Call
WhatsApp
Mail
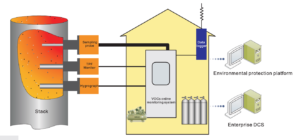
Introduction
Applications:
| Parameter | Range | Principle |
|---|---|---|
| NMHC | 0~1000ppm (customizable) | GC-FID |
| HC | 0~1000ppm (customizable) | GC-FID |
| Benzene series | 0~10ppm (customizable) | GC-FID |
| Oxygen | 0~25% | Zirconia |
| Temperature | 0~300℃ (customizable) | Thermal resistance or thermocouple |
| Pressure | -10kPa to +10kPa (customizable) | Pressure sensor |
| Flow velocity | 0~40m/s (customizable) | Pitot tube |
| Humidity | 0~40%vol (customizable) | Humicap or dry/wet oxygen |
-General Rarameters-
| Cabinet dimensions | 800mm*800mm*2000mm | Tracing pipe temperature | 120℃~150℃ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enclosure rating | IP42 | Power supply | 220VAC, 5000W |
| Working temperature | -20℃~50℃ | Work humidity | 0~95%RH (no dew fall) |
| Compressed air | pressure 0.4MPa~1MPa. The gas output is rated at 200L/min and shall be equipped with a 0.5 square meter gasholder. | External output | 4-20mA, RS232, RS485.etc; Protocol: modbus |
1) The Hydrogen FID (Flame lonization Director)
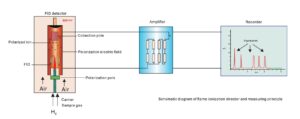
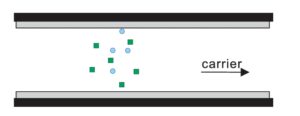
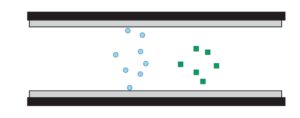
2)Chromatographic Column Separation Process

Copyright © 2023 esegas.com, All rights reserved.


Enviro Solutions Technology Co., Ltd (ESE Technology) is a gas analyzer manufacturer and leading provider in ODM/OEM services for gas analysis systems used by international famous brands.
We will contact you within 1 working day, please pay attention to the email with the suffix “[email protected]” .
We’ll send you the catalog as soon as you submit your email