With the continuous development of industrial technology, liquefaction plants play a vital role in modern industry. Liquefaction plants are mainly used to convert gases or gas mixtures into liquid form for transportation, storage, and application. In the liquefaction process, gas analyzers play an important role as a key monitoring device. In this paper, we will discuss the application of gas analyzers in liquefaction plants and their importance.

The Basic Process of a Liquefaction Plant
To facilitate transportation and storage, natural gas is cooled and compressed into a liquid state, known as liquefied natural gas (LNG). Natural gas has a volume ratio of 600:1 between gas and liquid, making it very easy to store and transport. Natural gas is cooled and compressed into a liquid state known as liquefied natural gas (LNG). Before the liquefaction process, the natural gas is purified to remove impurities such as total sulfur and benzene.
Quality norms for sulfur-containing finished natural gas are becoming more stringent, and tariffs are being introduced accordingly. At the same time, natural gas suppliers are required to treat the gas before liquefaction to prevent corrosion of the liquefaction equipment, and they are required to follow transportation pipeline protocols. As a result, the natural gas industry is in need of online analyzers that can measure multiple components simultaneously with fast response times.
Benzene, toluene, and xylene (BTEX) are present in the natural gas before liquefaction, and these substances can freeze solid at the low temperatures of the liquefaction process, causing clogging of the liquefaction equipment and resulting in shutdowns of the entire facility for maintenance. To prevent this from happening, the manufacturer removes the benzene before the liquefaction process and installs an online analyzer to monitor the benzene concentration before liquefaction loading to ensure that the benzene has been removed and that the downstream equipment is functioning properly.
The basic process of a liquefaction plant is described in detail below:
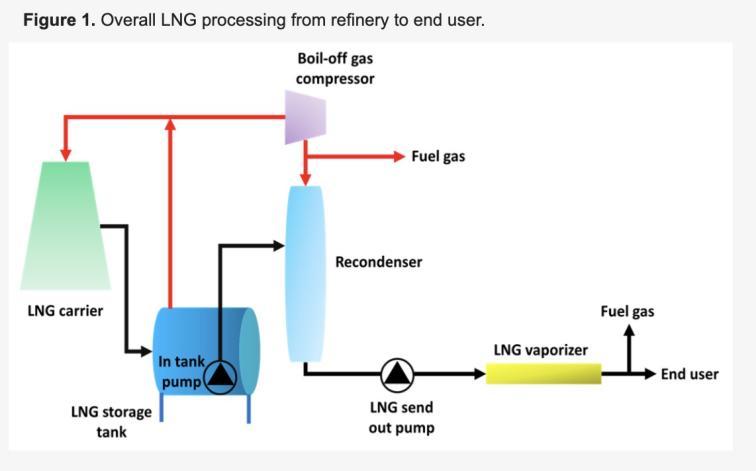
1. Gas cleaning and pre-treatment
In liquefaction plants, the source of gas can be natural gas fields, oxygen and nitrogen gases extracted from the air, or other industrial gases. These raw gases usually contain various impurities such as moisture, sulfides, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen. These impurities affect the liquefaction efficiency of the gas and the quality of the product, so the gas first needs to be purified and pre-treated.
The purification process includes the following steps:
- De-watering: Removal of water from the gas using a desiccant or condenser to avoid the formation of ice or water condensation during subsequent compression and cooling.
- Sulfur removal treatment: Remove sulfide from gas by adsorbent or chemical reaction to prevent corrosion of equipment and products by harmful substances such as hydrogen sulfide.
- Carbon dioxide removal treatment: Use methods such as adsorbent or membrane separation to reduce the carbon dioxide content in the gas to meet the requirements of the subsequent liquefaction process.
2. Compression
The purified gas enters the compression stage, where the pressure of the gas is increased by the compressor to make the gas molecules denser, thus facilitating the subsequent liquefaction process. The compression process significantly increases the temperature and pressure of the gas, creating conditions for subsequent cooling and liquefaction.
A key step in the compression process:
Compressors: Centrifugal, screw, or reciprocating compressors are used to compress the gas to the required process pressure, usually between tens and hundreds of megapascals (MPa).
3. Cooling
The compressed gas enters the cooling unit, where cooling reduces the temperature of the gas below the liquefaction temperature, thus transforming the gas into a liquid state. The cooling process requires an efficient cooling system and a cooling medium, usually liquid nitrogen, liquid hydrogen, or a refrigerant.
The main ways of the cooling process include:
- Conventional cooling: The gas’s temperature is lowered by heat exchangers and coolers, causing it to condense into a liquid gradually.
- Expansion Cooling: The use of expansion valves or throttling devices, so that the rapid expansion of high-pressure gases, lowers the temperature and liquefaction.
4. Separation
In liquefaction plants, the liquefaction process is usually accompanied by the separation and purification of gas components. Depending on the nature and needs of the gas, different separation techniques, such as distillation, adsorption, condensation, etc., can be used to separate the target components from the gas and obtain a high-purity liquid product.
Key steps in the separation process:
- Distillation tower: Using the difference in boiling points of different gas components, different components of liquefied gases are separated through the distillation tower.
- Adsorption and Separation: Adsorption of impurities in gases by using adsorbents to purify and separate the gases.
The basic process of a liquefaction plant consists of the key steps of gas purification and pretreatment, compression, cooling, and separation. Each step requires sophisticated equipment and control systems to ensure an efficient, safe, and stable liquefaction process. With the development of technology and process improvement, the production process of a liquefaction plant is constantly evolving and optimized to meet the growing demand for liquefied gases and environmental requirements.
The Role of Gas Analyzers in Liquefaction Plant Processes
Gas analyzers play a vital role in the basic processes of a liquefaction plant, mainly in the gas cleaning and pre-treatment phase, in the control and optimization of the liquefaction process and in the monitoring of product quality. The role of the gas analyzer in each process of the liquefaction plant is described below:

1. Gas cleaning and pre-treatment stage
During the gas purification and pre-treatment stage, gas analyzers are mainly used to monitor and analyze the impurity content in the raw gas to ensure that the gas meets the requirements and standards of the liquefaction process.
- Water analyzer: Used to monitor the moisture content of gases in real time. Moisture affects the subsequent compression and cooling process and may lead to equipment corrosion or reduced liquefaction efficiency.
- Sulfide Analyzer: Detects the concentration of sulfides, such as hydrogen sulfide, in gases. High concentrations of sulfides can cause serious harm to equipment and products.
- Carbon dioxide analyzer: Used to measure the amount of carbon dioxide in a gas. High levels of carbon dioxide can reduce liquefaction efficiency and affect product quality.
These analyzers can detect the impurity content in the gas promptly and help the operator adjust the purification equipment and process parameters to ensure that the gas purification effect meets the requirements.
2. Control and optimization phase of the liquefaction process
During the compression and cooling process, gas analyzers play a role in monitoring and controlling the gas components, helping to optimize the liquefaction process and improve productivity and product quality.
- Component analyzer: Monitor the main components in the gas, such as methane, ethane, etc. According to the real-time analysis results, adjust the operating parameters of the compressor to ensure that the gas meets the requirements for liquefaction.
- Temperature and Pressure Sensors: Used to monitor temperature and pressure changes during the liquefaction process in real time. By analyzing the sensor data, the cooling medium and cooling rate are adjusted to optimize the liquefaction process.
- Safety monitoring instruments: Detecting harmful components and concentrations in gases, such as hydrogen sulfide and oxygen. Timely detection of abnormalities and taking measures to ensure production safety.
These analyzers provide real-time data feedback to help operators adjust and control key parameters in the liquefaction process, ensuring a stable and safe production process.
3. Product quality monitoring phase
The ultimate goal of a liquefaction plant is to produce high-quality liquefied gas products, and gas analyzers play a key role in the product quality monitoring phase.
- Liquid Gas Chromatograph: Used to analyze the content and purity of various components in liquefied gases. Ensure that the products meet the relevant standards and quality requirements.
- Mass Spectrometer: Provides high sensitivity analysis of product components, which can detect trace impurities or impure substances and ensure high purity and quality of products.
- These analytical instruments provide accurate data support during the product quality monitoring stage to ensure stable and reliable quality of liquefied gas products.
Gas analyzers play an important role in various processes in liquefaction plants, from impurity monitoring in the gas purification and pretreatment stages to real-time control and optimization of the liquefaction process, to final monitoring of product quality, all of which provide key data support and technical guarantee for the operation of liquefaction plants. With the continuous progress of science and technology and the development of gas analysis technology, gas analyzers will continue to play an even more important and diversified role in liquefaction plants, providing reliable support for safe, efficient, and environmentally friendly industrial production.
| process stage | The Role of Gas Analyzers | specific application |
| Gas cleaning and pre-treatment stage | Monitoring and analyzing the impurity content in the raw gas to ensure that the purification results meet the requirements | Water analyzer: real-time monitoring of the moisture content in the gas, to prevent the corrosion of water vapor on the equipment sulfurizationSulfide analyzer: detects sulfide concentration and prevents hydrogen sulfide from harming equipment and products.CO2 Analyzer: Measurement of CO2 content to ensure liquefaction efficiency and product quality |
| Control and optimization phase of the liquefaction process | Monitoring of gas components to optimize compression and cooling processes for increased productivity | Liquid Gas Chromatograph: Analyzing the composition of liquefied gases to ensure product quality spectrometer: high sensitivity detection of trace impurities to ensure high purity and reliability of products |
| Product quality monitoring phase | Analyze the components and purity of liquefied gases to ensure that the quality of products meets the standards. | Liquid Gas Chromatograph: Analyzing the composition of liquefied gases to ensure product qualityMass spectrometer: high sensitivity detection of trace impurities to ensure high purity and reliability of products |
Technical applications of gas analyzers
Common gas analyzer technologies used in liquefaction plants include:
Infrared Spectrum Analyzer: For detection of organic gases such as methane, ethane, etc.
Gas Chromatograph: Used to detect impurities in gases such as sulfides, nitrogen, etc.
Mass Spectrometer: Highly sensitive gas component analysis can be realized, and trace gases can also be detected effectively.
Importance and Advantages of Gas Analyzers in Liquefaction Plants
Gas analyzers have importance and many advantages in liquefaction plants and other industrial sectors, where they play a key role in monitoring, controlling, and guaranteeing quality in the production process. The importance and advantages of gas analyzers are explained in detail below:
1. Real-time monitoring and control
The gas analyzer can provide real-time gas composition data and related parameters to help operators understand the changes of gas components and conditions in the production process promptly. Through the monitoring results, operators can adjust production parameters and optimize the production process to ensure product quality and production efficiency.
2. Ensuring product quality
In liquefaction plants, gas analyzers can accurately analyze gas samples to ensure that the components and purity of liquefied products meet the requirements. Through timely detection and analysis, it can avoid the quality of the product decreasing due to impurities or unqualified components, and improve the qualification rate of the product and market competitiveness.
3. Environmental monitoring and protection
Gas analyzers can not only monitor gas components in the production process but also detect the concentration of harmful gases, such as hydrogen sulfide and ammonia. Through timely detection and monitoring, gas leakage and pollution can be prevented and the health of the environment and ecosystem can be protected.
4. Improving productivity
Real-time monitoring of the production process and data feedback through gas analyzers can help optimize the production process and improve productivity and energy efficiency. Accurate data analysis helps to reduce energy consumption and production costs, improving overall production efficiency.
5. Safety and security
Gas analyzers can monitor and identify dangerous gases and potential risks in the production process, such as high concentrations of toxic or flammable gases. Timely detection and treatment of these risk factors help to safeguard the production site and prevent accidents.
6. Advanced technology, precision and reliability
Modern gas analyzers adopt advanced sensing and data processing technologies with high accuracy, sensitivity, and reliability. They are capable of accurately analyzing gas composition and characteristics to cope with complex industrial environments and variable production conditions.
7. Automation control and integration
Some of the gas analyzers can be integrated with automated control systems to realize automated monitoring and control of the production process. This integration makes production management more intelligent and efficient and improves the overall production level and management level of the plant.
In summary, the gas analyzer has an important position and multiple advantages in liquefaction plants. It can not only provide accurate gas analysis data to ensure product quality and production safety but also improve production efficiency and environmental protection. With the continuous progress of technology and the expansion of application scope, gas analyzers will play an increasingly important and extensive role in industrial production, providing strong support for the sustainable development of the plant and enhancing competitiveness.
Q&A
1. What is a gas analyzer? What is its role in a liquefaction plant?
A gas analyzer is a piece of instrumentation used to analyze and monitor the composition, concentration and properties of gases. In liquefaction plants, the role of the gas analyzer is to ensure the stability and effectiveness of the gas purification, compression, cooling and separation processes, as well as to monitor and control the quality and safety of the liquefied product.
2. In which processes of a liquefaction plant do gas analyzers play a key role?
Gas analyzers play an important role in key processes in liquefaction plants, including:
Gas purification and pre-treatment stage: monitoring the impurity content of the raw gas to ensure that the gas meets the liquefaction requirements.
Compression and cooling process: real-time monitoring of gas components and conditions to optimize the liquefaction process.
Product quality monitoring phase: analyzing the composition and purity of liquefied products to ensure that product quality meets standards.
3. How do gas analyzers ensure product quality in liquefaction plants?
By monitoring and analyzing the composition and characteristics of liquefied gas in real time, the gas analyzer can detect and correct abnormalities in the production process in a timely manner, ensure that the components and purity of liquefied products meet the requirements, and ensure that the quality of products is stable and reliable.
4. What are the advantages of a gas analyzer?
The gas analyzer offers the following advantages:
Real-time monitoring: Provides instant gas analysis data to help adjust production parameters in a timely manner.
High precision: High precision and high sensitivity analyzing ability to ensure accurate and reliable data.
Environmental protection: monitoring the concentration of harmful gases to prevent pollution and environmental impacts.
Safety and security: timely detection of dangerous gases and abnormalities to ensure production safety.
Improve efficiency: Optimize production processes to improve productivity and energy efficiency.
5. What are the technology and trends in gas analyzers?
The technology of gas analyzers continues to evolve, tending towards intelligence, portability, and multifunctionality. Future directions include higher data processing capabilities, wider application areas, greater environmental adaptability, and deeper integration with industrial internet and artificial intelligence technologies to bring more innovation and improvement to industrial production.
Conclusion
To sum up, a gas analyzer is an indispensable key equipment in a liquefaction plant, which guarantees the stability, efficiency, and safety of the liquefaction process through its application in gas component analysis, production control, and safety monitoring. With the continuous development of science and technology, the application of gas analyzers will be further improved and popularized, which will bring more innovation and improvement space for the liquefaction process.more information visit www.esegas.com

























