We research and development of ESE-IR-200 series NDIR-GFC Gas Analyzer , mainly based on non-dispersive infrared photoelectric (NDIR) detection technology, infrared wavelength filtering technology (GFC) and self-designed long-term optical path gas absorption cell (L-Cell) technology and the realization of gas in the infrared band quantitative analysis, this instrument mainly measures CO, CO2, CH4, and other gas concentration, with high precision, good stability, fast response time and other characteristics, fully meet the key control of carbon emission power plants, steel plants. Monitoring of greenhouse gases in the environment of non-point sources such as chemical parks and urban areas supports the verification of urban carbon emission monitoring and accounting results.
<tr><span style=”vertical-align: inherit;”>Response time≤60s
| Measuring principle</b> | Infrared absorption (NDIR)</span> |
| <span style=”vertical-align: inherit;”>measuring gas | CO, CO2, CH4 |
| Measurement range</b> | (0~10/50/500/2000) ppm, other ranges can be customized. |
| Sample gas flow</strong> | 0.8L/min±10% |
| Indication error | ≤2%FS |
| >yle=”vertical-align: inherit;”>drift | <span style=”vertical-align: inherit;”>≤±1%FS/24h |
| Preheat time | ≤60min |
| Output Interface | RS-232/RS-485/4-20mA |
Features:
Here are the key features and components of an NDIR-GFC gas analyzer:
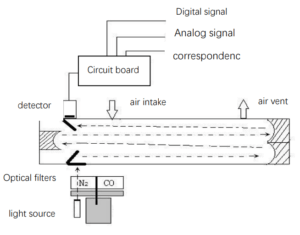
When the infrared light passes through the gas chamber, the gas molecules have an absorption effect on the infrared light with a specific wavelength. Meanwhile, the absorption relationship obeys the Lambert-Beer absorption law. The infrared light emitted by the light source enters the gas cell through the GFC modulation wheel. Next, the measured bubbles of the gas absorb the gas. Then, the infrared detector collects two signals of the light after the lens converges the light. Finally, obtain the measurement signal and the reference signal after signal processing. By analyzing the two signals, obtain the concentration of relevant components in the gas.

Measuring carbon dioxide (CO2) is important for understanding the role it plays in the environment and its effect on climate change. CO2 is a major component of Earth’s atmosphere, and it traps heat like a blanket, causing global temperatures to rise. Too m uch CO2 can lead to drastic changes in our weather patterns and ecosystems, so monitoring its levels is essential for predicting future climate conditions. Additionally, measuring CO2 can help us better understand our impact on the environment and make informed decisions about how to reduce emissions and slow down down down down down global warming. By analyzing CO2 data over time, we can develop strategies to mitigate the effects of climate change and ensure a sustainable future.
Before industrialization, the global average annual atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration was 278ppm (1ppm is one part per million). In 2012, the global annual average atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration was 393.1ppm. By April 2014 , the monthly average carbon dioxide concentration in the northern hemisphere atmosphere exceeded 400ppm for the first time. . 2. Global climate warming, the continuous aggravation of the atmospheric greenhouse effect leads to global climate warming, resulting in a series of global climate problems that cannot be predicted by today’s science. According to the International Climate Change Economics Report, if human beings maintain the current way of life, by 2100, there will be a 50% chance that the global average temperature will rise by 4°C.
Copyright © 2023 esegas.com, All rights reserved.


Enviro Solutions Technology Co., Ltd (ESE Technology) is a gas analyzer manufacturer and leading provider in ODM/OEM services for gas analysis systems used by international famous brands.
We will contact you within 1 working day, please pay attention to the email with the suffix “[email protected]” .
We’ll send you the catalog as soon as you submit your email