring businesses stay within permissible limits.
For example, in power plants, monitoring helps maintain emissions below government-mandated thresholds. This not only avoids fines but also builds trust with regulators and stakeholders by demonstrating proactive environmental responsibility.
Reducing Operational Inefficiencies
Inefficient processes often result in excessive emissions, indicating wasted resources. Emission monitoring identifies these inefficiencies, such as incomplete combustion in boilers or leaks in pipelines. With real-time data, operators can make adjustments to improve fuel-to-air ratios, fix leaks, or calibrate equipment for better performance.
Consider a chemical manufacturing plant: if VOC (volatile organic compound) emissions are higher than expected, monitoring data can pinpoint inefficiencies in production. Addressing these issues enhances output quality, reduces waste, and conserves energy, ultimately lowering costs.
Driving Sustainability Goals
Many industries are shifting toward sustainable practices to reduce their environmental footprint. Emission monitoring provides the baseline data needed to assess progress toward these goals. By measuring pollutants, companies can implement greener technologies, optimize energy use, and transition to cleaner fuels.
For instance, a cement plant using alternative fuels can rely on emission gas monitoring to ensure that the transition does not increase harmful byproducts. This data-driven approach ensures sustainability efforts align with operational efficiency.
Enhancing Decision-Making Through Data
Emission monitoring equips industries with critical data for decision-making. Instead of relying on estimates, operators can make precise adjustments based on real-time insights. For example, data showing high NOx levels in a power plant might prompt adjustments in burner configurations, reducing emissions and improving energy efficiency.
Long-term data trends also support predictive maintenance, reducing downtime. Monitoring can reveal patterns of increased emissions linked to equipment wear, allowing timely repairs or replacements before a failure occurs.
Application of ESE Gas Analyzer in Emission Gas Monitoring
Advanced tools like infrared gas analyzers and portable devices provide accurate and timely data, ensuring seamless integration into industrial workflows.

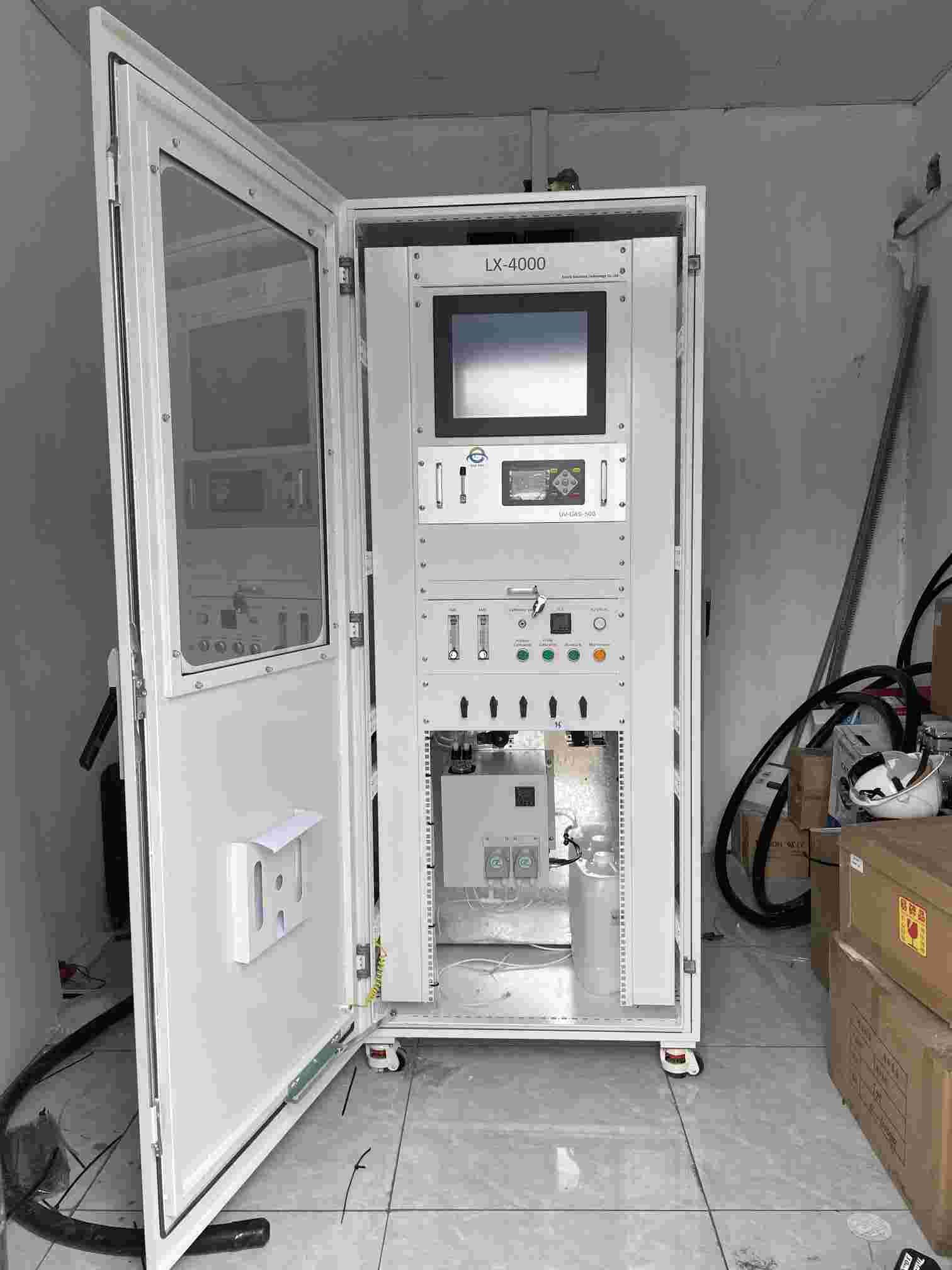
The Continuous Emission Monitoring System (CEMS) EM-GAS-500 developed and produced by ESE is to monitor the total air pollutant emissions from stationary sources, mainly used for industrial boilers, power plant boilers, industrial furnaces emissions monitoring, SO2, NO, NO2, O2, CO, CO2,
HCL, HF, H2O, etc dynamic continuous monitoring, simultaneous to measure gas flow, oxygen content, gas pressure, gas temperature, gas humidity, etc, automatically recording the total pollutant emissions volume and emission time.

Industries rely on various technologies for emission monitoring. Fixed continuous emissions monitoring systems (CEMS) are ideal for large-scale operations, offering precise and consistent data. Portable gas analyzers are suitable for on-the-go assessments, providing flexibility for small-scale or temporary setups. These tools utilize advanced techniques like infrared spectroscopy or electrochemical sensing to detect gases like CO2, NOx, and SOx, ensuring accurate and actionable insights.
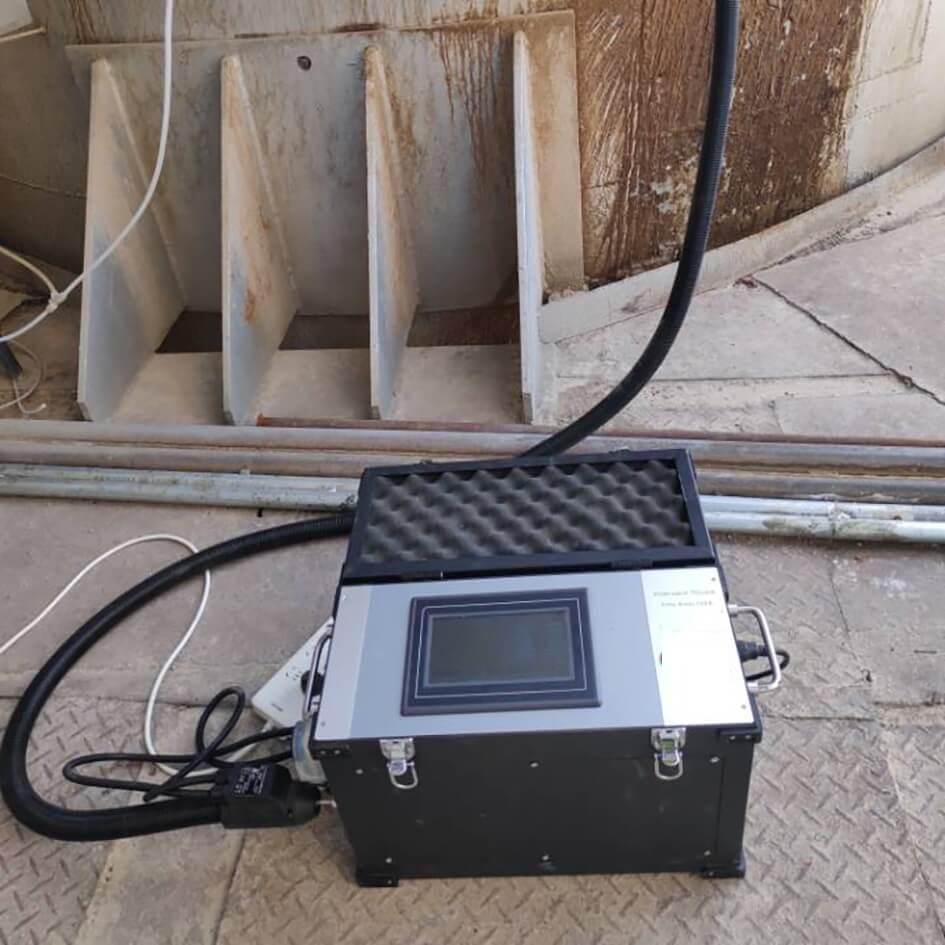

How Can Emission Monitoring Data Drive Industrial Process Optimization?
Data-driven decisions lead to smarter processes. Emission monitoring provides actionable insights to enhance efficiency and reduce waste.
Emission monitoring data highlights inefficiencies in industrial processes. For instance, combustion analysis can identify if boilers or furnaces are operating below optimal levels, allowing operators to tweak fuel-to-air ratios. Similarly, monitoring VOCs (volatile organic compounds) helps refine chemical manufacturing processes, reducing waste. By continuously analyzing emissions, industries can make incremental improvements that result in significant cost savings and better performance.
How Does Emission Monitoring Enable Economic and Environmental Benefits?
Efficient emission monitoring aligns industrial goals with environmental responsibility, enabling cost reductions, regulatory compliance, and a competitive advantage.

Reducing Operational Costs
Monitoring emissions helps industries optimize resource use and reduce waste, directly lowering operational expenses. For example, data from emission monitoring can identify inefficiencies in combustion processes, allowing adjustments to fuel-to-air ratios that enhance energy efficiency. This minimizes fuel consumption, reduces costs, and improves productivity.
In sectors like manufacturing or power generation, emission gas monitoring can reveal excessive energy use or gas leaks. Addressing these issues leads to immediate savings, with industries reporting fuel cost reductions of up to 15% through enhanced combustion efficiency and better equipment calibration.
Minimizing Regulatory Fines
Industries are bound by stringent environmental regulations that penalize excess emissions of harmful gases like CO₂, SO₂, and NOx. Non-compliance can lead to fines, costly shutdowns, or reputational damage. Emission monitoring systems (such as Continuous Emission Monitoring Systems, or CEMS) ensure real-time compliance by providing precise data and alerting operators before thresholds are breached.
For instance, a steel plant using emission monitoring technology was able to detect and mitigate pollutant peaks, avoiding fines and maintaining smooth operations. By proactively managing emissions, companies can save millions in potential penalties while ensuring long-term viability.
Supporting Sustainable Practices
Emission monitoring is a cornerstone of sustainability initiatives. It enables industries to measure and manage their environmental impact, helping them meet sustainability targets such as carbon neutrality or net-zero goals. This not only benefits the planet but also enhances corporate reputation among environmentally conscious consumers and investors.
Take the cement industry, a major contributor to CO₂ emissions. By integrating emission monitoring, companies can assess the efficiency of alternative fuels like biomass or waste-derived materials. Such practices not only lower emissions but also reduce dependency on fossil fuels, offering long-term cost and environmental benefits.
Enhancing Competitive Advantage
Businesses leveraging emission monitoring gain a competitive edge by aligning with market demands for greener operations. Companies showcasing reduced emissions are more likely to attract partnerships, secure government incentives, and win over eco-conscious customers.
For example, a food processing plant that optimizes its emissions through advanced monitoring might qualify for government tax credits or carbon trading benefits. These financial advantages position the company as both cost-efficient and environmentally responsible, making it a preferred partner in its industry.
Enabling Circular Economy Practices
Emission monitoring also plays a role in supporting circular economy principles by reducing waste and improving resource recovery. For example, refineries can use emission data to optimize processes that capture and reuse gases like CO₂. Captured CO₂ can then be repurposed for industrial applications such as carbonation or enhanced oil recovery, turning emissions into valuable resources.
Conclusion
Emission gas monitoring is more than a compliance tool; it’s a strategic approach to optimizing industrial processes. By leveraging cutting-edge technologies and actionable data, industries can achieve remarkable efficiency, align with environmental standards, and secure long-term profitability. Investing in emission monitoring is not just a regulatory necessity but a step toward a more sustainable and efficient future.
If you have any questions, don’t hesitate to contact us; we will respond as soon as possible!