
In the cement industry, clinker production stands as a cornerstone process, pivotal for producing the binding agent in concrete. However, this process is energy-intensive and emits significant amounts of gases, notably sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and carbon dioxide (CO₂). Effective monitoring of these emissions is crucial for optimizing production efficiency, ensuring product quality, and meeting environmental regulations.
Traditional gas monitoring methods often fall short in providing real-time, accurate data, leading to challenges in controlling emissions and maintaining process stability. This is where Non-Dispersive Infrared (NDIR) process gas analyzer, such as ESEGAS’s process gas analyzer, comes into play. These analyzers offer continuous, precise monitoring of gas concentrations, enabling operators to make informed decisions promptly.
By implementing NDIR-based process gas analyzer, cement plants can achieve:
- Enhanced Combustion Efficiency: Real-time data allows for optimal fuel-to-air ratios, reducing fuel consumption.
- Improved Clinker Quality: Stable kiln conditions lead to consistent product quality.
- Regulatory Compliance: Accurate monitoring ensures adherence to environmental standards, avoiding potential fines.
ESEGAS’s process gas analyzer, with its advanced NDIR technology, provides a reliable solution for the cement industry to monitor and control SO₂ and CO₂ emissions effectively, leading to sustainable and efficient clinker production. In this article, we’ll explore how this technology—especially ESEGAS’s advanced process gas analyzers—redefines clinker process monitoring.
Why Is Monitoring SO₂ and CO₂ Vital in Cement Kilns?
(SO₂ and CO₂)
Clinker production is the heart of cement manufacturing. It involves heating a precise mix of raw materials—primarily limestone, clay, and iron-rich additives—to temperatures exceeding 1,450°C in a rotary kiln. This intense heat transforms the raw mix into clinker nodules, which are then ground to produce cement.
In clinker production, sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and carbon dioxide (CO₂) are two critical emissions that demand close attention. Their sources and impacts extend beyond environmental concerns, directly influencing kiln performance and regulatory compliance.
Understanding SO₂: Its Origins and Impacts
SO₂ emissions primarily stem from sulfur compounds present in raw materials and fuels. When these materials are subjected to high temperatures in the kiln, sulfur compounds oxidize, releasing SO₂ gas.
Environmental Impacts:
- SO₂ contributes to acid rain, which can damage ecosystems, corrode infrastructure, and harm human health.
Operational Impacts:
- High SO₂ levels can lead to the formation of kiln deposits, reducing heat transfer efficiency and causing operational disruptions.
- Corrosive effects of SO₂ can deteriorate kiln components, leading to increased maintenance costs and downtime.
Monitoring SO₂ levels is essential to mitigate these risks and ensure smooth kiln operations.
Understanding CO₂: Its Origins and Impacts
CO₂ emissions in cement kilns arise from two main sources: the calcination of limestone and the combustion of fossil fuels. During calcination, limestone (CaCO₃) decomposes into lime (CaO) and CO₂. Additionally, burning fuels like coal and petcoke to achieve the necessary kiln temperatures releases CO₂.
Environmental Impacts:
- CO₂ is a significant greenhouse gas, contributing to global warming and climate change. The cement industry is responsible for approximately 8% of global CO₂ emissions.
Regulatory Impacts:
- Governments worldwide are implementing stricter CO₂ emission regulations, including carbon pricing and emission caps. Non-compliance can result in financial penalties and reputational damage.
Accurate CO₂ monitoring enables cement plants to track emissions, optimize processes, and comply with environmental regulations.
By understanding the sources and impacts of SO₂ and CO₂ emissions, cement manufacturers can implement effective monitoring strategies to enhance operational efficiency and environmental compliance.
Operational Challenges
Maintaining optimal combustion conditions is critical to minimize emissions and ensure clinker quality. However, several challenges complicate this:
- Temperature Control: Achieving and maintaining the high temperatures required for clinker formation demands precise control.
- Fuel Variability: Inconsistent fuel quality can lead to fluctuations in combustion efficiency and emission levels.
- Raw Material Variability: Changes in the composition of raw materials can affect the chemical reactions in the kiln, impacting both emissions and clinker quality.
Early gas monitoring technologies are not good at addressing these challenges. They may lack the responsiveness and accuracy needed to detect real-time fluctuations in emission levels, leading to delayed corrective actions and potential non-compliance with environmental regulations.
How Does NDIR-Based Process Gas Analyzer Enhance Gas Monitoring in Cement Kilns?
(NDIR Technology)
In the demanding environment of cement kilns, accurate and reliable gas monitoring is crucial. Non-Dispersive Infrared (NDIR) technology offers a robust solution for detecting specific gases like SO₂ and CO₂, essential for optimizing clinker production.
Understanding NDIR Technology
NDIR-based process gas analyzer operates by emitting infrared light through a gas sample. Each gas absorbs light at specific wavelengths; by measuring the absorbed light, the process gas analyzer determines the gas concentration. This method provides precise, real-time measurements, critical for maintaining optimal kiln operations.
Advantages in Cement Kiln Applications
NDIR technology offers several benefits tailored to the harsh conditions of cement kilns:
- Selectivity: High specificity for target gases like SO₂ and CO₂ ensures accurate readings without interference from other gases.
- Durability: Designed to withstand high temperatures and dusty environments, NDIR-based process gas analyzers maintain performance over time.
- Low Maintenance: With minimal calibration needs and long operational life, they reduce downtime and maintenance costs.
These features make NDIR-based process gas analyzer an ideal choice for continuous monitoring in cement kilns, ensuring both environmental compliance and operational efficiency.
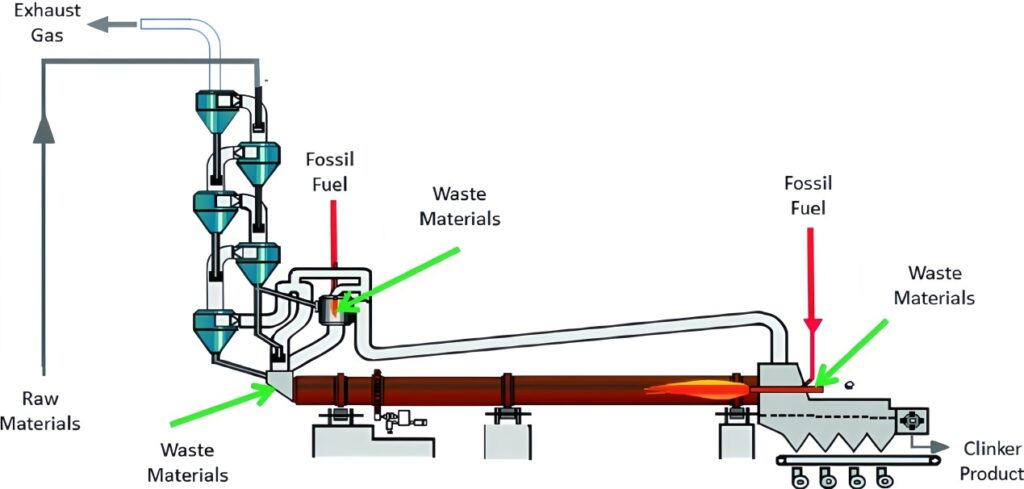
(Emissions Consideration in Cement Kiln)
To address the complex emissions profile of cement kilns, plants need precision tools that can operate in extreme conditions. This is where the ESEGAS process gas analyzer stands out. It doesn’t just measure gases—it gives plant operators real-time insights for smart, data-driven control.
Key Features: Built for High-Performance Environments
- Multi-Gas Detection: The analyzer measures CO, CO₂, CH₄, H₂, and O₂ simultaneously. This allows complete combustion profiling.
- NDIR + TCD Sensing: It combines non-dispersive infrared (NDIR) and thermal conductivity detection (TCD) technologies. This hybrid setup ensures accuracy and stability even under fluctuating gas compositions.
- Real-Time Feedback: Data refreshes quickly—providing immediate insight for adjusting air-fuel ratios or detecting anomalies.
These features offer a major upgrade from older stack samplers or periodic lab analysis. Instead of reacting to past data, operators can act in the moment.
How Can Cement Plants Strategically Implement Process Gas Analyzer?

(Cement Plant)
Integrating process gas analyzer into cement kiln operations requires thoughtful planning to maximize benefits and ensure long-term success.
Seamless Integration into Cement Kilns
Sometimes, you don’t need a full system overhaul to benefit. Strategic placement—such as at the kiln outlet or in the preheater zone—captures critical gas profiles.
- Automated Control: The analyzer feeds directly into kiln control systems. This enables automatic optimization of fuel input, air supply, and temperature.
- Compliance Reporting: Built-in logging and digital output formats make emissions reporting smoother and more transparent.
However, for better performance and more professional results, it also involves selecting the right system configuration and establishing robust maintenance and training protocols.
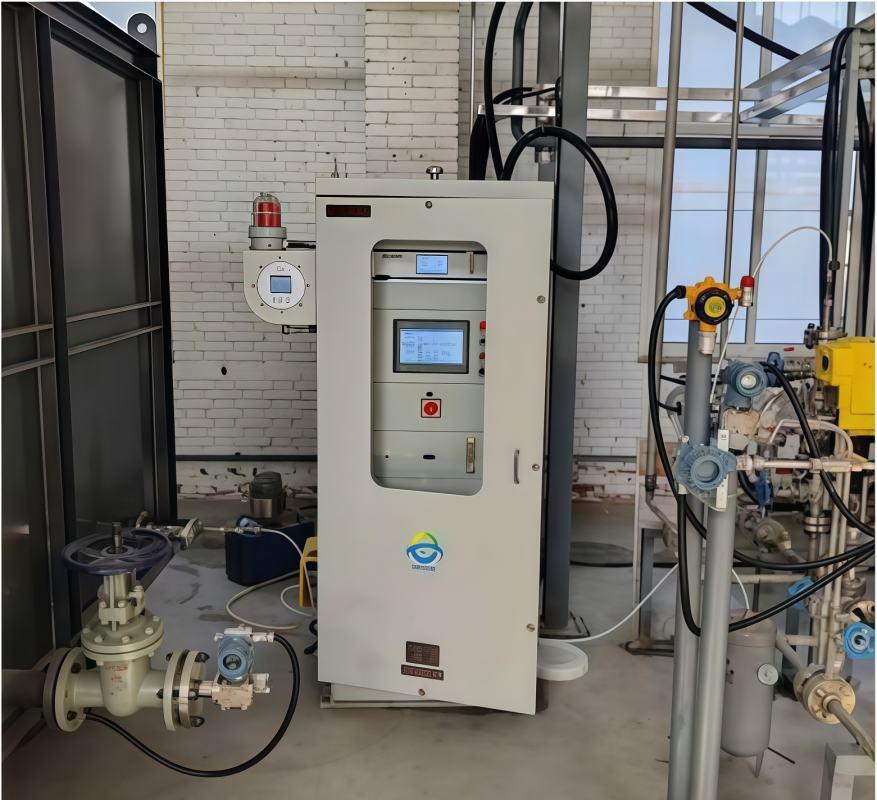

A. System Selection: Customization and Scalability
1. Customization to Kiln Requirements
Each cement kiln has unique operational parameters influenced by factors such as fuel type, raw material composition, and production capacity. Therefore, selecting a gas analyzer system that can be tailored to these specific needs is crucial. For instance, the ESEGAS process gas analyzer offers configurations that can be customized to monitor targeted gas components relevant to a plant’s specific process conditions.
2. Scalability for Future Regulatory Changes
Environmental regulations are continually evolving, often becoming more stringent over time. Implementing a gas analyzer system that is scalable ensures that a cement plant can adapt to future regulatory requirements without significant overhauls. Systems like the ESEGAS process gas analyzer is designed with modular components, allowing for easy upgrades or expansions to monitor additional gas species as needed.
B. Maintenance and Training: Ensuring Accuracy and Reliability
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the accuracy and longevity of gas analyzer systems. Establishing a maintenance schedule that includes routine checks, calibration, and cleaning helps prevent data drift and equipment failure. Given the harsh conditions within cement kilns, components such as sampling probes and filters should be inspected and serviced regularly to maintain optimal performance.
2. Comprehensive Staff Training
Educating personnel on the operation and interpretation of gas analyzer data is vital for effective utilization. Training programs should cover system operation, data analysis, troubleshooting, and safety protocols. By empowering staff with the necessary knowledge and skills, plants can ensure that the gas analyzer systems are used to their full potential, leading to improved process control and compliance.
By carefully selecting and maintaining NDIR-based process gas analyzer system , and by investing in comprehensive staff training, cement plants can enhance operational efficiency, ensure product quality, and meet environmental compliance standards.
What Are the Real Benefits of Process Gas Analyzer in Cement Plants?

(Cement plant cost and benefits)
Let’s go beyond the tech specs. When installed and used effectively, NDIR-based process gas analyzer can transform kiln operations on multiple levels.
1. Operational Efficiency
Real-time gas analysis allows plants to:
- Optimize combustion by fine-tuning fuel-air mix.
- Avoid overuse of fuel, cutting costs without compromising output.
- Respond faster to process fluctuations, improving kiln stability.
2. Better Clinker Quality, Less Downtime
- Stable gas conditions help maintain consistent temperatures and material reactions.
- Clinker quality becomes more uniform—reducing downstream grinding variability.
- Early detection of combustion issues prevents costly shutdowns or clinker overburn.
3. Environmental Compliance and Reporting
- Continuous monitoring keeps SO₂ and CO₂ within permitted levels.
- Real-time alerts help avoid exceedance before it happens.
- Detailed logs simplify mandatory reporting to local and national regulators.
With tools like the ESEGAS process gas analyzer, cement plants don’t just monitor emissions—they control them. In today’s regulatory climate and competitive market, that control is not a luxury. It’s essential.
Conclusion
In the dynamic landscape of cement manufacturing, precision and adaptability are paramount. The integration of process gas analyzer, such as ESEGAS’s IR-GAS series, into cement kiln operations offers a transformative approach to clinker production.
By adopting advanced gas monitoring technologies, cement manufacturers position themselves at the forefront of industry innovation, ready to meet evolving environmental standards and market demands.
Cement industry leaders should consider the strategic implementation of NDIR-based process gas analyzer to drive efficiency, ensure compliance, and maintain a competitive edge in the global market.
If you want to know more, contact with us please!

























