Gas analyzers are gadgets that facilitate the fixation of a vaporous compound in various gases. They are used across different industries and businesses, such as manufacturing, waste administration, and agribusiness. These devices are used to screen the gas levels of various tasks to ensure the numbers are within safe limits to keep products and workers alike safe.
Gas analysis makes it easier to improve well-being, effectiveness, and product quality. The process can also guarantee ecological consistency.
Types of Gas Analyzers
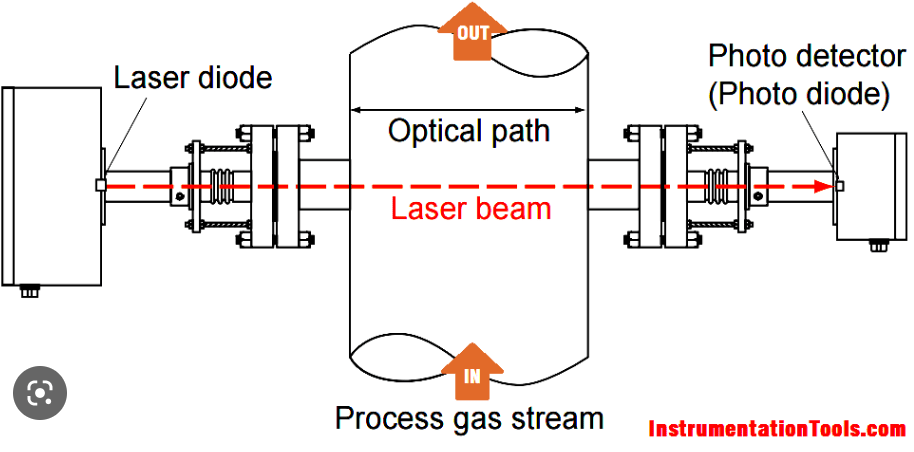
This kind of gas analyzer uses a sensor laser optical innovation to perceive and dissect the consonant fingerprint of a gas. The sensors do not deliver bogus cautions courtesy of impedance gases. This happens due to its capability to identify the harmonic fingerprint of each gas. On top of that, they are not susceptible to damage because they are optical. This is ideal if you need to recognize water fume, methane, and other gases.
This analyzer uses reactant ignition to measure burnable gases at fixations of Lower Explosive Levels. This sensor has been around for a long time. It estimates the temperature contrast existing between an idle dot and another coated in a chemical analyst. They are warmed together, but the dot with the impetus warms more. They react to combustible gases that might have outrageous variances in humidity or temperature, such as methane, butane, hydrogen, propane, acetylene, and carbon monoxide.
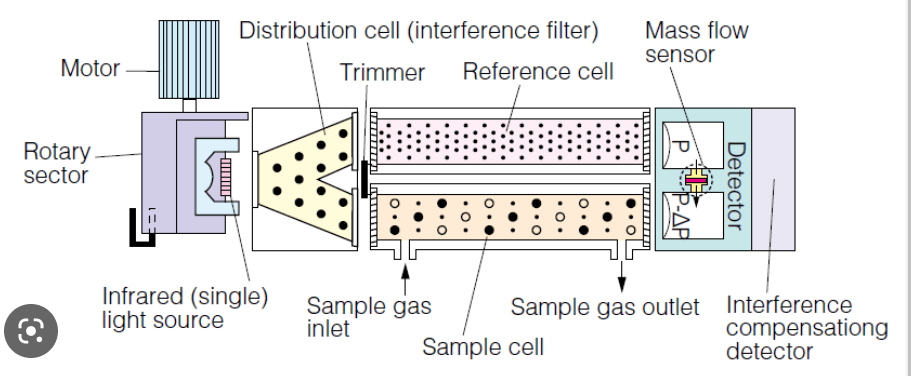
These devices measure two frequencies: a reference wavelength not consumed by the gas and the gas that absorbs frequency. They function well when it comes to telling hydrocarbon gases apart, especially in conditions with low oxygen levels. On top of that, they are good at the recognition of high convergences of hydride gases, halogenated hydrocarbons, or silicones. It is worth noting that they should not be used when hydrogen might be present since the gas is incapable of retaining infrared light.
The detectors falling under this category convert gas into the electric flow. After this, the gas is diffused into the sensor via a layer wherein it makes contact with a terminal and becomes oxidized. The electrochemical response in question results in an electric flow that goes through the outer circuit. These devices are perfect for distinguishing harmful gases in limited spaces with a lack or enhancement of oxygen and within the ppm range.
Factors Tested by Gas Analyzers
When you choose a gas analyzer for testing, the type of element to be analyzed should be the primary consideration. For your reference, we listed the different factors tested by different gas analyzers below.
Oxygen gas
These analyzers were made for the verification of oxygen content in flue gas analysis, combustion air oxygen enrichment, oxygen deficiency analysis, and the like. Models can be continuous, portable, hazardous location, or multi-gas. They each come with an electrochemical oxygen sensor component.
Hydrogen gas
Hydrogen analyzers use a thermal-conductivity detector for the identification of hydrogen gas, the elemental gas with the highest thermal conductivity value. The process involves the subtraction of other gases from the analysis for an accurate reading of the composition of the gas. They are especially useful in industrial applications, hydrogen production, and syngas.
Carbon dioxide gas
There are numerous industrial applications of carbon dioxide analyzers, including agricultural, food processing, combustion, landfill gas production, steel-making, and gasification operations.
Carbon monoxide gas
These analyzers are typically used with oxygen and temperature analyzers for the evaluation of burner performance and combustion efficiency. They are used in industrial facilities wherein personnel might suffer exposure to high levels of this gas. Infrared and electrochemical models are typically used in the analysis of carbon monoxide.
Methane gas
Methane analyzers are used in biogas, syngas, and landfill applications for the assessment of the composition and quality of gas production. They rely on infrared technology when it comes to the identification of hydrocarbons. There are advanced sensors capable of distinguishing methane from other hydrocarbons, which come in handy when there are significant quantities of non-methane hydrocarbons.
Hydrocarbons gas
Aside from methane, there are also other hydrocarbons generated throughout industrial processes. There are portable multi-gas and hydrocarbon-only analyzers used in applications like exhaust, gasification, and syngas.
Sulfur dioxide gas
Sulfur dioxide analyzers and multi-gas sensors use infrared technology in the determination of ppm values in heat treatment and process stream gases. You may choose from continuous and portable models that are suitable for various applications, even those that take place in hazardous environments.
Nitrogen oxides gas
Nitrogen oxide analyzers are used in combustion equipment like boilers, engines, furnaces, and flue gas monitoring applications. They are available in continuous wall-mounted and portable models. Aside from that, they can accommodate nitrogen dioxide, nitrogen oxide, and more oxides. Some units can be used in hazardous environments.
Aside from the aforementioned factors, helium, chlorine, hydrogen chloride, and lower explosive limit are also tested. On top of that, you might also want to look into analysis equipment capable of monitoring the temperature and velocity of gases. They are crucial factors in industrial processes and may provide more insight into the processes involved. If you want to see the bigger picture, you might want to take a look at non-contact optical velocity sensors and gas temperature analyzers as well.
Applications of Gas Analyzers
In general, a gas analyzer aims to enhance safety by measuring the concentration of a gas in a place that contains numerous gases. This is a device that alerts users when a gas concentration is either too low or too high. Below are several applications of gas analyzers.
Fuel Cells
Fuel cells can directly convert fuel to electricity without using an engine. They are typically used in the automotive sector. The use of fuel cells has been going up as they offer a source of clean power for vehicles although more research is needed before they can be deployed as a sustainable alternative to modern engine technology.
Gas analyzers are important since they can help bring down emission levels and the risk of contamination in fuel cells. Fuel cell contamination should be avoided and can be overcome by identifying what gases cause the contamination. A gas analyzer can be used to monitor and track changes in component gas levels so that they can be improved.
It is ideal to use a gas analyzer that offers repeatability, wide range, rapid response time, and linearity.
Gas Separation
Various sectors use gas separation technology as well. Among others, the list includes gas, environmental, and petrochemical storage. By separating carbon dioxide from atmospheric gases, it becomes possible to fight climate change and other negative conditions. It is possible to identify the carbon dioxide within the atmosphere with the use of gas analyzers, after which it is separated and then stored. When it has been stored safely, it can be developed for biogases.
It is important to use gas analyzers with fast identification routines if you want to improve gas separation processes.
Health
There are different sectors inside the health industry that calls for the analysis of compounds found in human breath. This includes human physiology, sports science, and medicine. It is possible to measure the concentration of those compounds with the help of gas analyzers. In turn, the results can tell a lot about diseases, stresses, and physiological changes.
Non-invasive gas analyzers are more comfortable to use for the subject. On top of that, they also offer a rapid response that allows for the real-time monitoring of changes.
These are only several applications of gas analyzers. It is not an exhaustive list, but it should give you a general idea of how these instruments can be utilized for different purposes. They can be very valuable for your business when you need to monitor gas levels.
End Notes
Gas analyzers come in handy for various applications across different fields, sectors, and industries. They are extremely useful when you need to monitor gas levels for whatever reason. It is important to find the right instrument that will address the problems you have and deliver accurate results. You also have to make sure that you find a device that meets industry standards regarding personal safety as well.
Whether you are looking for a replacement or just starting, ESE can help. Get in touch with them today to bring home the gas analyzer that will get the job done. From TDL laser gas analyzers to flue gas analysis, a team of experts will deliver cost-effective monitoring instruments and top-notch gas analysis equipment.pls feel free to contact with us [email protected]