
Waste incineration plants play a crucial role in managing municipal and industrial waste, transforming it into energy and reducing landfill use. However, this process emits various pollutants. These pollutants pose significant environmental and health risks, necessitating stringent monitoring to ensure compliance with environmental regulations and to protect public health.
Traditional emission monitoring methods often struggle to provide real-time, multi-component analysis. They may require multiple analyzers for different gases, leading to increased complexity and maintenance. Additionally, some methods have slower response times, hindering prompt corrective actions during emission spikes. These limitations can result in compliance risks and operational inefficiencies.
Enter Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) gas analyzers. FTIR technology enables simultaneous detection of multiple gas components in real-time, offering high sensitivity and specificity. FTIR gas analyzers address the shortcomings of traditional monitoring methods by delivering comprehensive, real-time analysis of multiple pollutants. Their integration into waste incineration plants is a proactive step towards improved environmental stewardship and operational excellence.
What Are the Key Emissions from Waste Incineration Plants and Why Do They Matter?

Waste incineration plants are designed to convert waste into energy, but this process inevitably releases a range of emissions into the atmosphere.
Primary Emissions: The Immediate Byproducts of Combustion
Primary emissions are pollutants released directly during the combustion process. They include:
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): A colorless, odorless gas produced by incomplete combustion. It poses serious health risks, including headaches and dizziness, and contributes to air pollution.
- Nitrogen Oxides (NOₓ): These gases, primarily nitrogen dioxide (NO₂) and nitric oxide (NO), are formed during high-temperature combustion. They play a significant role in the formation of smog and acid rain, impacting both human health and the environment.
- Sulfur Dioxide (SO₂): Generated from the combustion of sulfur-containing materials, such as certain plastics and textiles. SO₂ is a precursor to acid rain and can cause respiratory problems.
- Particulate Matter (PM): Tiny particles or droplets released during combustion. These particles can penetrate deep into the lungs, leading to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs): A group of organic chemicals emitted as gases from certain solids or liquids. VOCs can cause short- and long-term adverse health effects and contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone.
- Hydrogen Chloride (HCl): HCL emerges when plastics like PVC burn. This gas doesn’t just vanish into thin air. Instead, it reacts with moisture, forming hydrochloric acid. Over time, this acid eats away at machinery, hikes maintenance costs, and harms nearby ecosystems. For humans, prolonged exposure can irritate lungs and worsen respiratory conditions.
- Hydrogen Fluoride (HF): Released from burning fluorinated materials, HF bonds with airborne particles. When inhaled, HF penetrates deep into lung tissue. Chronic exposure links to bone damage and organ toxicity. Worse, it lingers in soil and water, disrupting agriculture.
- Ammonia (NH3): NH3 often sneaks in through nitrogen-rich waste. While modern plants use it to neutralize acidic gases (like HCl and HF), excess NH3 slips out as particulate matter. These tiny particles worsen air quality, contributing to smog and respiratory diseases..
- Dioxins and Furans: Highly toxic compounds formed during the combustion of chlorine-containing materials. They are persistent in the environment and can accumulate in the food chain, posing serious health risks.
These emissions are influenced by factors such as waste composition, combustion temperature, and oxygen availability. Effective combustion control and emission abatement technologies are essential to minimize their release.
Understanding these emissions is the first step toward implementing effective monitoring and control measures, ensuring that waste-to-energy processes are both efficient and environmentally responsible.
Why Are FTIR Gas Analyzers Ideal for Emission Monitoring in Waste Incineration Plants?

FTIR (Fourier Transform Infrared) gas analyzers have become a cornerstone in modern emission monitoring systems, especially within waste incineration plants.
1. Working Principle
FTIR (fourier transform infrared spectroscopy) operates on the principle that gas molecules absorb infrared light at specific wavelengths. Each gas has a unique absorption pattern, or spectral fingerprint. By measuring the absorption across a broad range of infrared frequencies simultaneously, FTIR gas analyzers can identify and quantify multiple gases in a single sample. This capability is particularly advantageous in complex emission streams, where numerous pollutants may be present concurrently.
2. Advantages
Unlike single-gas sensors or time-delayed sampling systems, FTIR gas analyzers can:
- Multi-Gas Detection: FTIR analyzers can simultaneously measure a wide array of gases, including SO2, NOx (NO, NO2), CH4, HCl, HF, CO, CO2, O2, H2O. Other gas components also can be customized as required, such as NH3, SO3, N2O, VOCs, etc. This comprehensive detection is crucial for accurate emission profiling in waste incineration processes.
- Real-Time Monitoring: These systems provide continuous, real-time data, enabling operators to monitor emissions as they occur. This immediacy allows for prompt adjustments to processes, ensuring compliance and minimizing environmental impact.
- High Sensitivity: FTIR analyzers are capable of detecting gases at low concentrations, even at parts-per-billion (ppb) levels. This sensitivity is essential for identifying trace pollutants that could pose significant environmental or health risks.
- Minimal Sample Preparation: Unlike some analytical methods, FTIR requires little to no sample preparation. This reduces operational complexity and enhances the efficiency of monitoring systems.
The ESE-FTIR-100 from ESEGAS exemplifies this power. It combines advanced optical design with robust construction, offering fast response times, low detection limits, and reduced maintenance needs. Its modular interferometer structure allows stable operation, even under tough plant conditions. Moreover, their abilities are to optimize combustion, reduce reagent use, and cut operational costs. In waste incineration, where emissions vary by fuel type and load, the adaptability of FTIR makes it a superior long-term choice.
How Does FTIR Gas Analyzers Compare to Other Gas Monitoring Technologies in Waste Incineration Plants?
Selecting the right gas monitoring technology is crucial for ensuring regulatory compliance and optimizing operations in waste incineration plants. Each technology offers unique advantages and limitations. The following comparative analysis highlights how FTIR stands out among common gas monitoring methods:
| Technology | Strengths | Limitations |
| Non-Dispersive Infrared (NDIR) | -Simple design -Cost-effective for single-gas detection -Stable long-term operation | -Limited to specific gases -Cannot detect gases like hydrogen -Requires periodic calibration |
| Gas Chromatography (GC) | -High precision for individual compounds -Suitable for complex mixtures -Widely used in environmental analysis | -Time-consuming -Requires complex sample handling -Not ideal for real-time monitoring |
| Electrochemical Sensors | -Compact and portable -Low power consumption -Cost-effective for specific gases | -Limited lifespan (6 months to 2 years) -Sensitive to temperature and humidity -Potential for cross-sensitivity |
| Tunable Diode Laser Absorption Spectroscopy (TDLAS) | -High sensitivity and selectivity -Fast response time -Suitable for trace gas analysis | -Limited to specific gases -Complex calibration -Higher initial cost |
| Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) | -Simultaneous multi-gas detection -Real-time monitoring- High sensitivity -Minimal sample preparation | -Higher initial investment -Requires skilled operation |
Among these technologies, FTIR offers a comprehensive solution for waste incineration plants by providing real-time, multi-gas analysis with high sensitivity. While the initial investment and operational expertise required are higher, the benefits in terms of compliance, efficiency, and long-term cost savings make FTIR a compelling choice for modern emission monitoring needs.
For more information on ESEGAS FTIR gas analyzers, visit their blog page: Gas Analyzer Manufacturers
What Are the Best Practices for Implementing FTIR Gas Analyzers in Waste Incineration Plants?

To fully leverage FTIR technology in waste incineration, strategic system selection, skilled operation, and continuous adaptation are key.
Start with choosing the right analyzer. Not all FTIR systems perform equally under harsh industrial conditions. For example, the ESE-FTIR-100 from ESEGAS offers reliable, real-time detection of multiple gases, including SO₂, NOx, CH₄, and VOCs. Its high-temperature tracing, modular design, and low detection limits make it ideal for waste-to-energy plants.
However, even the most advanced analyzer is only as good as the people operating it. Installing FTIR gas analyzers like the ESE-FTIR-100 is just the start. Smart integration makes the real difference:
- Regular calibration keeps your readings precise. High-temperature tracing and a White cell design, as in the ESE-FTIR-100, reduce drift and maintain signal quality.
- System integration turns raw data into actionable intelligence. Linking FTIR outputs to your DCS or SCADA system boosts operational responsiveness.
- Regulatory alignment matters too. Configure detection thresholds and reporting features to meet local and EU air quality standards—automatically.
FTIR isn’t just a sensor; it’s a smart upgrade to your plant’s brain. That’s why investing in comprehensive training is essential. Operators should understand not just how to use the system, but also how to interpret the data, troubleshoot errors, and respond to abnormal readings. Knowledgeable staffs minimize downtime and ensure reliable compliance reporting.
Lastly, no monitoring strategy should remain static. You can’t improve what you don’t measure—so monitor where it counts:
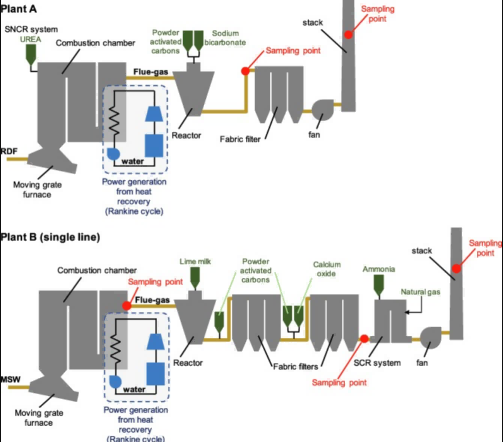
- Stack emissions are the final checkpoint. Real-time FTIR data ensures air quality compliance and protects your permit.
- Combustion chambers reveal how clean your burn is. Poor combustion means more pollutants. FTIR tracks key gases like CO and NOx.
- Flue gas treatment systems need careful oversight. FTIR verifies that scrubbers and filters are doing their job.
These zones offer the clearest insights into plant performance and emissions control. Regulations evolve, technology improves, and plant conditions shift. Review monitoring protocols regularly. Consider adding sensors, updating software, or tweaking integration with control systems. Continuous improvement keeps operations efficient and compliant, while reducing long-term risk.
Together, thoughtful equipment choice, skilled staff, and dynamic practices build a strong foundation for environmental excellence.
Conclusion

FTIR gas analyzers have redefined emission monitoring in waste incineration. Their ability to capture real-time data on multiple gases—from NOx to VOCs—gives operators a powerful edge. By spotting changes instantly, they help facilities meet strict regulations while improving combustion control and reducing pollution. Devices like the ESE-FTIR-100 offer unmatched flexibility, enabling precise measurements even in high-temperature, high-moisture environments. This shift from traditional single-gas monitors to FTIR systems isn’t just technical—it reflects a smarter, cleaner, and more accountable approach to industrial sustainability.
To stay ahead of evolving environmental standards and ensure optimal plant performance, consider upgrading your monitoring system. The ESE-FTIR-100 stands out with its modular design, multi-gas coverage, and low maintenance needs. Whether you’re building a new plant or enhancing an existing one, this solution delivers measurable results.
Learn more or request a consultation at: https://esegas.com/product/ftir-gas-analyzer/Taking this step today means cleaner air, fewer penalties, and a stronger commitment to environmental responsibility tomorrow.
























