I. Origin of CEMS
CEMS” is the abbreviation of Continuous Emission Monitoring System, which refers to a device that continuously monitors the concentration and total amount of gaseous pollutants and particulate matter emitted by air pollution sources and transmits the information to the competent authorities in real time, and is called “automatic flue gas monitoring system”, also known as “continuous flue gas emission monitoring system” or “flue gas online monitoring system”. It is called “Flue Gas Automatic Monitoring System”, also known as “Flue Gas Emission Continuous Monitoring System” or “Flue Gas Online Monitoring System”.
Conventional flue gas CEMS is mainly used in electric power, coking, cement, petrochemical, chemical, iron and steel industries, etc. According to the different sampling methods, conventional flue gas CEMS can be divided into three categories according to the measurement method: extractive monitoring system, on-site monitoring system and telemetry system.
II. Principle of operation of the CEMS system
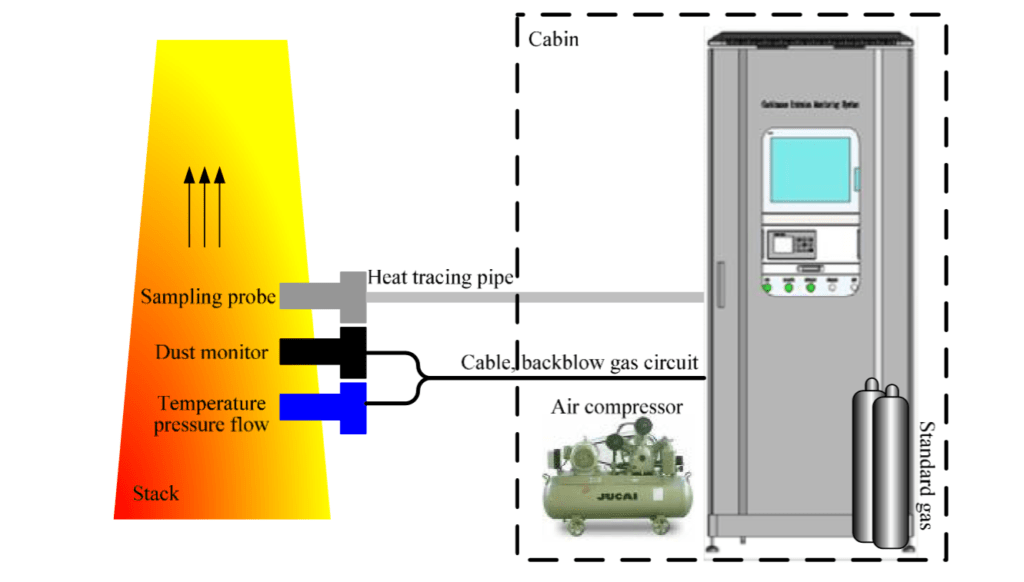
The gas in the flue is taken out by the heating extraction method (extraction condensation method) and transported to the pre-treatment unit, which sends the gas in the flue to the analyzing instrument after pre-treatment. Through the online gas analysis instrument (flue gas analyzer) to the flue gas in a variety of pollutants for continuous monitoring, the measured data will be displayed on the instrument, and finally through the digital mining instrument or VPN will monitor the data real-time transmission to the environmental protection monitoring network.

III. Precautions in the CEMS maintenance process
Heating and cooling units
Heating device and refrigeration device is an important equipment to protect the flue gas analyzer, which is the key object of attention in daily inspection and maintenance. Heating device temperature is generally controlled at about 130 ℃, in the absence of heating, moisture in the flue gas into the analyzer, resulting in filter blockage, analyzer damage, etc., while the formation of acid mist in the pipeline, which directly affects the measurement results; refrigeration device temperature is generally controlled at about 4 ℃, if the condenser temperature can only reach 6 ℃ and above the need for maintenance or replacement.
Peristaltic pump inspection
The peristaltic pump is used to drain water from the condensate cylinder of the chiller and to seal the sampling gas line. If the peristaltic pump is left inoperative for an extended period of time, condensate can enter the sampling pump and analyzer and cause damage to the equipment.
Blowback System Inspection
When checking the blowback system, check that the pressure of the blowback air source is within the normal range. For manual blowback, the system is switched to the maintenance state for blowback. For automatic blowback, the blowback time is set in the PLC control system and the measurement data is maintained so that no abnormal control system adjustment or equipment damage occurs due to blowback.
Periodic calibration of flue gas analyzers
The flue gas analyzer needs to be calibrated periodically for zero and range.CEMS monitoring stations are equipped with standard gases of high, medium and low concentrations of each measured medium factor and high purity nitrogen, and the calibration is completed by passing in another concentration of standard gas for comparison. The calibration cycle is at least once every six months. Automatic zero calibration according to the actual situation of the field equipment is set to 8-12 hours to automatically carry out a zero calibration, to avoid zero drift, to ensure the accuracy of analysis and measurement.
Consistency of parameter ranges
In the analyzer and standard gas selection should be noted that the analyzer range should be based on the flue gas measured in the media factor design concentration to choose, the range should not exceed the permissible limit value of the pollution source emissions two to three times, to ensure that the flue gas analyzer to measure the accuracy of the data; the selection of the standard gas should be based on the range of analyzers and the measured media factor is usually the usual concentration of the selection, should not be too high or too low (80% -100% or less of the range). (within 80%-100% of the range). The range settings of the upper computer, PLC and data acquisition instrument should be consistent.
IV. the operation of the important data SO2 detection is not allowed to solve the problem
What if the data is high?
There are two possibilities for high data: either the analyzer needs to be recalibrated, or there may be a buildup of thicker gases or liquids in the analytical line.
(1) Judgment method: firstly, isolate the sample gas and use the analyzer to measure the standard gas directly. If the measurement result is high, it belongs to the first situation, and recalibration can be done; if the measurement result is normal, it should belong to the second situation, and it is necessary to check the analyzing pipeline.
(2) Inspection method: The tubing should be inspected from the inlet of the analyzer to the inlet of the sampling probe. The general pipes are transparent corrosion-resistant pipes, and scale buildup is easy to see. More troublesome is the float flowmeter, sampling pumps, chillers, filters, sample gas valves, tracer lines, sampling probe scale is less easy to judge.
After pre-processing, it is fed into the analyzing instrument. Continuous monitoring of various pollutants in the flue gas is carried out by on-line gas analyzing instrument (flue gas analyzer), the measured data is displayed on the instrument, and finally the monitoring data is transmitted to the environmental protection monitoring network in real time through the digital collector or VPN.
What if the SO2 is low?
Low SO2 data is often accompanied by low data from the analyzer. There are two possibilities for low data: either the analyzer needs to be recalibrated or there is a leak in the sampling line.
(1) Confirmation method: add standard gas to the inlet of the analyzer to see if the measurement result is the same as the content of the standard gas. If it is the same, the sampling line is leaking; if it is different, recalibrate.
(2) Sampling line leaks in two major steps: confirming whether the leak is inside or outside the cabinet.
(3) judgment method: disconnect the sample gas valve inlet, blocked by hand, at this time the analyzer panel on the flow meter and float flow meter knowledge should be to zero. To zero is no problem inside the cabinet, less than zero is the internal problems of the cabinet.
What if the float meter flow rate is low?
Flow rate to zero is the most likely peristaltic pump into the ash. If the ash into the peristaltic pump, the peristaltic pump output is reduced. Peristaltic pump outlet jet weak, peristaltic pump inlet suction reduced. Open the cleaning.
It is also necessary to check the flow generation opening, check the piping between the sampling pump to the analyzer, equipment (including filters, chillers, peristaltic pumps, flow valves, float flow meters), to see if there are no leaks.
There is also the possibility of clogging the analyzer outlet. No matter how high the peristaltic pump outlet pressure is, if the analyzer outlet is clogged, the flow rate will not go up. Of course, this is less likely and can be checked last.
What if the O₂ measurement is not accurate?
Oxygen is of interest because, on the one hand, it is an important parameter for data conversion and, on the other hand, it can be used to determine whether the data are falsified.
If it is a three-component analyzer, the fault judgment method is the same as above. If not, the judgment steps are as follows:
(1) need to recalibrate, zirconia data will drift over time, recalibration will be accurate
(2) If the data is high, there may be leakage, which consists of two cases: system leakage and measurement point leakage. System leakage is the whole desulfurization or flue gas pipeline leakage, not easy to check. Measuring point leakage is generally caused by the flange is not fixed tightly, tighten can be.
V. the operation of the process of dust detection is not allowed to solve the problem
What if the optical measurement method is low on dust?
Most of the domestic dust measurement equipment belongs to the optical measurement, optical measurement method of low dust data is relatively rare. Generally is a signal processing problem, debugging signal processing, or simply recalibration can be.
What if the data from the optical measurement method is high?
The most likely cause is the lens clogging with dust. The transmitting and receiving lenses should be cleaned regularly. It is also possible that there is a signal processing problem, and after cleaning, if there are still problems with the data, it can be recalibrated.
VI. Management requirements during operation
Daily inspection CEMS
The operation and maintenance unit shall formulate the inspection protocol according to the HJ 75-2017 standard and the relevant requirements in the instructions for the use of the instrument, and carry out the daily inspection work and make records in strict accordance with the protocol. Daily inspection records should include inspection items, inspection date, the operational status of the inspected items, etc. Each inspection should be recorded and archived. Smoke online monitoring system daily inspection interval of no more than 7 days.
Daily Maintenance
According to the requirements of the flue gas online monitoring system manual on the system maintenance content, maintenance cycle or consumables replacement cycle, etc. to make clear provisions for each maintenance should be recorded and archived. Each time the spare parts or materials replacement, replacement of spare parts or materials, such as the name, specifications, quantity should be recorded and filed. If a licensed standard substance or standard sample is replaced, the source, expiration date and concentration of the new standard substance or standard sample should also be recorded. For the faults or problems found during daily inspection or maintenance, the system management and maintenance personnel should deal with them in time and record them.
Calibration and Verification of CEMS
Periodic calibrations should be.
- (1) Particulate matter CEMS and gaseous pollutant CEMS with auto-calibration function automatically calibrate the zero point and range of the instrument at least once every 24 hours, and test and record the zero point drift and range drift at the same time;
- (2) Particulate matter CEMS without automatic calibration should calibrate the zero point and range of the instrument at least once every 15 days, and test and record the zero point drift and range drift at the same time;
- (3) Direct measurement CEMS for gaseous pollutants without automatic calibration shall calibrate the zero point and range of the instrument at least once every 15 days, and shall test and record the zero point drift and range drift at the same time;
- (4) Extractable gaseous pollutant CEMS without automatic calibration shall be calibrated at least once every 7 days with simultaneous testing of the zero and range of the instrument and recording of zero drift and range drift;
- (5) The extractable gaseous pollutant CEMS shall be calibrated system-wide at least once every three months, requiring that the zero gas and the standard gas be issued from the monitoring station, and that the path through which the sample gas passes through the end of the sampling probes and the sample gases (which shall include the sampling pipeline, the filter scrubber, the regulator, the analyzing instrument, etc.) be consistent with the detection of the zero and the range drift, the value error, and the response time of the system;
- (6) Zero calibration shall be performed at least once every 24 hours for flow rate CEMS with automatic calibration function and at least once every 30 d for flow rate CEMS without automatic calibration function.