Start a journey to understand NDIR-GFC gas sensor technology. Grasp what makes it special. Explore its various facets. By the end, a solid knowledge of this key technology will be yours.
Basic Understanding of Gas Sensors!
Definition And Functions Of A Gas Sensor
In simple terms, a gas sensor is a device that detects and quantifies the presence of gases in an area. A NDIR-GFC (Non-Dispersive Infrared – Gas Filter Correlation) gas sensor, for instance, leverages the principle of infrared absorption to monitor gas concentrations.
Its function involves taking in ambient air, measuring gas density, and outputting the value in appropriate units.
Different Types Of Gas Sensors
– Electrochemical Sensors
Detect specific gases via a chemical reaction that produces an electrical signal. Primarily, it is used in environmental monitoring.
– Metal Oxide Semiconductors
High sensitivity to gas change mostly used to identify harmful gases in the environment.
– Catalytic Sensors
Operate via chemical reaction, primarily used for combustible gas detection.
– Infrared Sensors
Utilize IR radiation to measure gas concentration, like the NDIR-GFC Gas Sensor. It is applicable in hazardous environment monitoring.
– Photoionization Detectors
Use UV light to ionize gas, valuable for detecting volatile organic compounds.
– Ultrasonic Sensors
Employ sound waves to detect gas leaks, used extensively in safety applications.
– Zirconia Sensors
It measure oxygen concentration using zirconium oxide, crucial in automotive emissions control.
– Paramagnetic Sensors
Rely on gas magnetic property for detection, typically used for oxygen detection.
– Thermal Conductivity Sensors
Utilize the thermal properties of gases, helpful in detecting gas mixtures.
– Optical Gas Imaging Sensors
These sensors use imaging techniques for visualizing gas leaks, primarily employed in oil and gas industries.
Working Principle Of A General Gas Sensor
The working principle of a general gas sensor revolves around detecting gas concentration changes. For a NDIR-GFC gas sensor, infrared light travels through the gas chamber.
The gas absorbs the IR light, and the sensor measures the remaining light. The less light detected, the higher the concentration of the gas.
Deep Dive into NDIR Technology!
Detailed Understanding Of NDIR (Non-Dispersive Infrared) Technology
NDIR technology, standing for Non-Dispersive Infrared, makes use of specific light frequencies. Each gas has a unique absorption coefficient at certain infrared frequencies.
The NDIR-GFC Gas Sensor measures this coefficient to detect and identify gases. Essential parts include an infrared source, a gas chamber, and a detector.
Gases inside the chamber absorb light at specific frequencies, which the sensor then measures.
How NDIR Sensors Work?
– Infrared Source
The process starts here, where the sensor emits an infrared light.
– Sample Chamber
The light then passes through a sample chamber. The chamber contains the gas to be measured.
– Wavelength Filter
After the light passes through the sample, it goes through a filter. The filter lets only certain wavelengths through.
– IR Detectors
The filtered light hits the infrared detectors. The detectors measure how much light was absorbed by the gas.
– Gas Absorption
Each gas type absorbs different amounts of light. The more light absorbed, the more of that gas is present.
– Electronic Circuit
The detectors send the data to the electronic circuit. This circuit prepares the data for processing.
– Signal Processing
Algorithms in the sensor process the data. The processing determines the amount of light absorbed by the gas.
– Concentration Calculation
The processed data provides the concentration of the gas. The more light absorbed, the higher the concentration.
– Sensor Calibration
Calibration ensures the sensor provides accurate readings. Calibration is done in a controlled environment before the sensor is used.
– Temperature Compensation
Temperature can affect gas concentration. The sensor accounts for temperature to ensure accurate readings.
Common Applications Of NDIR Sensors
– Environmental Monitoring
NDIR sensors monitor air quality. They detect harmful gases in the environment.
– Industrial Safety
In industries, NDIR sensors ensure worker safety. They detect gas leaks that could be hazardous.
– Medical Diagnostics
In medicine, NDIR sensors detect gases in patient breath. This helps in diagnosing conditions like asthma.
– Automotive Emissions
Cars use NDIR sensors to control and monitor exhaust emissions. They help reduce pollution from vehicles.
– Home Appliances
At home, NDIR sensors detect gas leaks in appliances. This prevents accidents like gas explosions.
– HVAC Systems
Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning systems use NDIR sensors. They ensure optimal and safe operation.
– Mining Operations
In mines, NDIR sensors detect harmful gases. This helps protect miners from hazards like gas leaks.
– Leak Detection
NDIR sensors detect gas leaks in pipelines. Early detection prevents major incidents and damage.
– Fire Detection
In fire detection, NDIR sensors detect smoke and fire gases. Early detection can save lives and property.
Introduction to GFC (Gas Filter Correlation) Technique!

Detailed Explanation Of GFC Technique
Get to know the GFC technique – a key player in the world of gas sensors. The heart of the matter is NDIR-GFC Gas Sensor. This tool’s main task involves measuring gas concentration.
With its NDIR technology, non-dispersive infrared rays pass through the gas. Meanwhile, GFC technique adjusts the wavelength of the infrared rays. Yes, the job is tough.
However, NDIR-GFC handles it with precision. There’s more! This system excels in its filtering method, giving you high-quality results every time. Not forgetting the robustness that sets the device apart.
The Role Of GFC In Improving Gas Sensor Performance
– Enhanced Sensitivity
NDIR-GFC Gas Sensor boosts sensitivity. With greater sensitivity, detection becomes a breeze, even at lower concentrations. Trust, accuracy, and ease make this an industry favorite.
– Reduced Interference
NDIR-GFC limits other gases’ interference. The reduction in false alarms offers improved trust and reliability in measurements.
– Improved Selectivity
The GFC technique provides a bonus – increased selectivity. Specific gas types detected with ease lead to better safety in industries.
– Temperature Compensation
Fluctuations in temperature won’t bother NDIR-GFC. The sensor ensures stable readings despite temperature variations. So, you’ll get reliable data throughout.
– Humidity Impact Minimization
High humidity? No issue for the NDIR-GFC Gas Sensor. Its built-in feature minimizes the impact of moisture, offering reliable gas readings.
– Long-term Stability
Stability is a top feature of NDIR-GFC. The device assures consistent performance over long periods, ensuring confidence in its readings.
– Improved Accuracy
NDIR-GFC offers improved accuracy in gas detection. With precise measurements, trust in data quality grows.
– Response Time Reduction
Quick response times make NDIR-GFC stand out. The device detects changes in gas concentrations in record time, a feature much needed in critical situations.
– Calibration Stability
The NDIR-GFC Gas Sensor holds calibration well. Even with constant use, the device maintains accurate readings, ensuring high-quality data.
– Broad Wavelength Application
The broad wavelength range is another unique feature. It allows the NDIR-GFC Gas Sensor to measure different gas types, increasing its versatility.
Unpacking NDIR-GFC Gas Sensor Technology!
Comprehensive Understanding Of NDIR-GFC Gas Sensor Technology
In the gas detection industry, NDIR-GFC Gas Sensor technology stands out. A Non-Dispersive Infrared Gas Filter Correlation (NDIR-GFC) Gas Sensor uses light to detect gas levels.
Carbon dioxide, methane, and other gases absorb this light. Next, a special lens gathers light. Lastly, an infrared detector measures light. High light absorption signals high gas levels. Hence, gas presence and concentration get detected.
How NDIR-GFC Gas Sensors Work?
NDIR-GFC Gas Sensors work with infrared light. Once turned on, an infrared light source emits light. Then, the light travels through a gas chamber. Gas molecules in the chamber absorb light.
In fact, more gas molecules mean more light absorption. Afterward, a filter blocks certain wavelengths. Only light at specific wavelengths reaches the detector. Consequently, the sensor calculates gas levels based on light absorption.
Unique Features Of NDIR-GFC Gas Sensors
– Low Maintenance
NDIR-GFC Gas Sensors need minimal care. Their sturdy build requires fewer repairs and replacements.
– Long Life Span
Long-lasting sensors offer reliable service for years. In essence, NDIR-GFC Gas Sensors offer superior longevity.
– High Accuracy
These sensors provide precise gas measurements. Their technology minimizes errors for high accuracy readings.
– Wide Range Sensitivity
NDIR-GFC Gas Sensors detect a variety of gases. Moreover, their sensitivity spans a broad range of concentrations.
– Stable Calibration
Calibration stays consistent over time. Therefore, these sensors give dependable results.
– High Reliability
NDIR-GFC Gas Sensors are trusted by industry professionals. Their reliable performance ensures safety.
– Fast Response Time
These sensors respond swiftly to changes in gas levels. Hence, they provide prompt alerts.
– Specificity to Gas
NDIR-GFC Gas Sensors are particular about the gases they detect. Consequently, they offer more specific results.
– Resistant to Poisoning
These sensors resist chemical poisoning. As a result, they continue to work well even in harsh environments.
– Less Affected by Humidity
Humidity has minimal impact on NDIR-GFC Gas Sensors. Therefore, their performance remains consistent in diverse weather conditions.
| Feature | NDIR-GFC Gas Sensors | Electrochemical Sensors | MOS Gas Sensors | PID Gas Sensors | Optical Gas Sensors | Ultrasonic Gas Sensors |
| Maintenance | Low | High | Medium | High | Medium | Low |
| Life Span (years) | 10+ | 3-5 | 5-7 | 2-3 | 8-10 | 10+ |
| Accuracy | High | Medium | High | High | High | Medium |
| Sensitivity Range | Wide | Narrow | Wide | Wide | Narrow | Wide |
| Calibration Stability | Stable | Unstable | Stable | Unstable | Stable | Unstable |
| Reliability | High | Low | Medium | High | Medium | High |
| Response Time (seconds) | <30 | <60 | <30 | <20 | <60 | <30 |
| Specificity to Gas | High | Medium | Low | High | High | Medium |
| Resistance to Poisoning | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Effect of Humidity | Less | More | More | Less | More | Less |
Advantages of NDIR-GFC Technology!
– Greater Sensitivity
NDIR-GFC gas sensor shines in its sensitivity. Detects even minute gas amounts with precision.
– Enhanced Accuracy
High accuracy defines this technology. It reduces errors in measurement significantly.
– Better Stability
Stable measurements form the core of NDIR-GFC. Sensor readings remain constant over time, ensuring consistency.
– Wide Dynamic Range
NDIR-GFC technology displays a wide dynamic range. It measures low and high gas concentrations effectively.
– Resistance to Contaminants
Contaminants pose less threat to NDIR-GFC. The sensor stays efficient in varied environments.
– Long Sensor Life
The life span of NDIR-GFC sensors stands tall. It lasts longer, delivering consistent performance over time.
– Low Power Requirement
Energy efficiency marks NDIR-GFC. The sensor operates at low power, thus saving energy.
– Minimal Maintenance
It requires less maintenance, more convenience. The NDIR-GFC gas sensor requires minimal upkeep.
– High Signal-to-Noise Ratio
NDIR-GFC technology ensures a high signal-to-noise ratio. It keeps useful signals intact while reducing unwanted noise.
– Versatile Gas Detection
Not limited to specific gases. NDIR-GFC sensors detect a broad spectrum of gases.
Comparison between NDIR-GFC and Traditional NDIR Technology!
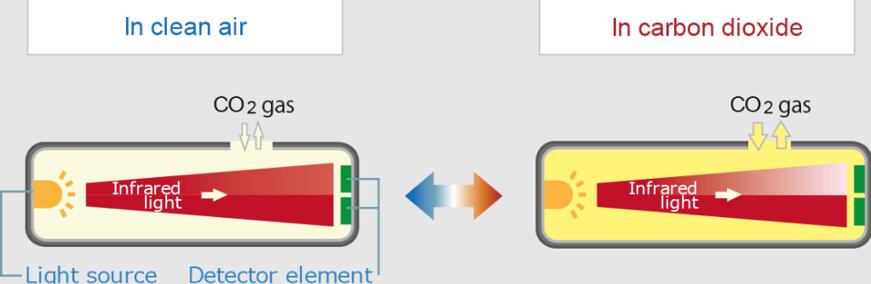
– Sensitivity Levels
NDIR-GFC surpasses traditional NDIR in sensitivity. The former detects even tiny gas concentrations, outdoing the latter.
– Calibration Stability
Stability in calibration is more evident in NDIR-GFC. Traditional NDIR might require more frequent calibration checks.
– Gas Specificity
Both technologies detect a wide range of gases. However, NDIR-GFC might prove more selective, enhancing specificity.
– Resistance to Contaminants
NDIR-GFC shows higher resistance to contaminants. In contrast, traditional NDIR might be more susceptible.
– Maintenance Requirements
NDIR-GFC requires less maintenance compared to traditional NDIR. Thus, reducing upkeep hassles.
– Dynamic Range
NDIR-GFC flaunts a broader dynamic range. Traditional NDIR might not measure extreme gas concentrations as effectively.
– Power Requirements
NDIR-GFC operates at lower power levels than traditional NDIR. Hence, it conserves more energy.
– Response Times
The response times of NDIR-GFC surpass those of traditional NDIR ensuring faster, more efficient gas detection.
– Signal-to-Noise Ratio
NDIR-GFC has a higher signal-to-noise ratio. Traditional NDIR might have more noise interference.
– Cross-sensitivity
Cross-sensitivity is less in NDIR-GFC. Traditional NDIR might react more to gases other than the targeted one.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance of NDIR-GFC Gas Sensors!

Common Issues And How To Solve Them?
Non-dispersive Infrared Gas Filter Correlation (NDIR-GFC) Gas Sensors hold critical functions. Each sensor features two infrared detectors.
One detects gas presence; the other serves as a reference. A problem arises when these detectors give false signals. A faulty sensor gives incorrect gas concentration readings. By replacing the faulty infrared detector, the sensor restores accurate measurements.
When the gas filter experiences wear and tear, sensor performance dwindles. A worn-out filter allows the gas to leak, causing inaccurate readings. In such cases, replace the gas filter promptly.
Moreover, incorrect temperature compensation causes sensor performance issues. Each NDIR-GFC Gas Sensor features a thermistor. The thermistor measures the sensor’s temperature. When temperature readings are incorrect, replace the thermistor.
Maintaining The Performance Of NDIR-GFC Sensors
Sensor performance depends on regular maintenance. All parts of the NDIR-GFC sensor need regular checks. Over time, dust and dirt can settle on the optical components. Hence, regular cleaning is necessary for efficient sensor operation.
Lenses and mirrors are integral parts of the NDIR-GFC sensor. The mirrors reflect the infrared beam onto the detectors. The lens focuses the beam.
Dust and dirt on these components will impede the infrared beam. So, cleaning these components with a soft cloth regularly keeps the sensor in good shape.
Importance Of Regular Calibration And Checks
Regular calibration of the NDIR-GFC sensor is paramount. Calibration checks the sensor’s performance against known gas concentrations. Regular calibration ensures accuracy in the sensor’s measurements.
NDIR-GFC sensors come with specific calibration intervals. Some need calibration every six months; others need annual calibration. Adhering to the manufacturer’s calibration intervals assures the sensor’s peak performance.
NDIR-GFC sensor calibration requires known gas concentrations. These are often provided in calibration gas cylinders. Sensor calibration with these cylinders ensures accurate measurements. Regular checks and calibrations keep the NDIR-GFC sensor working at optimal levels, ensuring accurate and reliable gas measurements.
Conclusion
So, a deep dive into NDIR-GFC gas sensor technology has been made. Now, understand the profound impact it can have. To take the next step, consider exploring the multitude of offerings at ESEGAS. Continue to learn, and harness the power of this advanced technology.