Toxic emissions from waste incineration are tightening regulatory pressure, yet many plants still lack real-time control. Flue gas analyzers offer a precise solution to monitor and mitigate harmful pollutants.

Flue gas analysis plays a critical role in waste incineration by monitoring hazardous emissions, supporting regulatory compliance, and optimizing combustion processes to protect both the environment and equipment.
While this answers the core question, many professionals in the field still wonder what specific gases are monitored, how technology works in practice, and how it integrates with regulatory requirements. Let’s explore these aspects further.
Why Is Flue Gas Analysis Critical in Waste Incineration?
Burning waste without monitoring emissions is no longer acceptable—health risks, legal penalties, and environmental damage are at stake. Regulatory bodies worldwide demand strict control over incinerator emissions. Yet many facilities still rely on outdated or incomplete monitoring systems, risking violations and public backlash. Flue gas analysis provides the visibility and precision needed to stay in compliance and operate safely.
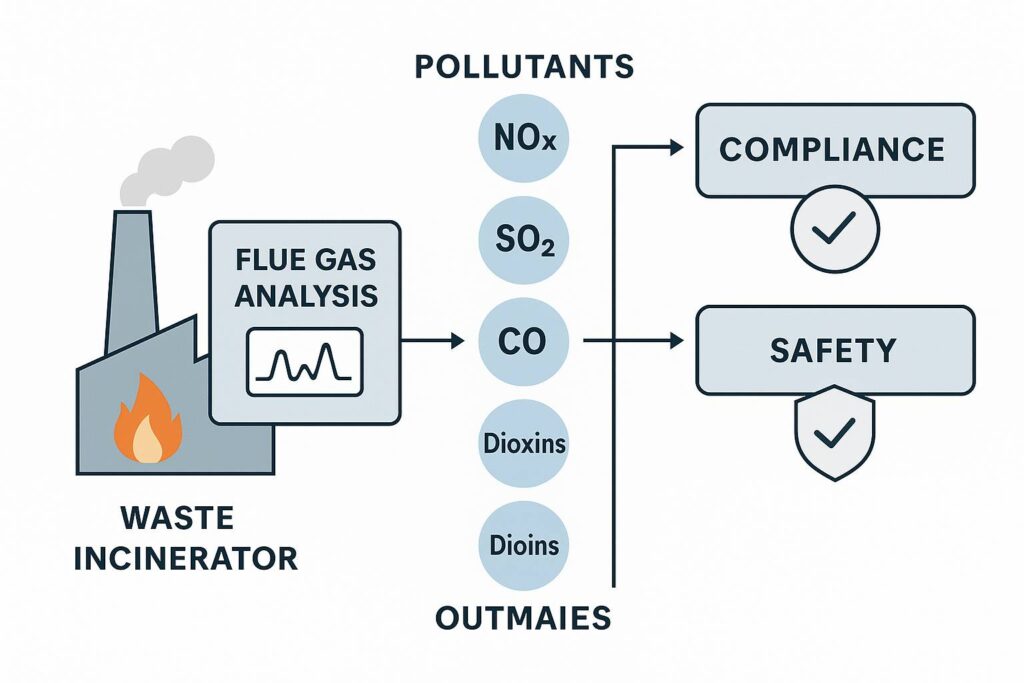
Flue gas analysis is essential in waste incineration because it detects and quantifies harmful emissions like NOx, SO₂, CO, and dioxins, ensuring environmental compliance and public safety. Real-time data enables immediate corrective action, preventing over-limit releases and supporting transparent, auditable reporting.
In incineration plants, combustion of municipal or industrial waste produces a volatile mixture of pollutants. Without continuous monitoring, substances like hydrogen chloride, heavy metals, and particulate-bound toxins may escape undetected, posing risks to surrounding communities. Moreover, unoptimized combustion can lead to incomplete waste breakdown and equipment degradation. Flue gas analyzers serve as the plant’s sensory system, offering a non-stop stream of critical data that informs burner control, emission treatment, and legal documentation. This makes them not only a regulatory tool, but a central pillar of responsible waste management.
What Pollutants Are Monitored by Flue Gas Analyzers In Incineration Plants?
Waste incineration generates a complex cocktail of pollutants—many invisible but highly toxic. Without precise, real-time monitoring, these emissions can surpass regulatory limits and pose serious threats to human health and the environment. That’s where flue gas analyzers prove indispensable: detecting even trace-level emissions before they become critical.
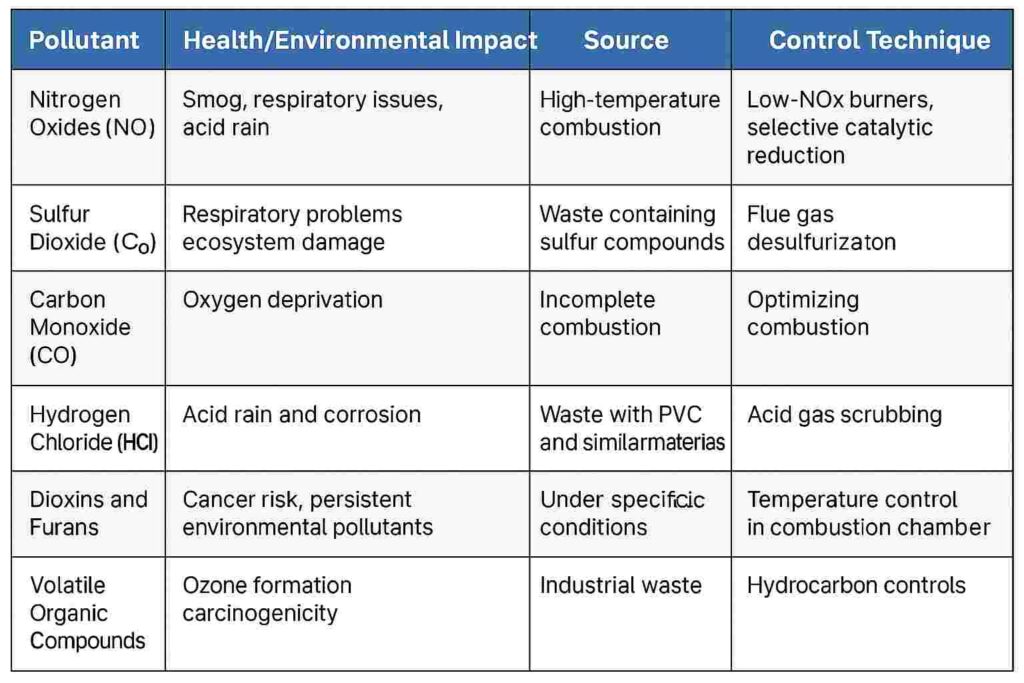
Flue gas analyzers in incineration plants monitor a range of hazardous substances, including gases, particulates, and acid compounds, all of which are tightly regulated due to their health and environmental impact.
To ensure full-spectrum monitoring and compliance with environmental standards, flue gas analyzers typically track the following key pollutants:
Formed during high-temperature combustion, NO and NO₂ contribute to smog and acid rain. Regulations typically mandate real-time NOx monitoring to assess combustion efficiency and control secondary pollution.
Produced from burning sulfur-containing waste (e.g., plastics, textiles), SO₂ is corrosive and harmful to the respiratory system. Monitoring its levels is essential for activating desulfurization systems.
A direct indicator of incomplete combustion. High CO levels suggest inefficient burning and potential formation of other unburned hydrocarbons.
Common in waste with PVC content, HCl is a precursor to acid rain and highly corrosive to equipment. Accurate HCl detection supports proper operation of acid gas scrubbers.
Trace-level toxic compounds formed under specific temperature conditions. While not continuously monitored in all systems, periodic sampling or specialized analyzers can measure these critical pollutants.
These include a wide range of carbon-based chemicals that can contribute to ozone formation and pose carcinogenic risks. Monitoring VOCs is vital, especially in industrial waste incineration.
Although not a gas, PM includes fly ash and soot, which often carry heavy metals and dioxins. Some advanced systems integrate opacity meters or dust sensors for PM tracking.
By monitoring these pollutants, incineration plants can fine-tune combustion, engage appropriate abatement technologies, and ensure they remain within legal emission thresholds.
How Does Flue Gas Analysis Support Operational Optimization?
Waste incineration without process feedback is like flying blind—inefficiency, equipment damage, and excessive emissions are almost guaranteed. As energy prices rise and environmental regulations tighten, operators must extract maximum efficiency from every combustion cycle. Flue gas analyzers offer the real-time data needed to fine-tune operations with confidence.
Flue gas analysis enables incineration plants to optimize combustion efficiency, reduce fuel consumption, prevent corrosion, and extend equipment life—transforming compliance tools into performance assets.
Here’s how flue gas analysis contributes directly to operational excellence:

- Combustion Efficiency Optimization:
By continuously measuring oxygen (O₂) and carbon monoxide (CO) levels, analyzers help operators maintain the ideal air-to-fuel ratio. Too much oxygen results in energy loss, while too little causes incomplete combustion and pollutant spikes. Fine-tuning these levels boosts thermal efficiency and lowers fuel costs.
- Real-Time Burner Adjustment:
Data from analyzers feeds directly into automated control systems, allowing dynamic burner modulation. This not only stabilizes combustion but also responds instantly to waste variability—especially important in municipal solid waste, which has inconsistent calorific value.
- Minimization of Unburned Components:
Monitoring unburned hydrocarbons (CxHy) and CO helps identify underperforming burners or poor waste distribution. This reduces the risk of secondary pollutant formation and unintentional residue accumulation in flue ducts.
- Corrosion and Fouling Prevention:
High levels of SO₂, HCl, and moisture can corrode boiler surfaces and degrade heat exchangers. Real-time analysis enables preventive action, such as temperature adjustment or reagent injection, before damage occurs.
- Optimized Use of Flue Gas Treatment Systems:
Knowing the exact pollutant load (e.g., NOx or dust concentrations) allows better control over reagents like ammonia or lime in downstream systems—reducing chemical use and operational costs.
In summary, flue gas analyzers are not just for environmental monitoring—they are core tools for process control that directly impact profitability, uptime, and environmental performance.
How Does Flue Gas Analysis Help with Regulatory Compliance?
Emission regulations are strict—and getting stricter. Non-compliance isn’t just costly; it can shut down entire operations. Waste incinerators are under intense scrutiny, and without accurate, real-time emission data, operators risk breaching environmental permits. Flue gas analyzers act as a continuous assurance mechanism, helping facilities stay compliant—and operational.

Flue gas analysis enables incineration plants to meet stringent emission standards through continuous monitoring, certified data logging, and automated reporting to regulatory authorities.
Here’s how flue gas analyzers support full regulatory alignment:
- Continuous Emission Monitoring (CEM):
Most environmental agencies, such as the EU’s Industrial Emissions Directive (IED), the U.S. EPA, and China’s GB standards, require Continuous Emission Monitoring Systems (CEMS). These systems use flue gas analyzers to provide uninterrupted, real-time measurements of pollutants like NOx, SO₂, CO, HCl, and dust.
- Certified and Traceable Data:
Modern analyzers meet international calibration and performance standards (e.g., EN 14181, USEPA PS-6). They generate legally admissible emission reports and maintain traceable audit trails to withstand regulatory inspections.
- Alarm Thresholds and Automatic Interventions:
Systems can be configured with alert levels for specific gases. When emissions approach or exceed permissible limits, alarms trigger corrective action or initiate shutdown protocols—preventing non-compliance before it happens.
- Integration with Environmental Management Systems:
Data from analyzers can be directly fed into plant-level compliance dashboards or national reporting networks (e.g., PRTR, Continuous Data Acquisition and Handling Systems). This simplifies compliance documentation and streamlines audit preparation.
- Support for Permit Renewals and Environmental Audits:
Historical analyzer data can demonstrate long-term compliance trends, improving credibility during environmental impact assessments and supporting faster permit renewals.
In essence, flue gas analysis transforms regulatory risk into a managed, measurable process—protecting plant licenses and reinforcing public trust.
Conclusion
Flue gas analysis is indispensable in the waste incineration industry. It is necessary not only to meet environmental regulations but also to improve plant efficiency, safety, and long-term sustainability.
























